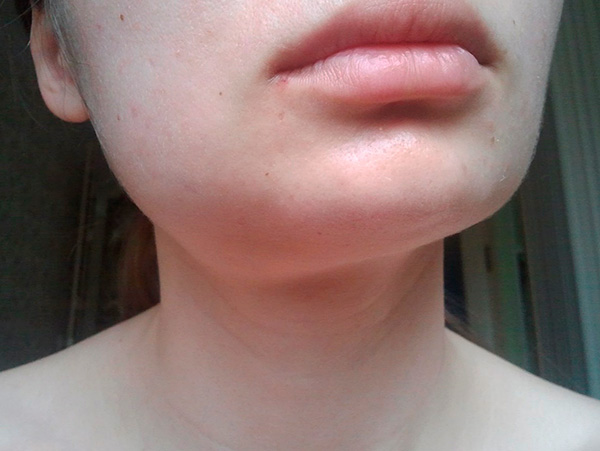
One of the most common problems that patients face after tooth extraction is the appearance of significant swelling of the soft tissues in the vicinity of the socket. Such edema can occur when any tooth is removed, but most often they are most pronounced when the chewing teeth (molars) are removed, including wisdom teeth.
Next, we will talk about this problem in more detail and consider the most exciting issues in this situation:
- Is it worth it, in general, to worry and whether it is urgent to run to the doctor if after removing the tooth the gums next to the hole or even the whole cheek is very swollen;
- How to prevent the development of serious edema, which, without additional intervention, could significantly complicate a normal life;
- What concomitant symptoms should be considered very alarming, in which it is advisable to seek medical attention as soon as possible;
- How much edema usually lasts after tooth extraction and how much your situation fits into the concept of the norm;
- What complications can arise if the situation is not properly assessed and the problem is left to chance;
- And also see what exercises will help with difficulty opening the mouth (this is often observed after complex removal of the lower wisdom teeth).
In which cases after tooth extraction, edema most often occurs
In order to better understand how and how to remove the swelling after tooth extraction, it is important to first understand the nature of the appearance of the swelling.
It is interesting that many people who came to the dentist's surgeon strangely forget that they came to the doctor already with edema, but they expect it to disappear immediately, almost on the first day after tooth extraction. After all, it would seem that the problem tooth has already been removed, why then the edema not only did not disappear, but it seemed to even increase?
A swollen cheek or lip (even before tooth extraction) can be the result of the development of periodontitis (in the acute stage), periostitis, or odontogenic osteomyelitis. A lot of people come to the doctor with an already running tooth condition, which is manifested by the so-called "flux". By its nature, flux is a purulent inflammatory process under the periosteum of the alveolar bone or body of the jaw of an infectious origin, the focus of which is almost always localized in the root region of a neglected tooth.
On a note
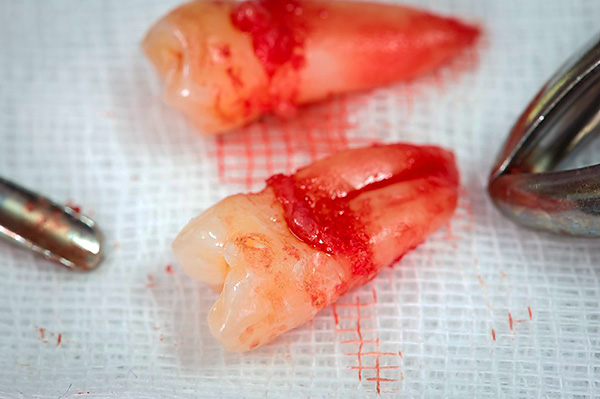
When a tooth that has been thoroughly destroyed by caries has not been treated for many years, it continues to gradually “rot”, and inflammatory processes occur on its roots. The body for some time restrains the onset of infection and limits its spread, surrounding the capsule shell - granuloma or cyst.
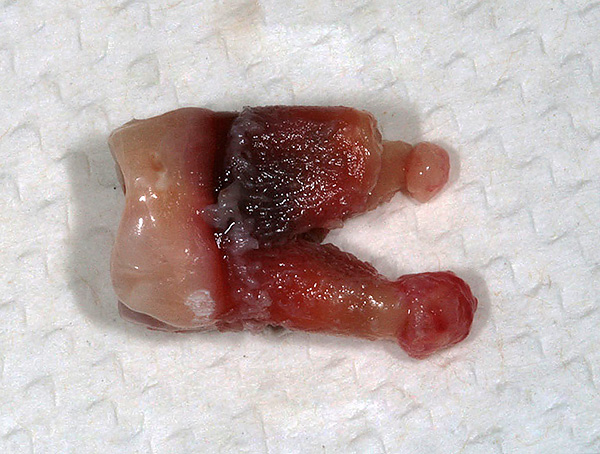
The photo below shows the extracted tooth with cysts on the roots:
However, the immunity resources are not unlimited, and the balance of forces can be disturbed in a variety of circumstances: with excessive load on the tooth, concomitant illness (SARS, for example), stress - all this can start the spread of infection into the jaw tissue, which will be accompanied by the accumulation of purulent in them exudate. Moreover, in such a quantity that the asymmetry of the face due to edema can be very pronounced.
As a result, in practice it turns out that in most clinical situations, a dentist-surgeon seeks people to remove a tooth, at least with an infection surrounding the root, and with a maximum of limited or diffuse purulent inflammatory processes (i.e., in the acute phase). Although the main problem is eliminated during tooth extraction, the infectious focus and edema can be felt for a long time.
Meanwhile, it is worth noting that sometimes relief comes immediately after tooth extraction: the feeling of fullness disappears, the swelling subsides, the pain stops. After extracting the ill-fated tooth with cysts on the roots, a person seems to start living anew (according to patients).
From the practice of the dentist
A number of dentists sometimes practice work without "cuts" to reduce the purulent contents in the wound after tooth extraction. In this case, facial symmetry broken due to edema is restored by squeezing the liquid from the gums onto a sterile gauze ball. Yes, it is sometimes painful, but it is possible to remove the swelling very quickly - the patient can immediately see in the mirror how much everything has become better. A swollen swollen face (cheek, lip) will decrease in volume by a factor of 2–3 within 5 minutes. ”
Not all people have an organism after removing tooth roots with granulomas, cysts, or even without them, equally quickly cope with the infection, which continues to be in the hole for some time. No tweezers can remove millions of bacteria from the wound, both harmless and pathogenic.
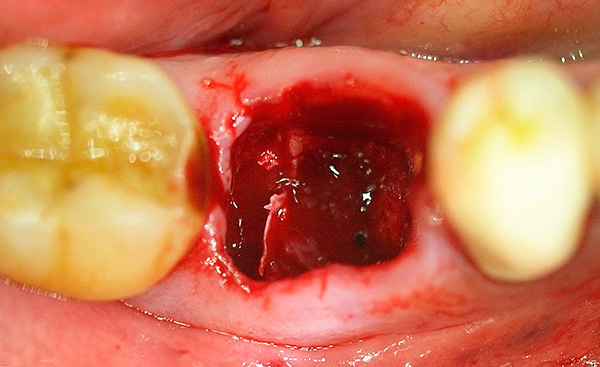
After tooth extraction, a blood clot fills the wound, which should allow immunity factors to deal with traces of infection and trigger the mechanism of successful healing of the hole. For many, this mechanism is triggered by a cascade of inflammatory reactions - as a result, often on the 2nd day after tooth extraction, pain, swelling, elevated body temperature and other unpleasant symptoms not only do not go away, but may even increase somewhat, causing anxiety in the patient.
Often this can be observed after the removal of the lower wisdom teeth: with difficult to erupt, exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, periostitis, etc. In the area of the molars of the lower jaw there is a large volume of friable tissues, well supplied and innervated. That is why the inflammatory reaction here is often accompanied by severe edema, fever and pain, especially when swallowing.
A reasonable question arises: can face swelling develop if a “quiet” tooth is removed? Indeed, not only dilapidated rotten teeth come to the dentist-surgeon, but also quite strong teeth with no infection on the roots.
And they are deleted, for example, for the following reasons:
- Due to malocclusion or injury to the cheek mucosa;
- Due to interference with orthodontic treatment (for example, on braces);
- Due to the obstruction of successful prosthetics (for example, it is necessary to remove an unnecessary tooth root or moving tooth);
- Or at the personal request of patients who fundamentally refuse to treat a tooth that could still be saved.
In such cases, edema after tooth extraction also occurs, but they, as a rule, are noticeably less pronounced compared with tooth extraction on the background of purulent exacerbation. However, in this case, especially if the patient does not take proper care of the hole, the wound can become infected with the subsequent development of significant edema, the appearance of pain and putrid breath. We will talk about these disturbing symptoms a bit later.
In the meantime, let's see how you can initially prevent the development of severe edema after tooth extraction, thereby making the postoperative period more comfortable. And what mistakes should not be made ...
How can you prevent the development of severe edema after tooth extraction?
There are many tricks to make sure that swelling on the face after tooth extraction does not occur at all - the resulting swelling will be small and will only affect the gums within the socket.
There are three main points that give a good effect in the complex:
- The use of cold on the first day after tooth extraction;
- Refusal from hot, hard and spicy food, as well as from active physical activity and warming up (bath, sauna, steam room, solarium, hot bath);
- Taking medications (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antihistamines, sometimes hemostatic).
To prevent severe swelling after tooth extraction, most dentists recommend applying cold to the cheek area from the side where the hole is located. Again, not all dentists recommend this method, as they are well aware that patients can follow the same instructions in very different ways. If the doctor tells the person on the track: “So that the cheek does not swell, apply cold during the day,” you can expect anything.

As a result, in winter, snow can become that saving “cold”: at best for 1-2 minutes, at worst for an hour or more. In summer, such a patient will like the freezer and the freezing in it (chicken, berries, dumplings), which, like snow, can cause severe frostbite on the face.
Not every dentist in a limited time will be able to convey to the patient that it is a cold compress. That is, it is not necessary to freeze the face before whitening, but it is important that there is a slight effect of cold on the skin. If there is a pack of frozen dumplings, then it should be wrapped in a towel, if the towel is thin - in several layers. Etc. That is, common sense is important here.
A hot water bottle is the best option. Again, if the water is ice - you need to wrap a towel with a towel, and when the water warms up - remove the towel or change the water. Retention time - 15-20 creased every 2 hours.

Cold, as a local decongestant, is certainly effective, but only in combination with common sense and detailed instruction.
It's important to know!
The use of cold is relevant only in the first day after tooth extraction. Relieving cold swelling on the second day will be a much less effective activity.
If cold constricts blood vessels and reduces blood flow in the wound area, then everything related to heating the body contributes to the development of severe edema (hot food and drinks, physical activity, bath, etc.). Refuse warming procedures should be 3-4 days after tooth extraction.
On a note
It is quite possible to take a shower and wash your hair, but you should adjust the water to a temperature of about 36-37 ° C so that the water is warm and not hot.
What else can prevent the appearance of edema after tooth extraction?
Those patients who suffer from diseases of the cardiovascular system should carefully monitor blood pressure and take medications recommended by your doctor to lower it. Indeed, edema and hematoma that occur after tooth extraction in such cases are largely the result of dimpled bleeding due to hanging pressure. Stable blood pressure is the key to comfort in the postoperative period.
As for drugs, there are many funds that prevent severe swelling and even reduce them if they have already formed. These drugs include antihistamines. The people know them, first of all, as anti-allergic drugs, but they can also be called decongestants.
When choosing a drug, contraindications to its use should be taken into account (for example, pregnancy, lactation, childhood, a number of diseases, etc.), as well as drug interactions with the simultaneous use with other drugs. To understand how this or that antihistamine drug in your situation will be effective and safe, the doctor must at the reception.
The same applies to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hemostatic drugs, glucocorticoids and other drugs, which determine how comfortable the postoperative period will be. Such medical assistance should be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
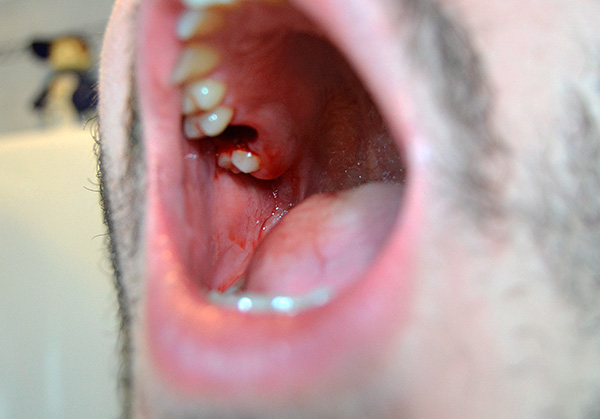
It should be noted that despite the efforts taken to reduce the severity of edema, it can still appear and cause discomfort.This is especially often observed after the removal of the retarded wisdom teeth on the lower jaw. The post-traumatic inflammatory process in connection with the anatomy and the peculiarities of the arrangement of wisdom teeth, even despite the efforts made by the doctor and patient, often leads to the appearance of sufficiently pronounced edema.
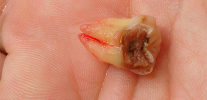
The image below shows a semi-reinforced wisdom tooth:
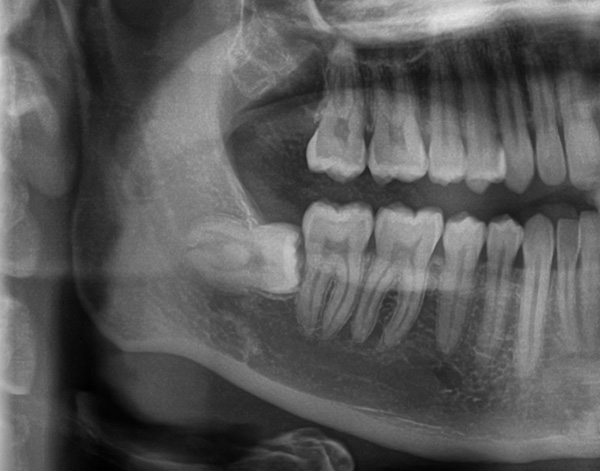
Do not panic right away. Usually, the edema reaches its maximum within 2-3 days after the removal of the wisdom tooth, and here it is important to control the condition as a whole, and not just one symptom. If there is a serious deterioration in health (fever to high values, intolerable pains that cannot be stopped even by analgesics, suppuration or bleeding from the hole), then you should consult a doctor immediately.
Now a few words about the appearance of a bruise on the entire cheek, neck or jaw after tooth extraction.
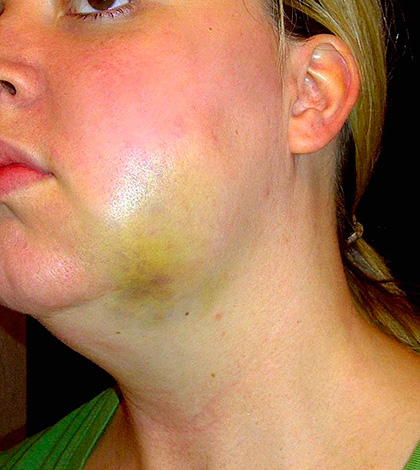
Do not panic when such a bruise appears, even if it looks threatening. After removal of the lower molars, an extensive hematoma is often observed along with edema (especially in patients with arterial hypertension) - at first the hematoma may have a bluish color, after 3-5 days it becomes yellow, and then completely disappears without a trace. The appearance of a hematoma after tooth extraction does not indicate any complications or errors of the dentist-surgeon, being quite an ordinary phenomenon.
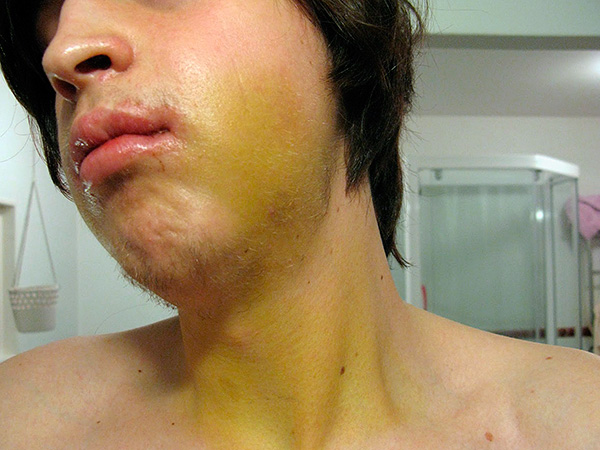
It is interesting
A hematoma can occur even when a gum is pierced with a needle during anesthetic administration. To prevent the appearance of an undesirable bruise after anesthesia, before a tooth is removed, a number of dentists ask that you squeeze the injection site with your hand for 1-2 minutes through the cheek. Some doctors believe that this is a relic of the past: modern techniques for working with imported anesthetics have almost no risk of developing extensive hematomas in vascular injuries. However, if there is a risk of developing a hematoma due to the individual characteristics of the patient, this technique of “pressing the injection site” can be considered relevant in our time.
What symptoms can edema accompany, and when should I run to the doctor as soon as possible
Even if, thanks to the methods described above, it will be possible to significantly remove edema after tooth extraction, this is not yet a complete guarantee of a successful course of the postoperative period.

The most common manifestations accompanying edema are:
- Fever;
- Worsening of well-being;
- The appearance of pain (especially when swallowing, chewing, and even during a conversation);
- Difficult mouth opening
- Paresthesia
An increase in body temperature most often occurs on the first day after tooth extraction. This is a normal reaction of the body in response to surgery, but only in this context: by evening it is as high as possible (up to 38.5 ° C), and by morning it is either 36.6 or slightly higher (no more than 37.5 ° C) ) In this case, we can say that the body is struggling in normal mode, coping with the inflammatory process.
The more teeth were removed at a time, the stronger the response of the body can be.
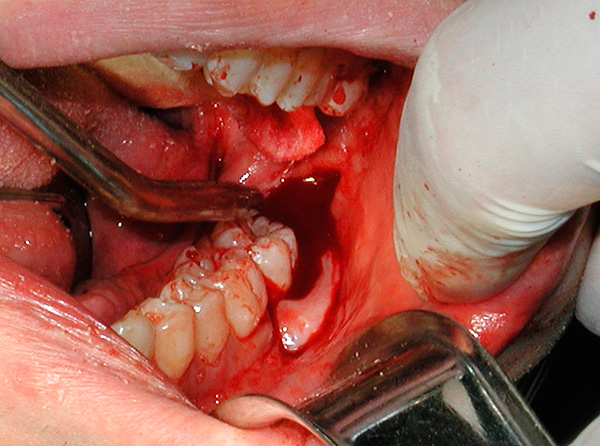
In the photo below - fresh holes after removing two teeth at once:
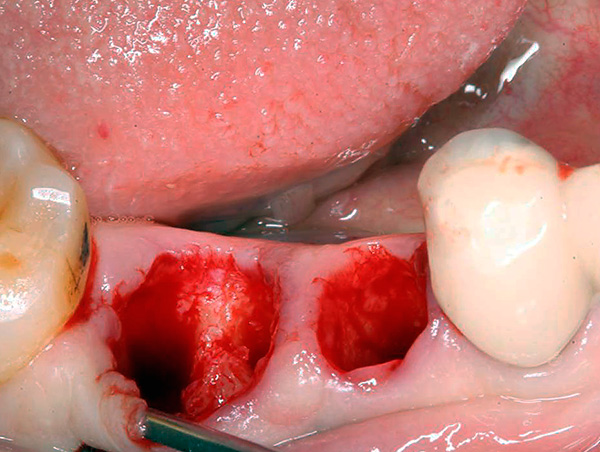
Thus, an elevated temperature of 1-2 days after removal should not be considered as a pathology, but it should be monitored 2 times a day at the same time (for example, early in the morning at 8 o’clock and then late in the evening at 20:00). If the temperature is above 38.5 ° C, or lasts more than 2 days, having high morning readings, then this is an occasion to consult a doctor.
The degree of deterioration of health after tooth extraction largely depends on the individual characteristics of the body of each person. If the body is weakened against other diseases, there are immune pathologies, or old age, then the well-being can significantly deteriorate, and the help of a doctor will be required. There can be no talk of any disability.Only the doctor can assess the condition after the examination, and if necessary, a sick leave for the prescribed number of days will be issued so that the patient can restore strength at home.
On a note
Some people are so "eager for battle" (that is, quickly to work) that they do not want to spend a couple of days at home treatment. Quickly remove the swelling, swallow a couple of painkillers, if the hole breaks and go! However, it is important to understand that after a surgical operation (and tooth extraction is an operation), the body needs to be given time to recover. Otherwise, non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations can lead to a series of progressive serious complications.
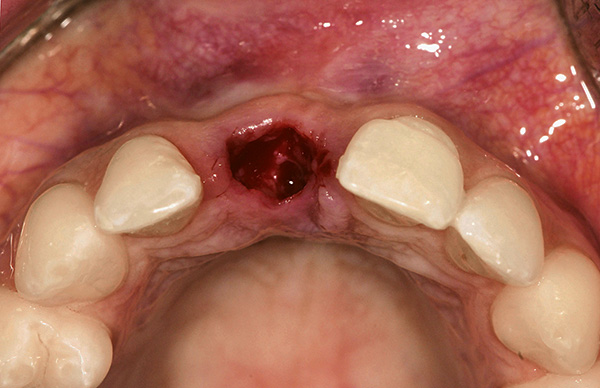
The appearance of severe pain against the background of developed edema is a frequent and perhaps the most unpleasant phenomenon, especially when the pain is not stopped by analgesics. Doctors almost always include painkillers in their recommendations to cope with the painful period in the first days after tooth extraction. However, with the development of tissue swelling, both mild and bursting, tearing and non-stopping pain medications can occur, which it is not possible to relieve with oneself.
With the development of acute pain for 2-3 and subsequent days after tooth extraction against a background of fever, severe swelling, putrid breath and other disturbing symptoms, you should urgently consult a doctor for help.
Swelling may be accompanied by difficulty opening the mouth (often observed when removing the lower wisdom tooth). It can hurt to open your mouth even a couple of centimeters. There is a strange sensation of pain when swallowing, as with angina, and on the one hand. This is due to the anatomical location of the eighth teeth: the spread of edema captures the masticatory muscles of the jaw.
Within 3-4 days, improvement usually comes - the soreness when opening the mouth decreases, and other symptoms (if any) also gradually disappear, that is, a positive dynamics is determined. If this does not happen, and the mouth still barely opens, or it gets worse, then you need to see a doctor.
Problems of a neurological nature are much less common - in particular, paresthesia, that is, loss of sensitivity in the area of the extracted tooth, as well as in the area of the lips, cheeks, and chin. This most often applies to cases of removal of the lower wisdom teeth (eights), less often - the lower sixth and seventh.
The cause may be excessive trauma in the area of intervention with damage to the mandibular nerve, less often paresthesia is a consequence of the development of edema, in which compression of the nerve trunk occurs. In the latter case, the loss of sensitivity is independently eliminated as the edema (hematoma) in the area of the extracted tooth decreases.
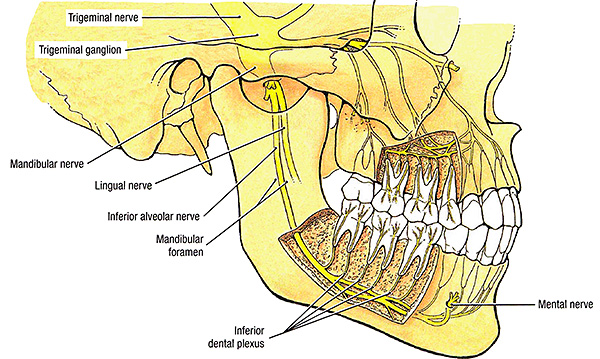
The timing of the restoration of the damaged nerve trunk is quite large: from 2-3 weeks to 1-2 years, depending on the severity of the violations. However, this process can be somewhat accelerated - it is important to consult a doctor with this problem in time, determine the cause of paresthesia, and start recovery procedures (physiotherapy) in a timely manner.
Feedback:
“I removed a wisdom tooth 3 months ago, which could not have erupted from the gums. I was immediately told that after such a difficult removal there will be swelling and can be very painful in the first days. After removal, I was prescribed antibiotics and oral baths with an antiseptic, as well as levomekol on the gum. I removed on Wednesday, and the biggest swelling puffed up on Friday, well, that weekend. I thought I won’t go to work, but on Sunday he disappeared completely, there was only a small yellowish bruise on his cheek ... "
Oksana, St. Petersburg
How long does edema usually last after tooth extraction?
If the doctor after tooth extraction did not pay due attention to the patient and did not inform him about the main recommendations for the care of the hole (this is often found in clinics), then even minor problems will cause a panic fear in a person. This is especially true of the appearance of edema and severe pain: due to the stress after a severe tooth extraction, the patient is simply afraid to see a doctor again, does not know whether the current situation is dangerous and what he should do.
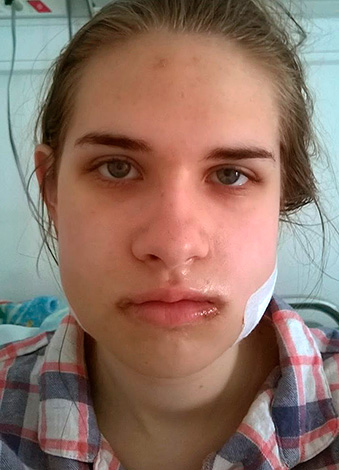
So, in this case it is useful to know how long the edema of the tooth extraction field lasts on average, as well as how long other unpleasant symptoms manifest themselves.
According to studies, it turned out that edema can reach its maximum in 2-3 days, and this is not a deviation from the norm, as well as a slight increase in body temperature, a slight deterioration in general condition, and the appearance of pain. All these are completely natural and regular manifestations of the post-traumatic inflammatory process.
However, often patients cannot independently decide how many days they can tolerate swelling or swelling of the face while it subsides, and when the dentist is still worth worrying about. Meanwhile, a number of dentists insist that patients bother them even with small deviations from normal health (with the appearance of swelling, aching pain, fever up to 38 ° C).
So what to do - go straight to the doctor if something starts to disturb after tooth extraction, or wait? The answer is: it never hurts to play it safe, and you should not wait until the swelling spreads to the neck or occupies half of the face (sometimes even eyes cannot be opened due to puffiness). If something bothers you, it makes sense, at least, to call a doctor and ask for advice, or make an appointment for an examination.

However, when there is a clear positive trend (the edema is insignificant and began to pass on 3-4 days, there is almost no temperature, severe pain, impaired opening of the mouth, paresthesia, putrefactive breath), then, of course, it’s not worth going regularly every two days to the doctor with questions about why the temperature is 37.2 and the gums ache a little.
The postoperative period lasts an average of 3 to 10 days. The main symptoms (edema, pain) can be very pronounced up to 3-4 days. Usually, all unpleasant phenomena disappear in a week, and in difficult cases in two weeks. And the main rule here is no self-medication without the advice and supervision of a dentist.
About possible complications
Now let's look at situations where edema accompanies possible complications after tooth extraction. In such cases, the edema does not subside until the underlying disease is eliminated.
Let's start with the most common complication - alveolitis. Alveolitis is a consequence of infection of the hole, that is, simply put, it is its inflammation. The degree of edema may be more significant. Often during alveolitis, suppuration of the gums occurs around the hole of the extracted tooth, sometimes suppuration develops when pressed.
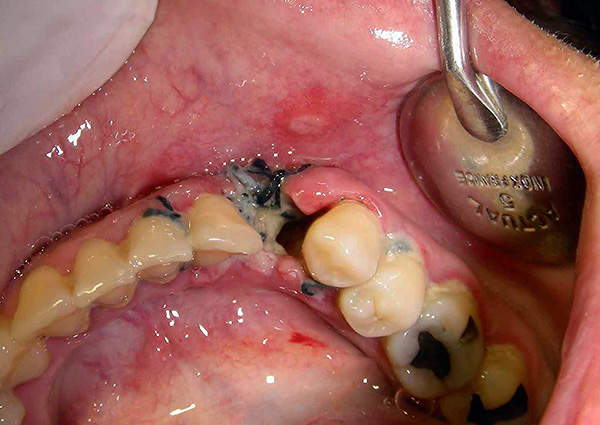
Alveolitis should not be treated independently, you need to consult a doctor. It is important to understand the main causes of this pathology:
- Fragments of a tooth or its root could remain in the hole;
- There is a granuloma or cyst at the bottom of the hole;
- The so-called “dry hole” (that is, without a blood clot protecting it);
- The falling into the hole of the remnants of food and their decay there;
- A gross violation of the doctor's recommendations (attempts to pick a hole with a toothpick, warm it, etc.)
A more serious complication is limited osteomyelitis of the tooth socket. In rare cases, with advanced alveolitis or its unsuccessful treatment, purulent-necrotic inflammation of the bony walls of the hole develops - osteomyelitis.
Its symptoms are very pronounced: a pulsating pain may appear in the hole, which extends into adjacent teeth, a person ceases to sleep normally, eats, cannot work. The temperature reaches high values, a strong edema develops, passing to the gum, bordering adjacent teeth, as well as to the soft tissues of the face. A person starts to worry about bad breath, there is an increase in lymph nodes.
In such cases, as a rule, specialized assistance is required in conditions of maxillofacial surgery.
Among the possible complications after tooth extraction is also worth noting an abscess and phlegmon.
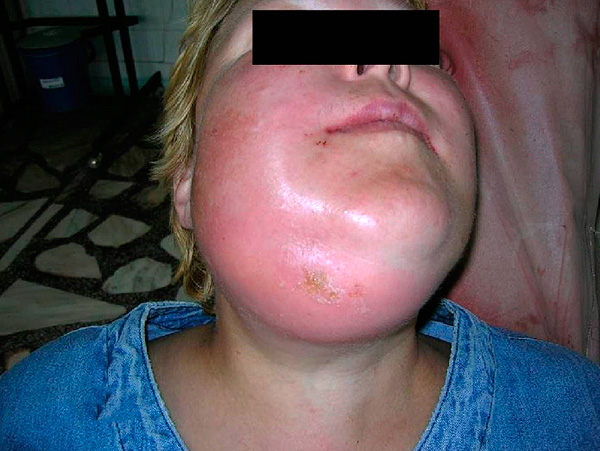
An abscess is a limited purulent inflammation, and a phlegmon is spilled (and can even threaten the patient's life). Often, with such severe complications, children come to the operating surgeons.
In a child (especially a weakened one), from the development of edema to an abscess and phlegmon can take a few days. Unlike adults, in children the factors of protection against fulminant infection are not always formed. Therefore, parents should remember that the formation of a pronounced edema in a child after tooth extraction (even milk) is an occasion to sound the alarm and run immediately to the doctor.
Special exercises for difficulty opening the mouth after extraction of molars
After removing the molar tooth (most often on the lower jaw, especially the wisdom tooth), many people begin to seriously worry about the fact that the mouth simply cannot be opened normally. Problems with opening the mouth (trismus) can be observed both against the background of severe edema, and without it. Sometimes the mouth cannot be opened even by 1-2 centimeters, which creates big problems not only with speech, but, above all, with food intake.
What can be done to get closer to the norm?
First of all, you need to keep in mind that removing the edema does not yet guarantee a successful solution to the problem of opening the mouth. If the trismus is “fresh”, then the jaw must be developed - otherwise, surgical intervention may be necessary. The terms of the disappearance of trismus are purely individual - from a week to 1-2 months (a lot depends on how difficult the extraction of the tooth was).
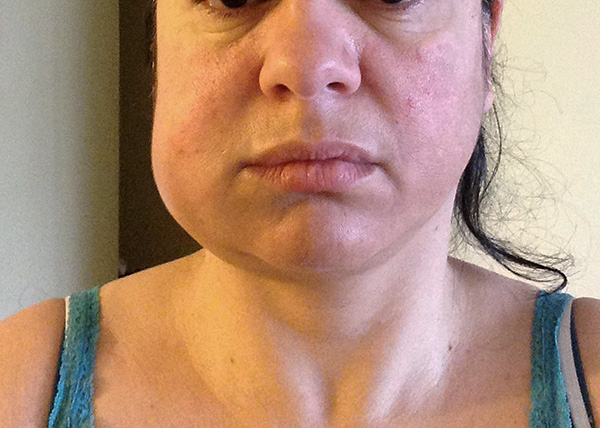
From the very first days after tooth extraction, you can independently perform gymnastics using chewing gum, or without it. Frequent and small chewing movements accelerate the development of the joint, even against the background of the inflammatory process in the area of the masticatory muscles. It is important to exercise without fanaticism, until you feel a slight pain, otherwise such exercises will only be harmful.
As for the more complex set of exercises, then a consultation with a dentist who deals with TMJ diseases is necessary. You will need exercise therapy - physical therapy for the maxillofacial region.
Here are some examples of exercises to improve your mouth opening:
- Without muscle tension, a quiet opening of the mouth (as far as possible) at a slow pace in a position with the head thrown back;
- Lowering the jaw and with a small effort pushing it forward;
- With an open mouth (as possible), voice enhancement with the pronunciation of the sound "a";
- Gently pull the lower jaw down with both hands, using the thumbs to grab the chin with the head tilted back.
The alternation of tension and relaxation of the muscles of the maxillofacial region has a significant therapeutic effect with the competent and systematic implementation of each exercise.
In especially severe cases, especially when Trismus has been around for several months or more, mechanotherapy is required - a set of exercises using special devices. Most often, mechanotherapy is carried out in conjunction with physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation, thermal oral baths, paraffin therapy, and others).
What you need and do not need to do after tooth extraction
Video review of the effects of removing a wisdom tooth (by day)

An interesting and useful article, but the pictures are disgusting, frightening .... Well, how nice is it yourself to look at it? And especially to the person who pulled out a tooth or is just about to do it.