
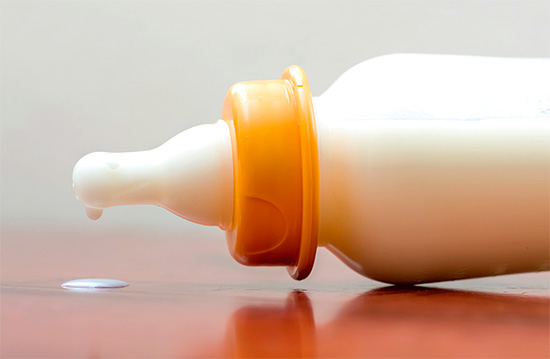
Bottle caries is a disease of young children aged mainly from 2 to 3-4 years. The rather original name of this disease is due to one of its causes: bottle caries in children develops because of the habit of drinking milk or milk mixtures from a bottle before bedtime or in the middle of the night, after which a large amount of food remains in the mouth for the whole night, which are the main cariogenic factor.
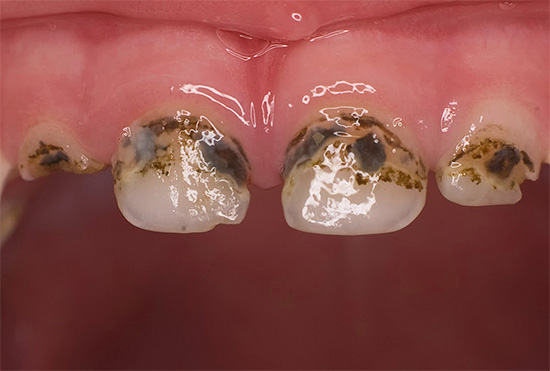
The following photo shows a typical example of bottle caries:
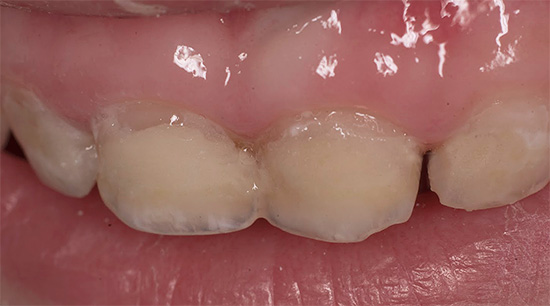
By analogy, bottle caries are also called "nursery", "kefir", "milk", there are even the names "nipple caries" and "night feeding caries" - these terms also clearly indicate the main sources of the problem and the age of the patients. In medical directories, all of these terms do not exist at all: by the nature of the course and primary causes, the disease is typical caries, and the name "bottle caries" is common.
Causes of the disease
The main reasons for the development of bottle caries are the same as are characteristic of other types of carious lesions: damage and further destruction of tooth tissues under the influence of acids produced by bacteria that multiply in the oral cavity. The food for these bacteria is mainly the remains of carbohydrates, which settle on the teeth after feeding. But the reasons for the presence of such food debris in the mouth and the inability of the body to suppress the activity of bacteria are secondary and affect the risk of bottle caries in different ways.
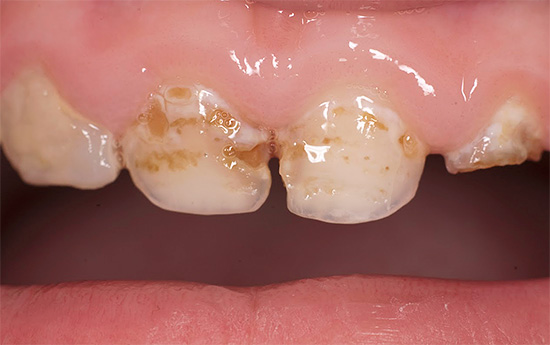
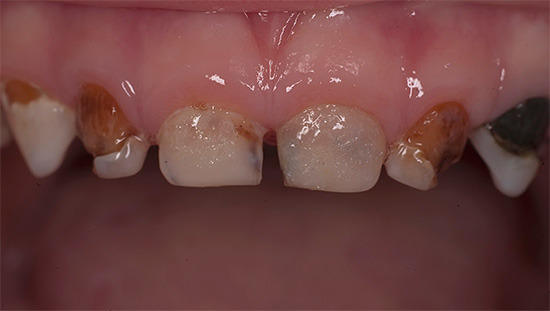
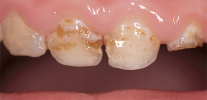
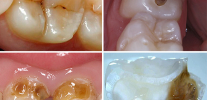
Photos of teeth with bottle caries before and after treatment:
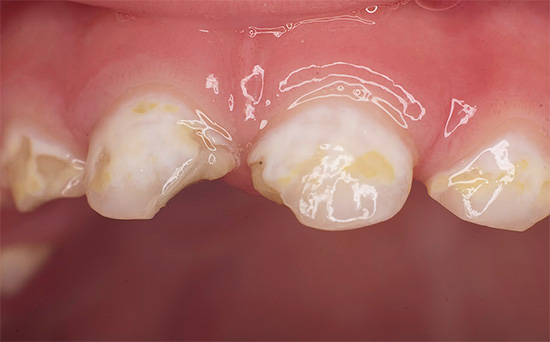
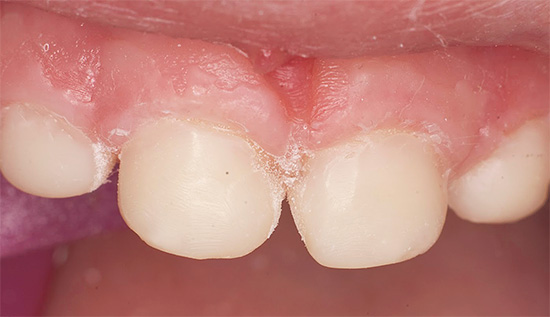
Most dentists consider nighttime feeding of the baby to be the main reason for the development of bottle caries. And it doesn’t matter whether the child eats from the bottle or sucks the breast - lactose (milk sugar) is found in both mixtures and breast milk, it is also an ideal substrate for the development of bacteria.
But in itself, this reason does not always lead to the onset of the disease: in many cases, children who are fed at night do not develop caries. And vice versa - in some small patients, signs of bottle caries appear even with a clear feeding schedule with the last meal before bedtime and brushing your teeth after it.
Therefore, other factors play an important role in the occurrence of bottle caries:
- Weakened immunity and insufficient bactericidal properties of the baby's saliva: in the usual case, the child’s own protective forces should be enough to suppress the activity of bacteria in the mouth. In children who (or who) do not brush their teeth, eat at night and do not have caries, it is saliva that protects teeth from decay. The converse is also true: if the ability of saliva to resist bacteria is less pronounced, then the teeth can be affected even with good oral hygiene. At the same time, other diseases of the body - for example, diabetes mellitus, influenza, intestinal infection, can affect the decrease in bactericidal qualities of saliva. In any case, the child can be weaned from night feedings and carry out proper brushing. In such conditions, the development of caries will be significantly slowed down, and attentive parents will always have time to show the baby to the dentist when you can still save and leave the tooth unscathed.
- Errors in the preparation of the diet of the baby. Sweets, sweet cereals and juices, confectionery and flour products, the remains of which are retained on the teeth, contribute most to the reproduction and prosperity of microflora in the mouth. The lack of rough foods, such as carrots and apples, which erase plaque when chewed, also affects the condition of the teeth.There may also be a shortage in the diet of foods high in calcium and phosphorus - fish, natural dairy products.
- A regional factor may also affect: with a lack of fluorine in drinking water, tooth enamel weakens and is damaged more quickly by aggressive acids.
In general, proper oral hygiene is always important - a bottle of milk before bedtime will be less harmful to the teeth if the child brushes his teeth after feeding.
Heredity is also considered a cause of bottle caries, however, in the vast majority of cases, parents justify their laziness and unwillingness to brush their child’s teeth or teach them to do it themselves. Remember: even with a genetic predisposition, proper oral hygiene and a healthy diet will significantly reduce the likelihood of tooth decay!
Feedback:
“Six months ago, we noticed just such a sore in our elder (3.5 years). At first, it seemed to me that he had damaged his teeth with something, because exactly under the gums on the three front ones, such dashes became yellowish. It was as if he had hit something and chopped. The dentist looked at this matter and said that it was bottle caries. Indeed, we don’t drill the children especially, it seems we tried to learn how to brush our teeth, but neither Andryusha, nor even Rolik do this regularly. Well, they are both calm. Andrei sat in a chair normally, the doctor put simple fillings on him with two teeth, and on one he processed it without any drill. Now for half an hour in the evening we are both playing brushing. ”
Anna, St. Petersburg
Appearance of teeth with bottle caries
In the photo below - typical bottle caries at a late stage of development. In some places, tooth enamel has completely collapsed, and deep lesions of dentin are visible, which quickly darkens due to pigmentation by various food colors and bacterial waste products:
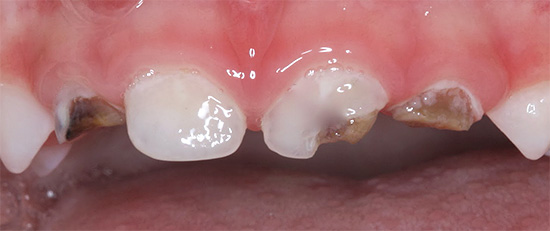
At the earliest stages, bottle caries can manifest itself in the form of light dull spots (stage of a white or chalk spot), which over time take the form of roughness on enamel, gradually deepen and darken.
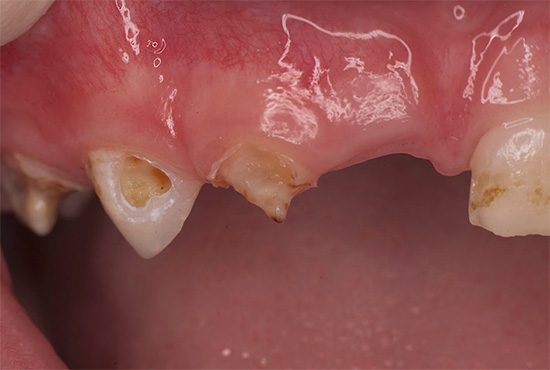
Further on the photo - average caries, covering several teeth at once. Such a simultaneous lesion is a characteristic diagnostic sign of bottle caries:
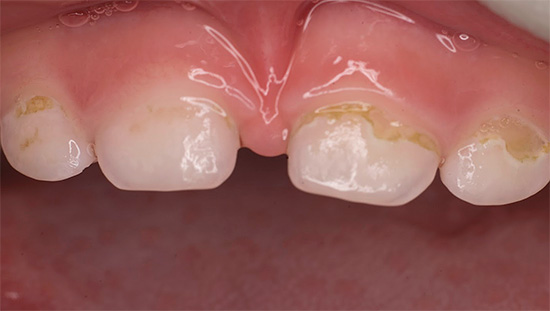
As a rule, bottle caries first affects the front upper four teeth of the child. The carious process often begins in the gum zone, quickly covers the entire tooth around the gum along the perimeter and penetrates into the deep layers of enamel. Damage to the gingival area of the tooth is a characteristic feature of bottle caries.
Generally speaking, deep bottle caries indicates an irresponsible attitude of parents to the health of the child: It’s easy to notice the pathology already in the early stages, and only parents who can pay attention to the baby’s teeth only with constant complaints can bring a child with half-decayed teeth into the clinic.

Important!
Bottle caries can develop not only on several front teeth, but also on one single tooth and molars. Therefore, the child should regularly and thoroughly inspect all teeth, not just the front ones.
Bottle caries treatment: rules and features
The main rule that parents should remember: treat tooth decay always needed! Excuses, they say, do not need to treat bottle caries, because milk teeth and so fall out - this is a crime before the child.
Premature decay of primary teeth often leads to disturbances in the location of permanent teeth and to defects in the development of the jaw, often spoils the diction of the child and leads to lisp.Yes, and simply rotten teeth over the years are an occasion for constant ridicule of a child by peers, which may be the reason for the formation of an inferiority complex in him.

Comment of the pediatric dentist
Premature tooth decay is, first of all, an infectious process in the oral cavity. Infectious foci are localized in the decaying teeth themselves with food lingering there, as well as on the roots of milk teeth, leading to a risk of impaired development of the rudiments of the permanent teeth underneath. Any infection in the mouth, especially such a serious one, is a risk of developing maxillofacial diseases (up to "fluxes" and the appearance of serious inflammatory processes in the bone tissue) and a number of related diseases or their deterioration.
If caries is detected, the child must be shown to a good dentist.
Successful treatment of bottle caries in children is possible at almost any stage of the development of the disease, but with deep damage to the tooth, it can be significantly complicated by the proximity of the pulp chamber to damaged tissues.
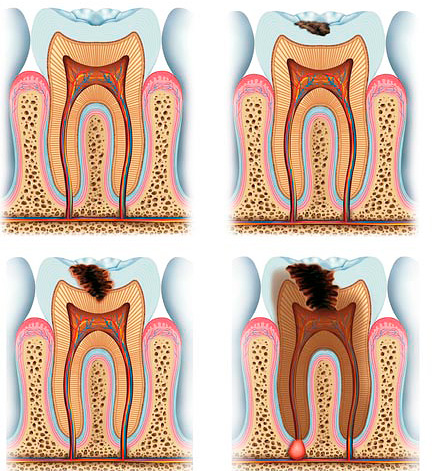
Fundamentally, the treatment of bottle caries in children does not differ from the management of other types of illness, however, it is methodologically much more difficult due to the fact that it is difficult to force the child to sit in an open-mouth chair for a long time. In many cases, professional procedures require anesthesia, which frightens many parents. That is why it is very important to notice the signs of caries at the earliest stages of its development, when the disease can be treated without using a drill with special drugs as directed by a doctor, and on their own at home.
Feedback
“We are 2 years and 8 months old. Caries began, the doctor said that it was bottled - we still suck the dummy before going to bed and eat yoghurts at night. Dark scuffs appeared on two teeth of the upper front ones, as if they had been painted with something. We went to the dentist, there is a special children's room, with drawings on the walls, toys, a doctor in a bright coat. And to no avail. Sasha immediately rushes into a cry, only her mouth is opened in a chair. I had to do anesthesia. It is very unpleasant, before that I had to specifically pass several tests, in general, so restlessly, everything looks like a serious operation. But the doctor says that usually the child is getting used to the second or third visit and makes it possible to do everything without anesthesia. But in general, don’t be afraid of him, it’s better than six months later the teeth will rot at all. ”
Tatyana, Odintsovo
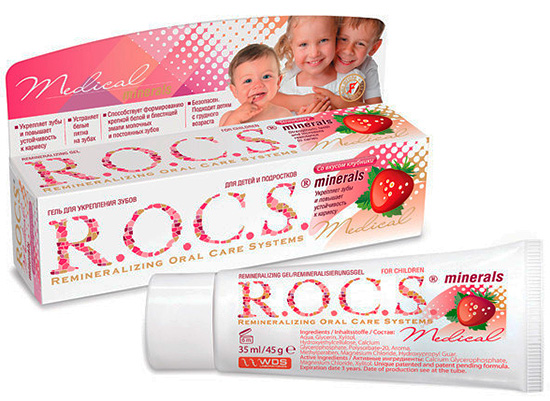
At the stage of a white or weakly pigmented spot, it is often possible to almost completely restore the damaged area of enamel using remineralizing therapy methods. At home, for this, the teeth are regularly treated with special gels such as R.O.C.S. Medical Minerals or GC Tooth Mousse. But one cannot decide on treatment on their own with their help: only the doctor should determine the stage of development of caries and prescribe treatment.

Professional methods are more effective in the early stages of bottle caries development, when the doctor treats the porous damaged enamel surface with special infiltrants (ICON system). This procedure takes 1-1.5 hours, is quite laborious, requires the use of a rubber curtain (rubber dam), and in young children it is performed under general anesthesia.
Significantly easier to implement is the silvering of teeth with caries at an early stage. It can be performed by the smallest children without anesthesia. For a short period (about a month), a layer of finely dispersed metallic silver formed from its salts on the surface of the tooth reliably protects against caries.
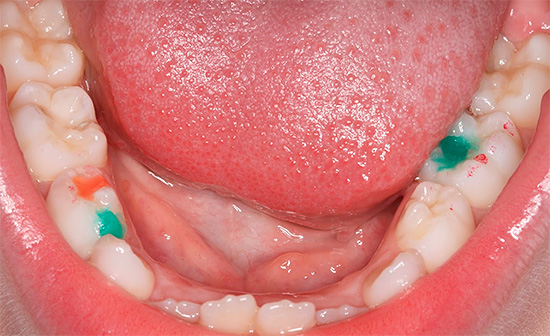
The photo shows an example of silvering of milk teeth:
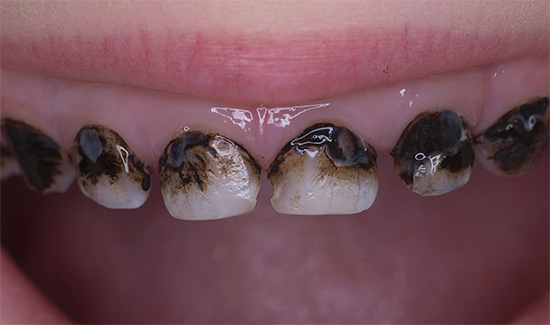
The disadvantages of this method are the need for constant updating of the silvered layer and the unaesthetic appearance of the teeth (they look almost black).Actually, in order to replace the silvering method with more aesthetic and one-time procedures, modern protection methods were developed, for example, the aforementioned ICON system.
On a note
Many dentists are negative about the silvering technique, based on the frequent darkening of the teeth after it, as well as in connection with the dubious effectiveness of the procedure (especially when dentin is involved in the carious process). If the clinic has modern equipment, silvering should be abandoned only because the fight against carious black teeth will lead, at best, to cured black and ugly teeth. This can cause psychological trauma to the child in the team of children who will laugh at him.
Here are some more photos of silver-plated teeth:
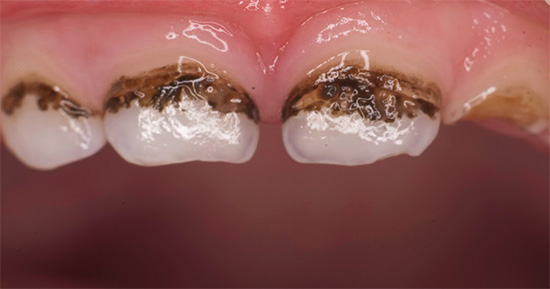
In elite clinics, silvering of the teeth is not done today.
If the areas of the tooth damaged by caries are very dark, this often indicates damage to the dentin and the need to remove the affected tissue with a drill. In this case, general anesthesia is sometimes used. After disinfection, the cleaned cavities are filled with filling material.
For the manufacture of fillings on milk teeth, glass ionomer cements, compomers and light-curing composite materials are used. Most often, dentists prefer to treat deep bottle caries in children using glass ionomer cement. Although this is an older material, it provides a constant release of fluorine compounds into the demineralized tooth tissues surrounding the filling. In addition, cement fillings are prone to abrasion along with the deciduous teeth themselves, and therefore, even with prolonged wear, they do not protrude beyond the edges of the teeth and do not affect the child’s bite.
From the practice of the dentist
Most dentists are of the opinion that the treatment of bottle caries in babies up to 2 years old most often requires the use of general anesthesia (anesthesia), since a high-quality restoration of the function and effectiveness of affected teeth, as well as their aesthetics, requires 2 or more hours. A child in consciousness will never let you do such a great job, and breaking it into separate tricks is an extra psychological trauma. However, even such an effective method as dental treatment under anesthesia has contraindications, therefore, it is necessary to determine with the doctor the possibility of its use in a particular child, acceptable risks and complications. The level of equipment of the clinic and the professionalism of doctors significantly affect the outcome of the upcoming treatment.
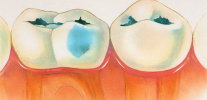
Colored fillings used today are made from compomers, which release fluorides in tooth tissue, like glass ionomer cements, but are very stable and aesthetic, like light curing composites. Their main charm lies precisely in the bright colors of the material, which captivate the children and make the whole procedure look like a game.
This is true for children older than 4-5 years who can compete with peers and show off their colorful fillings. Thus, the treatment of bottle caries in them turns into entertainment, and the doctor gets a calm child in a chair.
On a note
The price of a color seal is not much higher than the cost of a simple compomer. This means that if the clinic calls one and a half or two prices for a simple filling for such a childhood joy, then this is a frank overestimation.
How to prevent the onset and development of the disease: prevention from the first months of life
Mer prevention of bottle caries in children several, and they are all divided into two types: measures of local protection against caries and measures of systemic prevention.
The first include:
- Brushing teeth is important for all children who have at least one tooth.For the smallest children (up to a year old), they use simple gauze swabs dipped in water, tea or chamomile broth, soft brushes worn on one of the parents’ fingers, and special wipes (Spiffies, Teeth). From a year and a half, a child can already be taught to use a children's toothbrush.
- The use of anticariogenic gels for dental treatment.

Systemic prevention consists of the following actions:
- Compliance with diet, refusal of night feedings and feedings after brushing your teeth.
- Correction of the diet, a decrease in the number of sweets, flour products in it, an increase in the number of fresh fruits and vegetables, fish, dairy products, greens.
- Observance of basic hygiene measures: do not lick the spoon with which the child eats, or a dummy falling on the floor. Cariogenic bacteria from the parents mouth may not be familiar to the baby.
From the practice of the dentist
Many dentists and pediatricians are of the opinion that sweet juices are fatal to deciduous teeth, as they contain easily fermentable carbohydrates, which quickly form plaque. If the child is already accustomed to juices, it is not difficult to wean him: the juice must be gradually diluted with boiled water until it turns into water, and it can be given to the baby even at night without the risk of developing bottle caries.
In general, the child should be weaned as soon as possible from the nipple and in no case should it be smeared with jam or syrup. A healthy child can calm down and fall asleep simply with the help of a petting parent.
And if the baby is naughty and crying for no apparent reason, this is an occasion to show it to the doctor. Do not be afraid of doctors: no one better than them recognizes the disease at a stage when it is still not difficult to cure. And be healthy!
Interesting video: in detail about bottle caries (expert says)
How to take care of the baby’s teeth from birth

I live in Bratsk, Irkutsk region. Our doctors do not even know what bottle caries is, and they say that there is no such type of caries. I turned to Irkutsk - and I was glad that I knew this, agreed to cure. Now you have to go for 1000 kilometers, but the main thing is that the baby’s teeth are healthy 🙂
Julia, please write the address of the clinic that agreed to treat your child’s teeth in Irkutsk. Urgently needed.
I live in the city of Brest. Doctors in Lode have been treating bottle caries since we were 14 years old, but what, until then, would a child walk with rotten teeth? And so that his peers laugh at him. Tell me, where in the city of Brest can such a caries be cured?
Friends went to Minsk. The child is 2 years old. Under anesthesia they treated.
What bottle caries at the age of 14, what are they treating permanent teeth at this age!