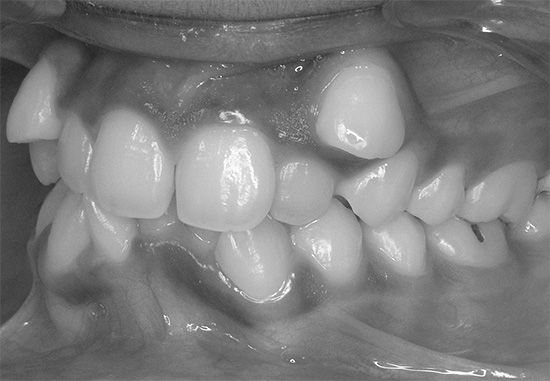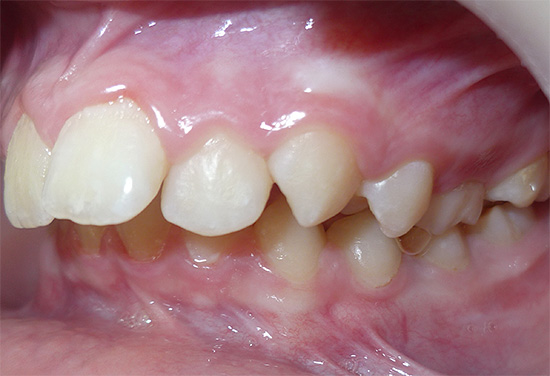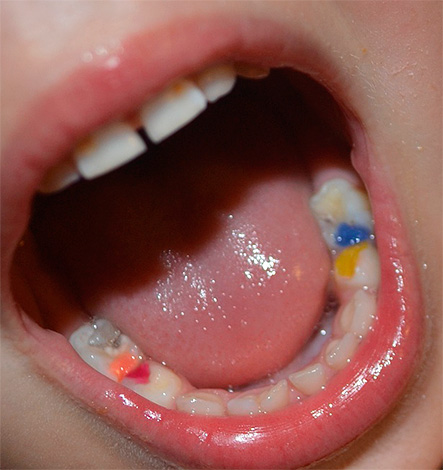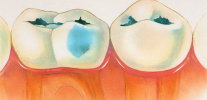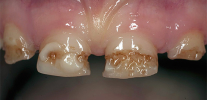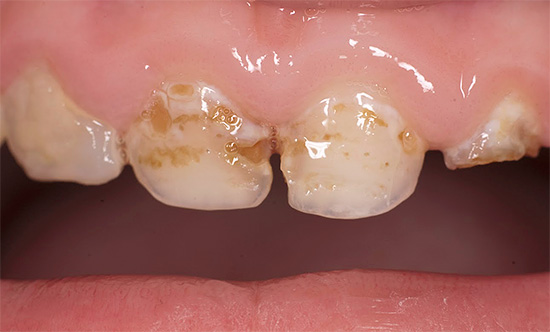
Baby teeth with caries in children must be cured. The approach of some parents, “They will fall out anyway, there’s nothing to torment the child and spend money,” is a crime in front of the baby’s health.
The timely treatment of decay of deciduous teeth is even more relevant than the treatment of permanent teeth. And that's why:
- The normal eruption of permanent teeth and the formation of a bite largely depends on the health and timely change of primary teeth. A complete set of milk teeth forms the correct jaw size. If they are destroyed by caries and fall out or are removed ahead of time, then the jaw may not be formed in the right way. This is highly likely to lead to a malocclusion in the future or a curvature of the teeth, their ugly location. As a result, for an untreated caries in a milk tooth, a child, having matured, will be paid at best with braces, at worst - with staggered teeth and psychological complexes.


- Caries on baby teeth can be complicated by pulpitis and periodontitis, because of which cysts may appear in the basal zone, and the rudiment of a permanent tooth may also be affected.
- Neglected caries often a cause for ridicule in the children's team.
- Also, do not forget that the appearance of caries is a sign of a violation of the rules of oral hygiene, an improperly made diet or a lack of minerals in the diet, and sometimes a symptom of immunity problems. If you ignore these problems at the beginning of your life, then by the middle of his child can come up without any healthy teeth and with a set of concomitant diseases.
- With the early removal of chewing milk teeth, the child will not be able to chew food normally. As a result, an insufficiently processed food lump will enter the gastrointestinal tract, which can lead to digestive disorders.
From the practice of the dentist
Often, parents do not even treat serious forms of complications of caries, and periodontitis in a child can turn into periostitis, osteomyelitis, abscess or phlegmon. Moreover, the death rate among children from caries complications is higher than in adults, since with certain weakening immunity factors, the process from pulpitis to abscess and phlegmon in a child can take several days and even occur within a day.
Therefore, the first thing to do when detecting decay of deciduous teeth in a child is to contact a pediatric dentist. After the examination, the doctor will tell you how and what teeth will need to be treated, what methods and means should be used for this, and how to make the treatment as comfortable as possible for the child.
On a note
Only in very rare cases can tooth decay really be left untreated. Usually, the doctor makes this decision if the child’s tooth change has already begun, tooth decay is found on the tooth, which is likely to fall out within six months, and the disease itself is sluggish, chronic. In this case, caries simply does not have time to lead to serious consequences. However, we repeat: only a professional dentist can make such a decision on the basis of an examination of the child.
Specific features of the treatment of primary teeth
Treatment decay of deciduous teeth in children It is carried out taking into account the specific structure and life cycle of the teeth themselves.
So, for example, baby teeth are quickly erased. This is a normal process that must be considered when selecting the material of the seal. If the material turns out to be harder than the tooth itself, then after a certain time the filling will begin to protrude beyond the surrounding tissues and stop the child from chewing.
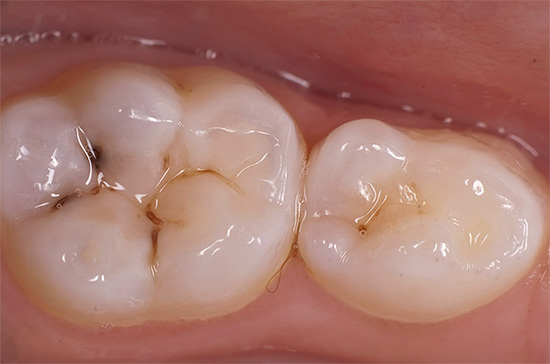
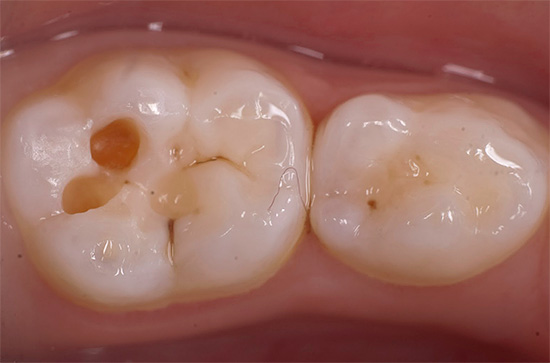
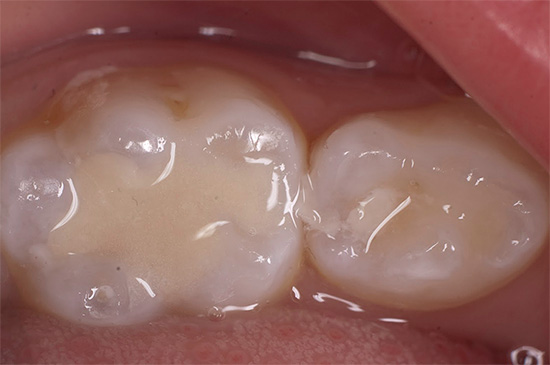
Typically, glass ionomer cements are used in the treatment of decay on baby teeth. In this case, in addition to the abrasion of the filling, which occurs naturally simultaneously with the walls of the tooth adjacent to it, there is an infiltration of fluorides into the tissues surrounding the filling, which, in turn, contributes to their additional mineralization and strengthening.
In addition, children often have bottle and blooming cariesthat are developing very fast. While parents have time to notice the disease and bring the child to the doctor, the pathological process can spread to most of the teeth and damage some of them especially badly. As a result, almost all teeth will have to be treated, and this will need to be done within several sessions and the therapy itself will be very tiring for the child.
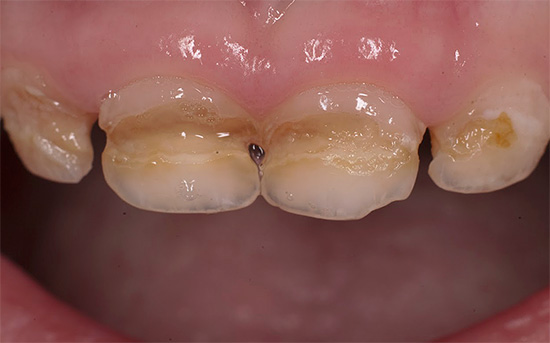
Methods for treating caries at different stages of the disease
In the early stages of caries, when only tooth enamel is damaged, conservative remineralizing therapy can usually be dispensed with. A drill is not used with it: demineralized areas of teeth are first cleaned, and then treated with special preparations that make it possible to restore damaged enamel.
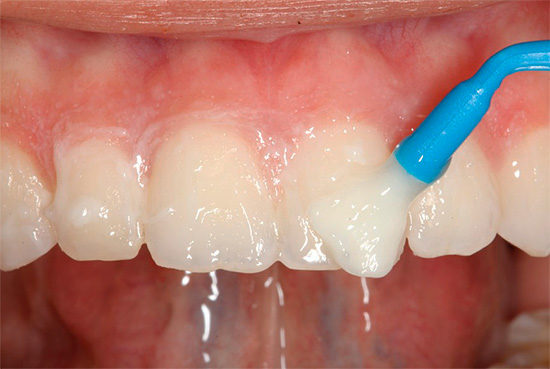
Today, ICON technology is also widely used to treat initial caries: ICON technology is applied: a special composite material is applied to the damaged area of the tooth, filling all the pores resulting from a carious lesion. This material hardens and provides reliable and long-term protection of the treated area from further destruction.
Thanks to ICON's caries treatment technology, regular dental examinations of a child become even more relevant. To treat decay of deciduous teeth in the early stages without a drill and fillings is much more effective and easier than subsequently tormenting a baby in the event of a far-reaching destruction of enamel and dentin.
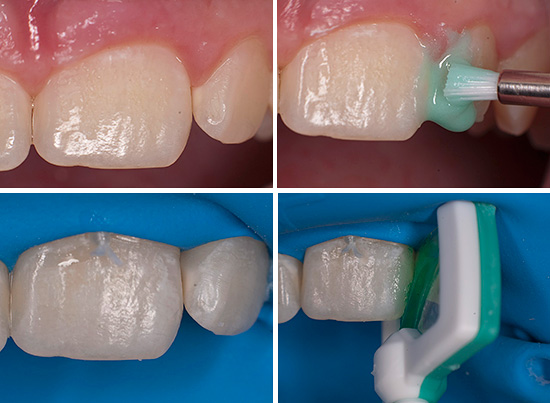
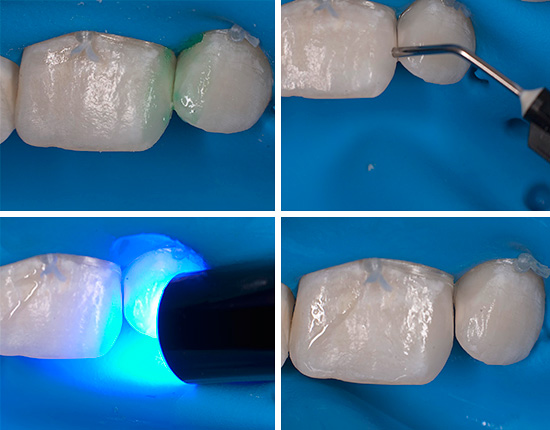
However, it should be borne in mind that for cervical defects located close to the gingival margin, the ICON technique is limited to use due to too thin and weakly mineralized enamel (dentin cannot be infiltrated with the drugs used). Children under 3 years of age should not use the technique.
Parent Tips
Regular examinations of teeth in a child allow not only to reveal hidden carious processes and determine the cariogenic situation in the oral cavity, but also to designate for parents a set of necessary rules to save tooth surfaces not affected by caries. It is important to start the cleansing already with the appearance of the first milk tooth. In this case, it is enough to wipe the tooth with special wipes or use a fingertip toothbrush for these purposes.
The first real toothbrush bought by a child should be:
- With very soft bristles;
- With a small and not traumatic rounded head;
- With comfortable grip for holding.
Teaching brushing should take the form of a game. It is worth starting from 1-1.5 years. Monitoring cleansing of all surfaces accessible to the brush and helping the child in this is carried out by adults. The combination of brushes with children's toothpastes is recommended not earlier than 2 years, when the child learns to spit.
Another method of conservative treatment of caries of deciduous teeth without a drill, silvering, is increasingly recognized morally obsolete today. With it, silver salts are applied to carious areas, which leads to the death of bacteria here (silver has bactericidal properties) and subsequently to the protection of these areas from repeated caries lesions.
From silver salts on the surface of the treated area, finely dispersed metallic silver having a dark gray color is restored. It very spoils the appearance of the teeth, and with them the child’s mouth looks no better than with caries. In addition, silvering must be repeated once a month, which can be quite problematic.
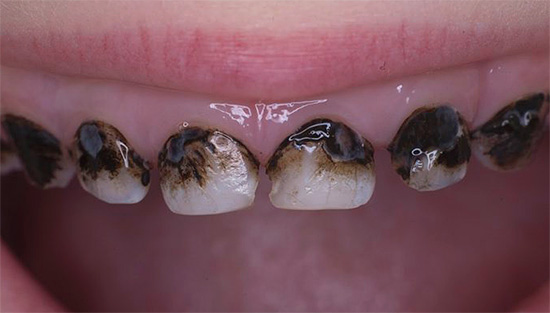
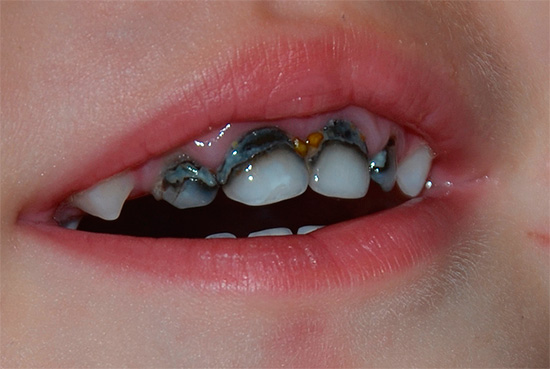
In general, the effectiveness of the silvering of teeth, as a way to prevent the development of caries, is quite low.
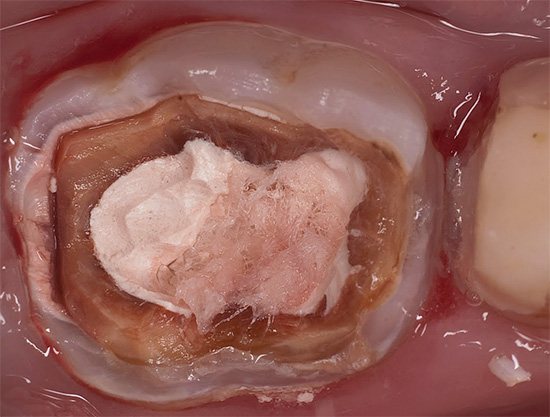
With the penetration of caries under the enamel and damage to the dentin, the infected cavity is excised, disinfected and filled with filling material. In some clinics, carious damage is cleared without a drill using a jet of abrasive material or special substances that dissolve the affected tissue. In addition, in some clinics, a laser is used to remove affected tissues, but for prescribing it to a doctor, the age of the child and the specifics of a particular clinical situation must be taken into account.
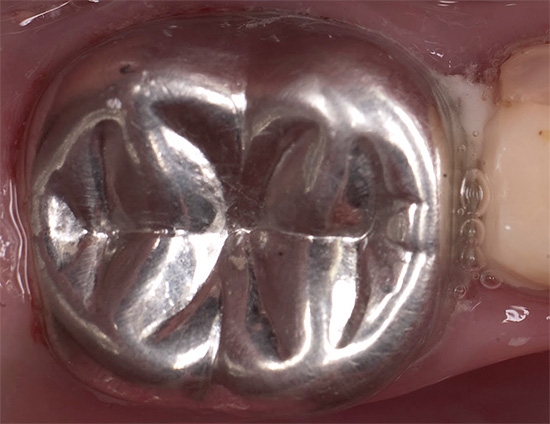
In rare cases, for example, in severe forms of bottle caries, long before the teeth change, children install crowns using a special technology (while the tooth is not turned). For chewing teeth, such crowns are usually made of metal, and for incisors - of composite materials. The installation of the crown in this case is done in one visit to the dentist, and the crowns on the front teeth are installed in just 20-25 minutes.
Anesthesia, local anesthesia and pain-free treatment: psychological aspects of therapy in children
No less difficult than the actual caries therapy is the control of the patient during the treatment procedure. Children themselves are restless, and keeping them still in a chair for at least half an hour is incredibly difficult.
The problem is aggravated if the child is frankly afraid of the dentist or drill and expects that it will hurt. He may simply not open his mouth. And the younger the child, the more acute this problem is. It is solved in several ways:
- Many children over 6-7 years old are quite obedient and the presence in the office of one of their parents allows them to sit quietly.
- The presence in the office of distracting design elements (for example, drawings on the walls, toys under the ceiling), a TV near the chair, a bright dressing gown by the dentist - all this distracts and keeps the attention of the child, who can devote to examining these objects or watching the cartoon all the time the treatment lasts .

- The use of colored fillings. If a child knows what it is, he willingly endures it all the time, just to get such a seal and then brag to his friends.

- Local anesthesia for children who are afraid of pain during dental treatment. Before the injection itself, the child is treated with gum anesthetizing gel, and the baby does not feel any injection or pain during further work.
- Sedation of nitrous oxide, in which the child relaxes, his sense of fear is dulled, a short sleep may occur.
- Anesthesia
It is anesthesia that parents are usually most afraid of. This is wrong: most drugs used today for general anesthesia are safe. Moreover, before the treatment itself, the child is tested and the necessary examination is carried out to make sure that he does not have individual contraindications to the use of anesthesia. And the doctor himself uses anesthesia only if other means and methods do not allow manipulation.
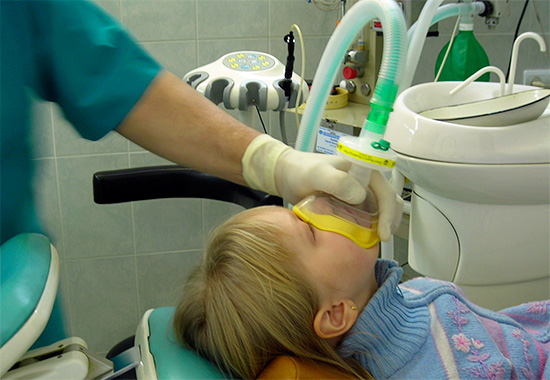
Many parents are afraid that anesthesia may affect the mental development of the child, worsen his memory, and lead to a delay in the development of speech. Theoretically, such situations are possible, but they are extremely rare. Statistics show that such complications of anesthesia in children are extremely rare, and in many cases the cause of the developmental disruption is not anesthesia itself, but a strong fright in the hospital or the consequences of a disease that was treated under anesthesia.
Feedback
“In Sweden, in addition to anesthesia, there are no options. She is three years old, she trusts a doctor, sits down in an armchair, does not cry, but simply says no. She said the doctor doesn’t. It is impossible to force her, as this is violence against the child, and she refuses. I had to do anesthesia.She came out of it for a very long time, but there were no consequences. ”
Anna, Malmo
In cases with running bottle caries in children under the age of 3 years, anesthesia is the only opportunity to perform manipulations. For treatment, it may take at least 2-3 hours, and it is impossible to force the baby to sit motionless all this time in an unfamiliar environment.
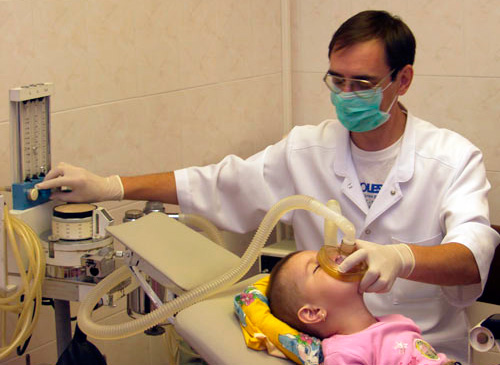
In any case, the final decision is always made by the parents. The doctor himself will not do anesthesia and perform surgery if he has concerns about the consequences of using anesthesia for the child.
Practice shows that in the vast majority of cases, common sense wins and parents agree to anesthesia instead of risking the health and beauty of the child in the future.
Feedback
“My son is 4.5, my daughter is 2 years old. We went for an examination, two small holes were found in my son, and in my daughter - on 5 teeth caries, there is a plaque and one tooth is already without a top. The doctor immediately offered us anesthesia. Although the clinic is good, I was somehow scared. I read about Sevoran at home, it seems there’s nothing wrong with it, but anyway anesthesia for 2.5 hours is more than appendicitis is done! They decided to refuse, they coped with their son. And the cartoons showed him, and promised everything in the world, and they read fairy tales, but they healed their teeth, one for each visit. And Sasha didn’t even open her mouth. She said no, that's all. What to do here? I had to do anesthesia, but everything was in order, nothing happened. ”
Eugene, Moscow
Why treat milk teeth if they fall out anyway? Parents note
Interesting nuances regarding the treatment of deciduous teeth under general anesthesia