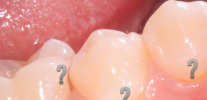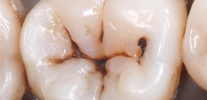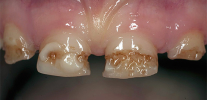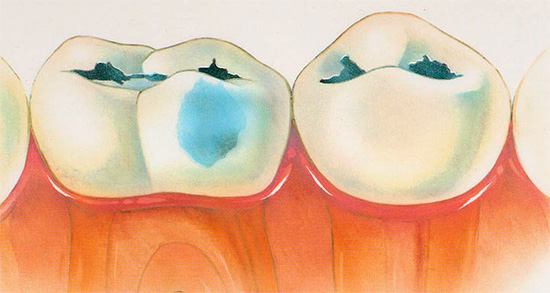
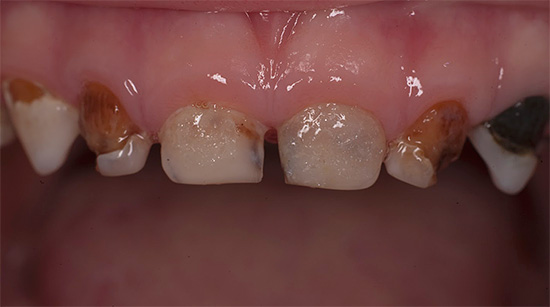
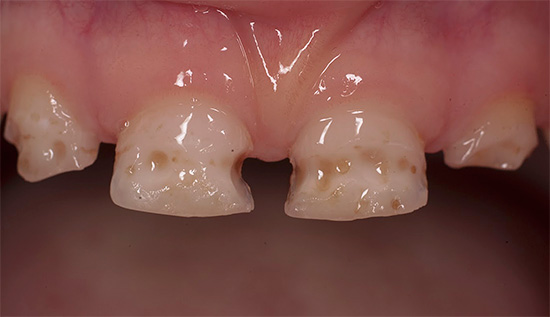
The decompensated form of caries is, in fact, an intensively developing caries, a pathological process that is very active in the hard tissues of the tooth and leads to their rapid destruction. Often carious cavities with this form of the disease are multiple and are present in many teeth at once.
In dentistry, there are several classifications of caries. When classifying the severity of the process, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- compensated;
- subcompensated;
- decompensated.
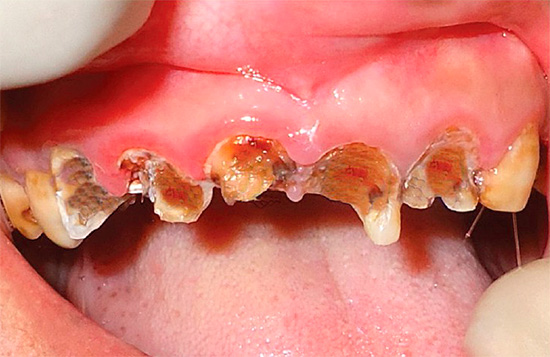
Decompensated (acute, blooming) caries is the most dangerous form, as it develops much faster than in compensated and subcompensated forms. Acute caries can lead to tooth loss in just a few weeks. In this case, enamel and dentin are destroyed very quickly, and the transition from the initial stage to the deep occurs many times faster than in the chronic course of the disease.
On a note
The name “decompensated form” itself means that the development of the carious process is not compensated in any way by the response of the body. It is in the absence of any obstacles that the process proceeds especially quickly and with very serious consequences.
The reasons for the development of pathology in decompensated form are reduced bactericidal properties of saliva, lack of oral hygiene, an unfavorable diet and hereditary factors, an unhealthy lifestyle. Sometimes acute caries develops due to weakened immunity.
Diagnosis of decompensated caries
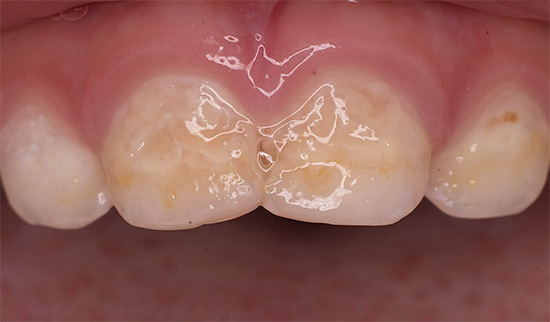
Acute caries is most dangerous when the tooth is not treated. But unlike other forms, it is easily detected. The main symptoms that signal a serious problem are as follows:
- multiple noticeable external manifestations of caries on the surface of tooth enamel;
- acute prolonged pain in the teeth;
- strong reaction to cold, chemical, mechanical irritants.
If you experience such sensations in the oral cavity, you should immediately consult a dentist.
Important:
If the carious lesion of the surface is very small, but the described symptoms are present, you should not postpone the visit to the doctor. Under a small entrance there may be a large carious cavity. An additional clue will be the loss of enamel shine, its grayish or chalky shade.
The dentist easily diagnoses the decompensated form of caries by the following signs:
- wide base carious form;
- narrow entrance;
- a large amount of softened dentin;
- sharp pains in the process of sounding.
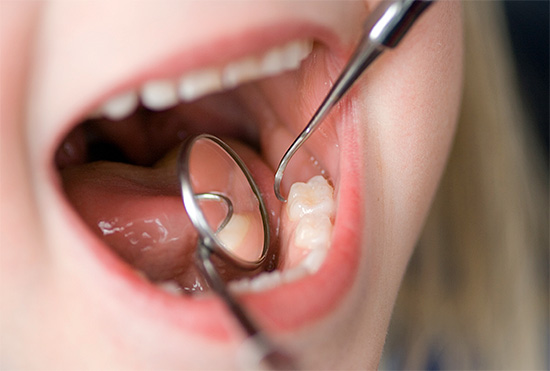
A probe and a dental mirror are usually sufficient for diagnosis. But if the carious cavity in a separate tooth is hidden from view, an x-ray is taken or transillumination is used (method of “highlighting” hidden carious areas bright luminous flux of lamps). Also, with a decompensated form, fissurotomy is often used (this is a method for the diagnostic search for hidden caries using prophylactic excision of “darkened” fossae and enamel cavities on chewing teeth).
Who is at risk
The decompensated form of caries develops the faster, the lower the body's resistance. Therefore, the acute form is most often observed in people with weakened immunity.
There are several groups of patients who are most at risk of this pathology:
- children with baby teeth;
- people who have recently had infectious diseases;
- people with metabolic disorders;
- elderly people with weakened immunity.
To avoid the development of acute caries, it is recommended to undergo a planned rehabilitation of the oral cavity 1-3 times a year.
Hazard of decompensated form
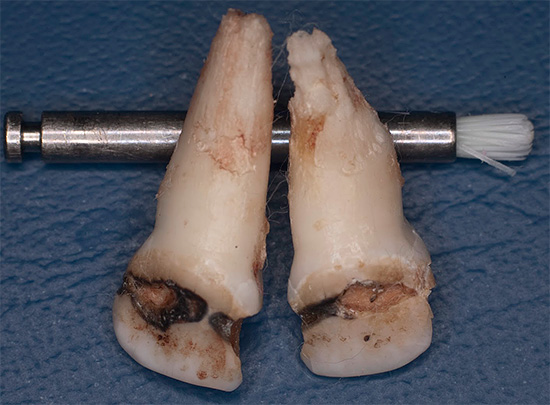
Acute caries is dangerous for many reasons. A neglected form of the disease often leads to the following problems:
- the development of pulpitis and periodontitis;
- periodontitis development;
- tooth splitting;
- tooth loss.
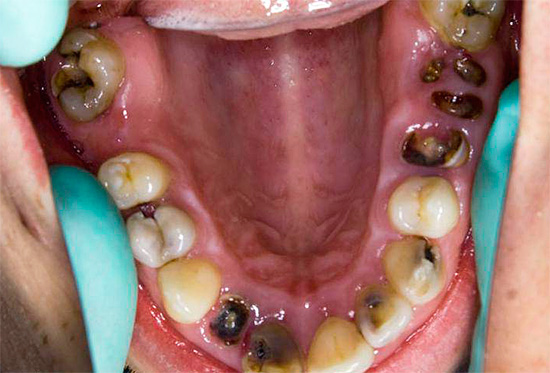
In addition, the decompensated form is a signal of a malfunction of the whole organism. Untreated caries it is often the result of a decrease in the production of saliva and a decrease in its bactericidal properties, which affects the general condition of the oral cavity as a whole. In pregnant women, this can affect the general physical condition of the expectant mother and the health of the fetus.
Types of disease
Acute caries has two forms:
- moderate acute;
- deep sharp.
The difference between medium and deep acute forms is the size of the carious cavity. With moderate acute caries, there is no need to remove the nerve, and the tooth can be treated and restored. With acute acute caries, depulpation is usually required, and with severe tooth decay, it is necessary to remove it.
Since in the acute form of pathology, the destruction of tooth tissues occurs very quickly, and children are most susceptible to the disease, in pediatric dentistry their following group is adopted:
- Compensated form (I group);
- Subcompensated (II group);
- Decompensated (group III).
Groups created for the implementation of follow-up.
Children's dentist Vinogradova T. F. identified several dispensary groups:
- healthy teeth;
- compensated form;
- subcompensated form;
- decompensated form.
Children with a compensated form are examined once a year, with a subcompensated - 2 times, with a decompensated - 3 times. Remediation reduces the risk of complications during the development of caries, the number of fillings and extracted teeth decreases. Also, the need for treatment is almost halved, the number of annual scheduled examinations is reduced.
Monitoring risk groups allows you to keep track of a number of criteria:
- general decay;
- anamnesis of life;
- health status;
- the severity of the disease.
Remediation planned and timely caries diagnosis in adults and children, they provide an opportunity not only to cure it in the initial stages, but also to prevent the development of blooming caries.
How is the treatment of blooming caries
The treatment of a decompensated form of caries can conditionally be divided into three stages:
- removal of all tooth tissues affected by caries;
- nerve removal (if necessary);
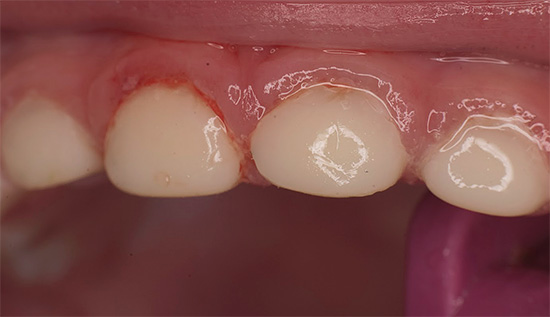
- tooth restoration.
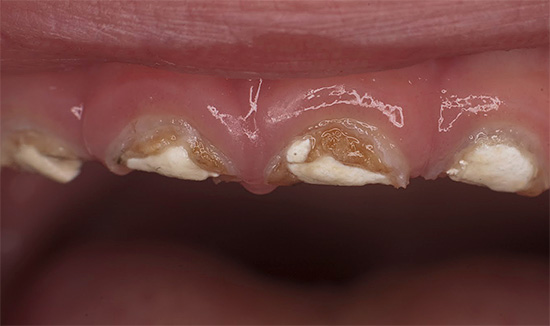
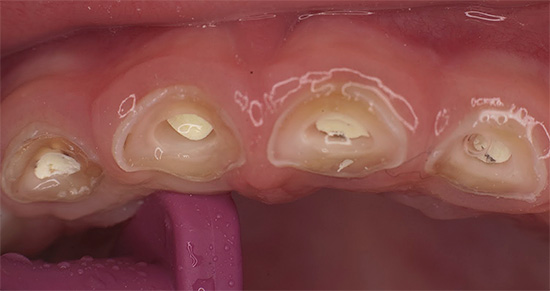
Since blooming caries is very painful, all stages of treatment are carried out under local anesthesia or under general anesthesia (less often). That is, for the patient, the procedures are painless. Modern anesthetics are absolutely safe, hypoallergenic, so this treatment is available even for pregnant women.
Removal of affected tissue is predominantly carried out using a drill. But this is not the only opportunity. There are more modern methods: flushing with a dental sandblast, evaporation with a dental laser. Unfortunately, these modern methods do not yet have a good evidence base for their effectiveness in treating serious carious lesions, and have not received wide distribution in our country.
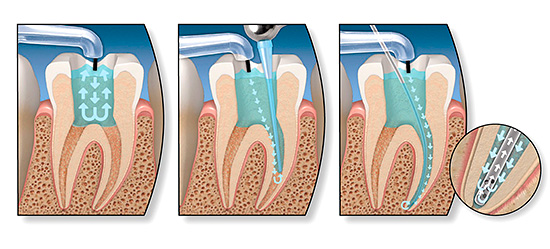
At the next stage of treatment (if there is a need), the dental nerve is removed using special equipment. Then the dental canals are cleaned and filled.
Restoration is the last stage of treatment. With the help of filling materials, the dentist restores the original shape of the tooth.
The treatment of acute caries is a complex and lengthy process. Most often, it takes place in two visits.During the first, the affected tissues are removed and drug treatment is performed. During the second visit, tooth restoration is performed.
Prevention of a decompensated form of the disease
To prevent the development of acute caries for everyone. Even with a hereditary predisposition, dental problems occur when oral hygiene and poor nutrition are not followed.

Prevention of the decompensated form of the disease is quite simple. For its implementation it is necessary:
- brush your teeth in the morning and evening;
- use fluoride toothpaste;
- floss interdental spaces;
- Do not eat too cold and burning food, drinks;
- limit the amount of soft and sweet food, since after its intake, a plaque forms on the teeth, which contributes to the demineralization of enamel;
- Visit the dentist 1-3 times a year.
Planned reorganization of the oral cavity makes it possible to detect caries at the earliest stages and prevent its transition to acute form. Regular visits to the doctor allow you to detect weaknesses in the care of your teeth and gums in time, make adjustments and stop their diseases. Therefore, a visit to the dental clinic to check the condition of the teeth should be the rule for everyone who cares about their health.
Useful video: what is important to know about the treatment of caries and its complications
And here is the actual treatment of a tooth with a drill and the installation of a seal
How to properly brush your teeth with a toothbrush