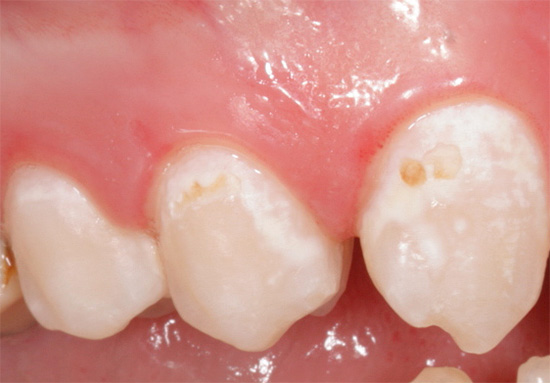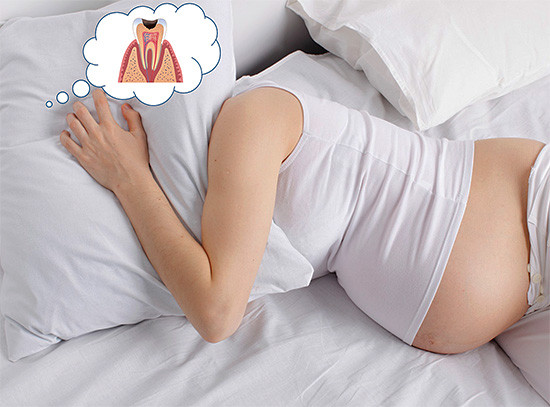
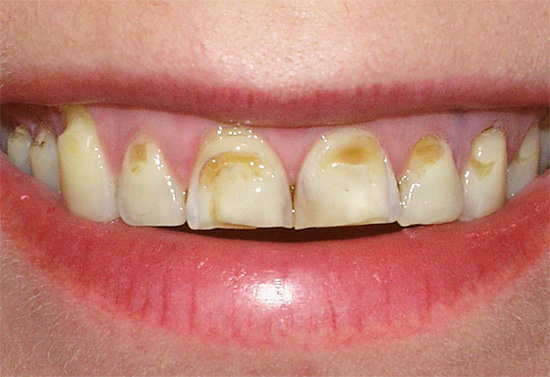
Caries during pregnancy occurs as a whole more often than in other periods of a woman’s life, and often proceeds very actively at this time, sometimes even in an acute form. The concerns of expectant mothers regarding the possible effect of caries on the fetus, as well as fears about whether it is possible to treat teeth at all in such a crucial period, are quite understandable.
In some cases, during pregnancy, caries only begins its destructive work (and many try to wait this time), and the most noticeable and sensitive consequences of tooth damage await a woman after childbirth.
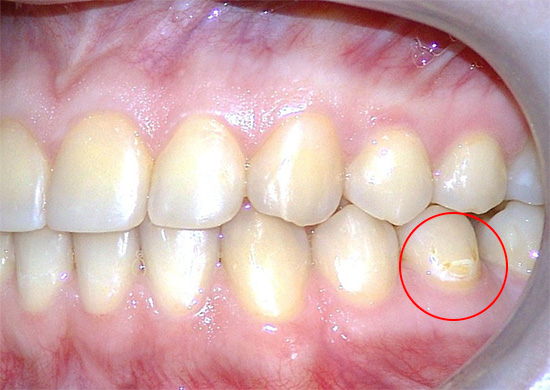
On a note
The statistics are eloquent:
- Caries is found in 91.4% of women with a normal pregnancy and in 94% with toxicosis.
- The average intensity of tooth damage in pregnant women is from 5.4 to 6.5 (this is a high level);
- Enamel hyperesthesia (hypersensitivity) is observed in 79% of women during gestation.
It is believed that caries itself during pregnancy does not have such a negative effect on the fetus as its treatment can have. Using this common belief, many pregnant women are wary of visits to the dentist, and the reason for this is because future mothers do not understand the nature of caries and the dangers that they are fraught with.
Let's see what is actually more dangerous and more likely to affect the fetus - caries or its treatment, and also see how you can make a healthy baby and at the same time keep your teeth in excellent condition.
Does caries affect the fetus?
To begin with, it is useful to remember that tooth decay is a disease caused by pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity. It is believed that through microdamages of soft tissues, these bacteria can penetrate into the bloodstream, enter the fetus and cause various pathologies
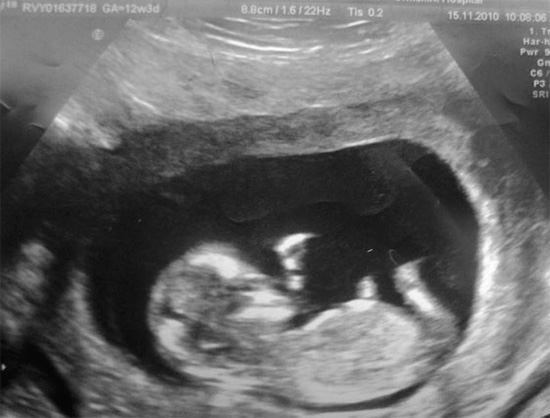
However, the probability of this is extremely small: through the placental barrier, bacteria manage to penetrate only in extremely rare cases., and the inhabitants of the oral cavity have practically no chance of surviving in the tissues of the embryo and exerting any influence on it. These abilities are mainly possessed by viruses. But, as is the case with any infectious disease, the presence of caries in pregnant women involves a number of hygienic procedures and careful oral care.
Caries and pregnancy are more closely linked precisely through the physical condition of the mother. For example, constant pain in a caries-affected tooth (which, incidentally, is not uncommon during pregnancy) leads to a woman’s inability to eat normally, a general deterioration of her emotional state. All of this in combination can really have some negative impact on the development of the fetus.

In addition, complicated caries also affects pregnancy by the fact that in case of lesions, for example, periodontal disease, an inflammatory process occurs that can affect the general physical condition of the expectant mother: increase body temperature and the need for antipyretic drugs, exacerbation of toxicosis, and malfunctions digestive system.
But nevertheless, the main and most real danger of caries during pregnancy is the possibility of its transition to an acute form, severe damage to many teeth at once and their loss by a woman in a fairly short time. In other words, caries is usually more dangerous for the mother than for the fetus.
The same is true in the case of caries in a nursing mother. Only the reasons for refusing a visit to the dentist differ here: if a pregnant woman is more often afraid that the treatment of caries will harm the unborn baby, then the nursing mother does not have a trivial 2-3 hours to go to the clinic.
Causes of caries in pregnant women
Caries during pregnancy is largely due to the same reasons as in cases with other categories of patients: poor oral hygiene, an abundance of snacks during the day, and a passion for sweets.

But many women come to the fore for additional reasons, caused precisely by gestation:
- A decrease in the concentration of calcium and fluorine compounds both in saliva and in the blood due to some consumption for the needs of a developing embryo. At the same time, calcium is not consumed from the teeth themselves, as many believe incorrectly. But the remineralization of enamel and its strengthening, always occurring in other periods due to the action of saliva, during pregnancy can slow down or even stop. As a result, enamel becomes weakly mineralized and is more easily damaged by the acidic waste products of bacteria.

- Hormonal changes in the body and, again, the corresponding changes in the composition of saliva, which leads to a decrease in its bactericidal properties. Simply put, saliva of pregnant women in some cases is less effective in killing cariogenic bacteria.
- Dietary changes - pregnant women can be thrown to different extremes, they often have a strong craving for sweets and starchy foods.
- Disorders in dental care - due to fatigue, toxicosis, worries and fuss, some expectant mothers regularly forget to brush their teeth, or do not do it thoroughly.

In addition, many pregnant women manage to hear enough from friends and relatives of the allegations that it is impossible to treat teeth during pregnancy, and simply do not go for preventive examinations. And as a result, they miss the moment when the tooth could still be cured absolutely safe for the fetus.
Treatment of caries at different stages of pregnancy: is it dangerous and how is it carried out?
Caries during pregnancy can not only be treated, but it is also necessary. Sometimes, due to the risk of acute development of the disease, timely treatment for some pregnant women is the only way to prevent generalized caries. Of course, the very management of the disease should take into account the position of the patient.
The main danger arising from the treatment of caries during pregnancy is the risk of exposure to fetal anesthesia drugs. All anesthetics are absorbed into the bloodstream and can pass through the placenta, and some of them are quite capable of adversely affecting the developing embryo.
Therefore, by the way, it is so important to see a dentist throughout pregnancy - if caries is detected at the very early stages of its development, treatment can be carried out using remineralization methods without anesthesia, without a drill and unpleasant sensations. But already launched caries without anesthesia will really heal.
Often you can not do without anesthesia in the treatment of caries complications: with pulpitis or periodontitis, this approach is unacceptable, since a pregnant woman may experience pain shock.
As a rule, treatment of secondary caries during pregnancy, especially if the pathology proceeds in a chronic form, dentists prefer not to conduct until the beginning of the second trimester. It is in the first 12-13 weeks that all the organ systems of the fetus are laid, and the risk of negative effects of drugs on it during this period is maximum, although it is still small. Starting from 14-15 weeks, the use of special anesthetics allows the rehabilitation to be carried out safely.
On a note
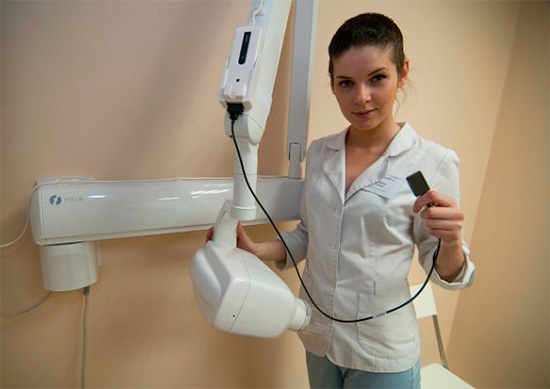
X-ray of teeth during pregnancy is categorically not applied. If the cavity is hidden from the eyes - try to resort to other methods. They even try not to study the quality of filling the channel with the help of X-rays.
Modern radiography on a visiograph has several times less radiation exposure. In case of urgent need it can be done only from the second trimester of pregnancy on this unit.
Using local anesthesia, regardless of the duration of pregnancy, acute pulpitis, purulent periodontitis and periostitis are treated.In the treatment of caries, even deep caries, the doctor begins treatment without the use of anesthesia and makes an injection only if the patient begins to feel pain when excising carious areas of dentin.
As anesthetics for treating pregnant women in dentistry, specially adapted drugs are used, for example, Septanest and Scandonest at a dilution of 1: 200 000. Pregnancy is not a contraindication for their use, and after 3 hours after the injection they are not detected in the blood.
Dentist's opinion:
Pregnancy is not a contraindication in other drugs, judging by the instructions. The fact is that a decrease in the concentration of adrenaline, and in Scandonest also preservatives, minimizes risks, but does not eliminate them. In any case, I observed on the popular portals that the articaine drugs are positioned as relatively safe for local anesthesia with relative risks, therefore they are done in case of emergency, one of which is pain!
Towards the end of pregnancy, therapy is further complicated by the fact that when sitting in the dental chair due to the specific position of the fetus, the load on the inferior vena cava and the aorta increases, which leads to a decrease in pressure and a possible loss of consciousness in the patient. To avoid this, the pregnant woman lays in a chair a little on her side, which allows to reduce the load on the part of the fetus. At the same time, the risk of teratogenic effects of anesthetics on the fetus by the end of pregnancy becomes minimal.
It is possible to take pain medications on your own at home only with completely unbearable pain and the inability to consult a doctor at the moment. If it comes to this - the doctor should see the tooth as early as possible. A good dentist will do everything possible to cure the mother’s tooth and not harm the unborn baby.
If you decide to take an anesthetic drug yourself, then keep in mind that taking almost any drug in some cases may well have negative consequences. It is possible to choose “self-medication” in the individual case so that even a single dose of a strong pain medication will affect the health of the mother and the fetus. Do not forget about individual intolerance and side effects of each drug, especially since painkillers have a whole range of them.
Feedback
“At one time I went to a clinic in which until 20 weeks pregnant women were not treated at all. Before pregnancy, I did not think about this, but when I came in the third month with initial caries, they turned me around. They said that you need to walk another two months, and then they will heal. This is disgrace! At the spot stage, caries is treated without anesthesia or without any medications; nothing affects the fetus there at all. And after two months they will open my tooth, put a seal, God forbid, my nerves will be removed. I had to change the clinic, the tooth was cured, without a filling and without anesthesia. Now, I’m already playing with a little one, but I have a healthy tooth. ”
Anna, St. Petersburg
Prevention of caries and proper preparation for pregnancy
Prevention of caries in pregnant women should begin before pregnancy begins. At the planning stage, the expectant mother should be checked by the dentist, heal all diseased teeth, remove plaque and tartar. The doctor at this time will draw up a schedule of preventive visits that will need to be observed (it is not known what cariogenic situation in the mouth will be with the onset of pregnancy and fetal development).
On a note
In the first trimester of pregnancy, it is not recommended to carry out any traumatic manipulations, in contrast to the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, where the leading role, in addition to dental health, is the hygienic condition of the oral cavity
Such a question is often asked: “Is it possible for pregnant women to conduct occupational hygiene?”.There is a list of diseases in which ultrasonic (US) brushing of teeth and the Air Flow apparatus cannot or do not recommend: epilepsy, the presence of a pacemaker, nasal breathing disorders, asthma, chronic pulmonary diseases in exacerbation, HIV and hepatitis, sexually transmitted diseases, high blood sugar or diabetes mellitus, SARS, herpes and airborne diseases, malignant neoplasms.
Most often this is due to aerosol, which rises during brushing from plaque and stone. A cloud of wet dust and infection can cause respiratory failure in a pregnant woman, and increased blood sugar - the risk of prolonged bleeding from the gums during a traumatic manipulation. In some cases, the possibility of carrying out manipulations in a pregnant woman can be determined with an adjacent specialist (gynecologist, endocrinologist, therapist, ENT doctor, oncologist).
Directly during pregnancy, the prevention of caries requires:
- Compliance with the rules of oral hygiene: teeth are brushed after each meal, preferably with pastes selected by the dentist; after random acts of vomiting with toxicosis, the mouth is rinsed with a solution of soda to neutralize acids from the vomit.
- Compliance with diet, restriction in the diet of sweet flour and chocolate products.
- Compliance with all the requirements of the dentist - the use of systemic prophylaxis, professional brushing, a visit to the dentist for routine examinations, etc.

Practice shows that the right caries prevention during pregnancy, although it should be systemic and regular, it usually does not present difficulties. Moreover, it is the main guarantee that during pregnancy and lactation a woman will keep all her teeth in good condition.
An interesting video: is it possible to treat teeth during pregnancy and what is important for every expectant mother to know
Some other important nuances of caries treatment during pregnancy