Teething in children usually begins from 4-7 months and lasts up to 2.5-3 years. This is a natural physiological process, and usually it does not worsen the baby’s health, however, in some cases, you may still feel worse, especially when the most painful of the teeth - the first incisors - climb. As a rule, they erupt most painfully, and their appearance in a child can often be accompanied by anxiety, increased salivation, swelling and soreness of the gums, impaired appetite, and sometimes a violation of stool and fever up to 37-38, and sometimes up to 39 ° С .
Next, we will consider the most effective means and methods with which you can to some extent anesthetize the gums when teething and at the same time not harm the baby. At the same time, we also note the most common mistakes of parents, which can only aggravate the situation.
Means and methods commonly used for painful teething in children
All the drugs that are used for painful teething in babies can be divided into medications and non-medications.
The medications with which anesthesia is performed include the following:
- Anesthetizing gels are often also called cooling because of the “freezing” effect characteristic of anesthetics (such gels provide almost complete relief of pain for some time);

- Anti-inflammatory drugs (sufficiently relieve pain and inflammation);
- Homeopathic gels, ointments, tablets, suppositories, drops and syrups (many do not know about this, but all such remedies are used for the placebo effect).
The use of medications alone to anesthetize gums in infants is not always sufficient, therefore, in addition to medications, non-medications and methods of pain management are also used. Here, first of all, it is worth noting the use of various teething teeth, as well as gum massage.
On a note
In addition, it so happened that many parents actively use various folk remedies, such as soothing warm tea, cool mashed vegetables and fruits, diluted clove oil, cold gauze lotions and even breast milk. With the right approach, such methods of gum anesthesia in babies also have a right to exist - it is only important to understand that in most cases they are relatively ineffective.
Analgesic ("cooling") gels
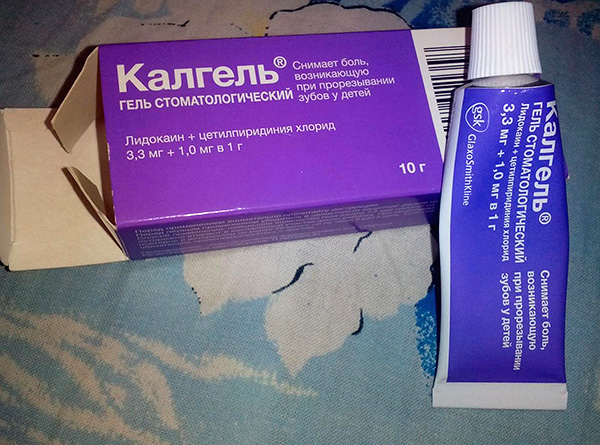
Among the “cooling” gels for gum anesthesia, one of the most popular today is Kalgel and Denthol Baby.
Calgel contains lidocaine hydrochloride (anesthetic) and cetidylpyridinium hydrochloride (antiseptic). Lidocaine quite effectively relieves pain in the gums when teething, and sometimes completely eliminates it for a while. Cetidylpyridinium hydrochloride protects the gums from bacterial damage.
On a note
Lidocaine injections were previously widely used in dentistry for pain relief during dental treatment (today, more effective drugs have replaced). It should be noted that this substance sometimes causes an allergic reaction, therefore for the first time it is better to use the gel with its content in the minimum amount - for testing.
Calgel's advantage is rapid analgesia, which occurs only a few minutes after its application, as well as the ability to use in infants from 3 months.
Like other painkillers, Kalgel is used topically: a small amount of it is applied to the inflamed area of the gums (no more than 6 times a day).Using this drug, it must be borne in mind that there is a small likelihood of a baby developing an allergic reaction to its components - therefore, after using the drug, the child should be carefully observed.
On a note
Kamistad analgesic gel is also popular on the basis of lidocaine, but it is important to consider that it is used only for children over 12 years old (for example, with stomatitis, gingivitis). The fact is that the concentration of anesthetic in it is increased, and in a baby it would cause too much numbness of the mouth and tongue, as well as increased salivation (there may be problems with swallowing this saliva).
As for the "cooling" gel Denthol Baby - its main active ingredient, which relieves pain, is benzocaine. It provides a quick analgesic effect, which manifests itself after a couple of minutes after rubbing into the gums and can last up to 20 minutes.
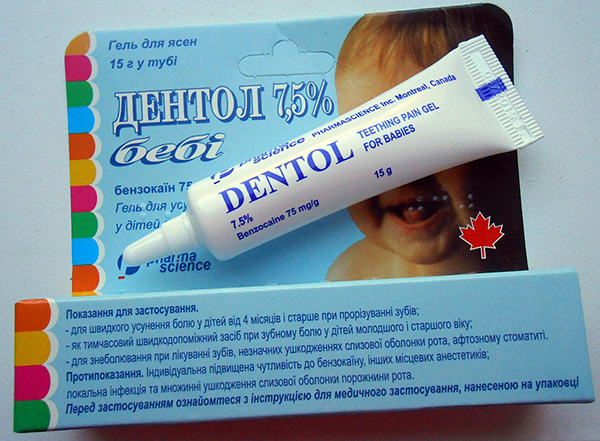
According to the instructions, Dentol Baby gel can be used in infants starting from 4 months of age (no more than 4 times a day and no longer than 7 days in a row). As in the case of Kalgel, it is worth remembering the possibility of developing an allergic reaction to the components of the drug.
In general, we can say that a significant advantage of “cooling” gels based on anesthetics is a well-defined and rapidly onset analgesic effect (in this regard, many anti-inflammatory and, especially, homeopathic remedies are much inferior). Meanwhile, many parents still avoid using gels with anesthetics, not wanting to “stuff the baby with chemistry.”
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Of the anti-inflammatory drugs used to relieve teething pain, the most commonly used in infants today is Holisal gel. Its main active substance, choline salicylate, has a combined effect: local analgesic (relieves pain), anti-inflammatory and antipyretic.
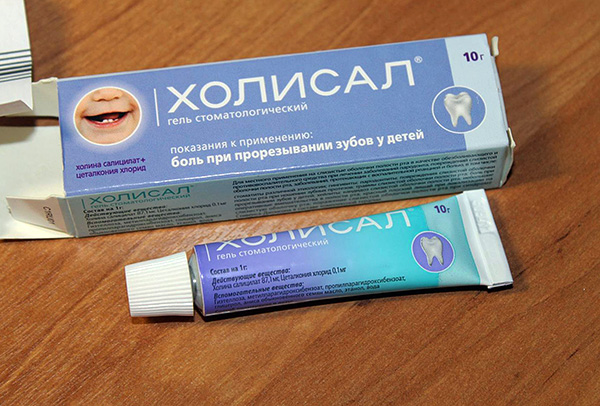
The composition of Holisal also includes:
- Cetalkonium chloride (provides bactericidal, antiviral and antimycotic effects);
- Gel ethanol-based, which helps for a long time to keep active active substances on the mucous membrane, prolonging the overall effect.
The analgesic effect can last from 2 to 8 hours. With regard to age restrictions - the instructions note only the need for careful use in children under 1 year old.
The drug is used no more than three times a day.
On a note
Although the instructions say that the pain can be relieved within two to three minutes after applying the gel, in reality, everything can be far from so rosy. The effect does not occur as quickly as when using gels based on lidocaine or benzocaine. In addition, the baby may not like the burning sensation that is felt for some time when Holisal gets on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity (imagine at the same time that the baby’s gums will already be painful and inflamed).
Homeopathic remedies - gels, suppositories, tablets, drops and syrups
Of the homeopathic remedies that make teething easier, Dantinorm Baby drops, Baby gel “First teeth” gel, Pansoral gel “First teeth”, and sometimes Viburkol candles are often used. The basis of these drugs are plant components (usually extracts of certain plants).
It should be understood that when evaluating the effectiveness of homeopathic remedies, the difference between placebo (dummy) and the “medicine” itself is often not revealed at all. This means that any positive effect of treatment is often caused by a natural recovery after an illness, and not by the influence of one or another remedy on the body.
Simply put, you can’t guarantee that homeopathic remedies will really ease the pain when the child’s teeth are cut. To some extent, the very fact of using any of these drugs can be considered as a distracting procedure (a child can calm down a little just from what he observes his feelings when using these funds). It is also a way for parents to convince themselves that they are not just sitting idly by and doing something useful - they give the child harmless "medicines" based on herbs.
How effective and safe are teethers?
Of the non-medications that facilitate teething in infants, so-called teethers are often used. In addition to performing its main function, biting them is a kind of preparation for the child to eat adult food and the chewing process, and also helps in the correct formation of the bite and the growth of the jaw.
Such procedures promote gum massage - the teether acts as a massager, thereby increasing blood flow to the gums and, as a result, teething is facilitated.

On a note
The principle of operation of these devices is that when a child’s teeth are cut, he constantly tries to bite something with his gums, and at this moment they give him a teether - the baby chews him gusto and thereby massages the gums. At the same time, due to the form and material, the teether is completely safe, pleasant for the child, stimulates the outflow of blood and lymph from inflamed gums, followed by the weakening of pain, and also accelerates the process of teething.
It is clear that the baby cannot quickly anesthetize the gums with the help of such means, however, in general, during the teething period they can significantly alleviate the condition of the child.
Teethers vary in shape, size and material used for manufacturing. They can have various modifications: in the form of toys, rattles, books or a special fingertip with a brush. You can also find cooling teethers filled with water (they are put in the refrigerator for a while and then given to the baby), and even vibrating ones. There are many varieties, and the best option in each case can be selected individually, depending on the age of the child, his level of development and preferences.
Like other means, teething has its own advantages and disadvantages.
The main advantage is that when they are used, gum massage is carried out and teething is really facilitated to a certain extent.
The disadvantage is the inability of teethers to quickly and pronouncedly remove painful sensations in the baby. It should also be borne in mind that cheap models may contain harmful substances that can cause allergic reactions and gum irritation.
Gum massage
Another way to reduce pain when teething is to some extent is to massage the gums. Its effectiveness is about the same as that of teething, but the plus is that, if carried out correctly, you can be sure that the force is applied to the zone that currently needs it most.
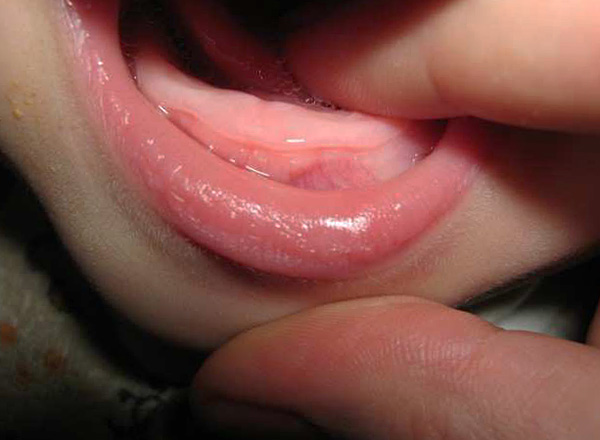
Usually, a massage is done for the first time before dinner in order to track the baby’s reaction to the new procedure. In this case, the child should feel good and be disposed to communication. If the baby feels unwell, has a fever or has problems with stools, it is better to postpone gum massage.
On a note
Another contraindication for massage is difficulty in teething, which is accompanied by bleeding. In this case, it is usually recommended to avoid any additional mechanical effect on the gum.
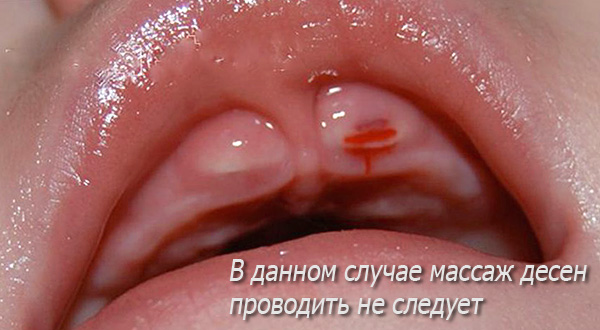
If the condition of the child is normal, then the massage will be pleasant and useful for him.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to prepare:
- Wash hands thoroughly (with a disinfectant);
- Cut nails;
- If the massage will be carried out using a special massager – fingertip, then it is pre-disinfected (you can also carry out the procedure using a special napkin-fingertip, which is specially designed for such cases).
Massage is carried out from the edges of the areas that concern the child to the teething area, but without affecting it. At the same time, such techniques are used: rubbing the gums, stroking, pressing and a combination of these actions.
At the end of the procedure, oral hygiene is performed (brushing and rinsing the mouth with water). It is recommended to teach a baby to hygiene from the period of his newborn, therefore, by the time active teething begins, the child is already getting used to it.
Folk remedies to facilitate teething
As noted above, often parents of babies resort to the use of various folk remedies, presumably to reduce pain in a child with difficult teething. Typically, these methods of pain relief are used due to their accessibility and popularity with older relatives (grandparents), who often act as reputable consultants.
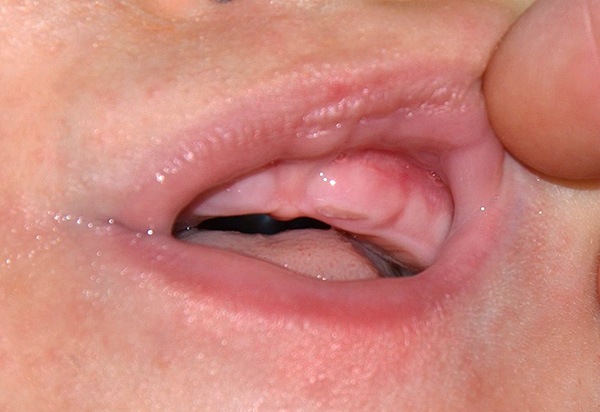
A classic example - often try to anesthetize the gums in a child with diluted clove oil. It is believed that it can relieve inflammation in the gums and has an analgesic effect. There is nothing terrible in this (as well as in the use of homeopathic preparations), but it is only important to consider that pure clove oil is never used, since it can lead to burns of the mucous membrane.
The analgesic effect attributed to breast milk is also widely known. So, it’s known that if a child’s teeth are cut, it’s enough to give him a breast so that he calms down. In fact, of course, the actual anesthesia does not occur here - the child, when in contact with the mother’s breast, calms reflexively, even if his gums continue to hurt. Nevertheless, the procedure is really effective, and makes it easier for the baby and his parents to survive a difficult period.
On a note
A popular method for relieving toothache by applying garlic to a diseased tooth is by no means applicable to a child. In the best case, this will lead to a chemical burn of the gums, and in the worst, to pulp necrosis in an still uncut milk tooth, followed by the development of pulpitis and (or) periodontitis.
Teething Features
With the appearance of milk teeth, the correct selection of complementary foods becomes very relevant, so that it not only does not increase pain in the gums of the baby, but also contributes to its calming.

It is useful during this period to give the child fibrous mashed potatoes made from fruits and vegetables - apples, pears, carrots - which, when the baby tries to chew, provide gum massage and pain relief. It is good if such mashed potatoes are not that cold, but at least slightly cool - this will not lead to a cold, but it helps to relieve pain.
It is advisable to give complementary foods to the baby before milk, and if the entire portion of the food consists only of complementary foods, then after it give the baby water to wash off the food residues from the gums - because of the large amount of carbohydrates, bacteria can develop in them that can increase inflammation when teething teeth.
Teething surgery
The process of teething (nature and timing) is one of the indicators of the normal development of the baby. However, serious erosion can sometimes occur in teething.
For example, retention - difficult teething, refers to pathologies of tooth development and may be associated with diseases and injuries of teeth and jaws. Depending on whether the child has complete retention, or is incomplete, different diagnoses are possible, sometimes associated with the overall work of the whole organism.
Another pathology is dystopia, in which a completely erupted tooth is not in the place where it should be (sometimes it even extends beyond the dentition).
Extra teeth can also be observed - an example is shown in the photo below:
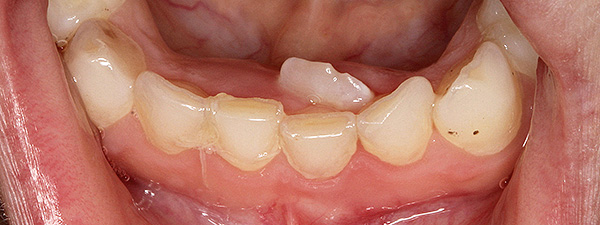
Serious violations of the timing of the appearance of deciduous teeth can also be attributed to pathologies. So, there are concepts of early, premature or belated teething. Of these, the earlier is quite rare, and belated - more often.
On a note
There are cases when a baby can be born with already erupted milk teeth. Most often these are central incisors.
Premature teething can be explained by the individual characteristics of the child, and such cases are less likely than others to be considered as pathologies.
Belated teething can be considered a disease if its time is very delayed. Various reasons can lead to this: disturbances in mineral metabolism, heredity, diseases of the bone-cartilaginous base, digestive disorders, decreased activity of the thyroid gland, etc.
The treatment of these diseases deals with pediatric and surgical dentistry. Depending on the cause of the teething disorder, treatment methods are individually selected, and this can be either means aimed at improving the general condition of the baby’s body, or surgical intervention.
Common Parent Mistakes
Among the most common mistakes made by parents during a period when a child's teeth are being cut, the following can be noted:
- The use of too large quantities of medications (for example, Nurofen, Panadol, as well as cooling gels, ointments), including the too frequent use of drugs. This can lead to various side effects, often more severe than teething. It should be understood that teething in a child is a normal physiological process, and it is important only to help the baby a little, and not with excessive zeal to treat him from a nonexistent disease;

- Inadequate care for the hygiene of the child’s oral cavity (residues of milk and complementary foods in the oral cavity are an excellent substrate for the development of microorganisms, which under favorable conditions can significantly aggravate the inflammatory process in the gums);
- The use of antipyretic drugs at a low temperature in the baby (up to 38 ° C).
When to see a doctor
In general, parents need to remember that the doctor will prescribe the most effective and safe means for their child, as a professional with extensive experience. Moreover, it is not necessary to consult a pediatric dentist in this case - the appointment of a pediatrician who has seen such situations many times before will be quite effective.

Consult a doctor in the following cases:
- If it is obvious that the methods used to relieve pain in the baby are not effective enough (it is possible that the problem may not be related to teething alone);
- If the baby has a high temperature for a long time against the background of painful teething;
- If a bluish swelling is observed in the area of teething on the gums (these may be teething cysts);
- With the development of severe side effects from taking medications - rash, itching, redness, swelling.
In all these cases, it is necessary for the doctor to examine the child and give further recommendations - attempts to independently cope with the problem will be associated with too high a risk of aggravation of the situation.
If you have personal experience with using various methods of pain relief for teething in your baby, be sure to share the information by leaving your review at the bottom of this page.
First aid for teething in the baby
What is important for parents to know about the appearance of the first teeth in a child



I liked the article, it is clearly written, and not in medical language. We anesthetize with dentinox gel. And anesthetizes, and cools, and tastes good. The daughter is never naughty when using, she even enjoys the sweet taste. Already 12 teeth have grown so))
And we only use Holis gel. Already the third child we have, all gums were smeared with this gel during teething. Children really like him; they open their mouth with pleasure and give their gums to be anointed. So it does not contain lidocaine, which is very good, but anesthetizes as it should, all children sleep normally after use.
I gave Dantinorm Baby a drop of water for my baby, they relieved pain very quickly, irritability and tearfulness disappeared, and the appetite was good and the gums did not hurt so much.
I have a granddaughter, 1.7 months. At once, all the teeth climbed, the gums of the tumor, can’t eat, we smear with calgel.
And we have been living in hell for two months now. We wake up every night at night, poorly eat and sleep during the day. We are 9 months old and already have 8 teeth, 9 and 10 are on the way, the lateral incisors come out. I tried both calgel and the baby leader with lidocaine, and drops of baby dantinorm, nothing helps. There is no temperature, but the gums are sore and even bleed a little. Bought holisal gel, let's see what will happen next. But this is torment, just awful! We don’t know what else to do. Can a pediatric dentist somehow help?
Hello, Elena. There is no need to go to the pediatric dentist now, as this specialist carries out dental treatment (and correction of the bite), which is irrelevant in your case. I would recommend contacting a pediatrician - he will examine the child and refer you to a specialist, or prescribe treatment on his own.