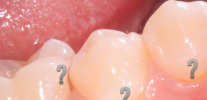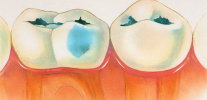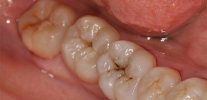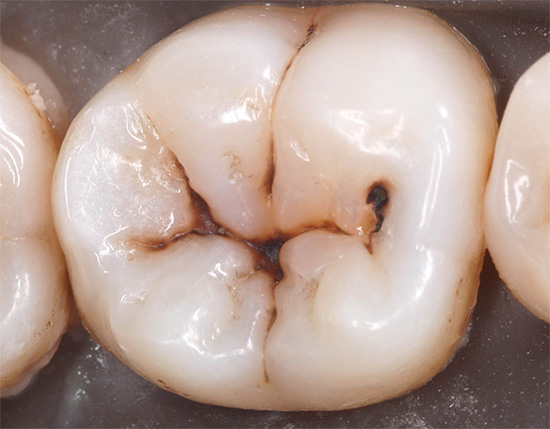
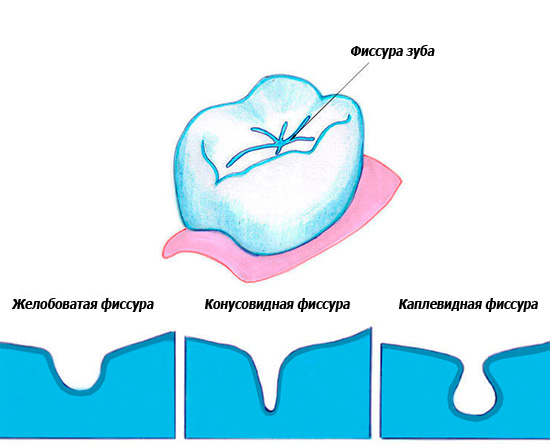
As the name implies, the feature of fissure caries is that it affects the so-called fissures - the natural anatomical structures of the tooth, which look like grooves and grooves on the chewing surface. According to statistics, this type of caries is the most common.
Most susceptible to fissure caries children with baby teethas well as adults with very deep or closed fissures. Such cavities, even with very thorough cleaning, cannot be completely eliminated from plaque and food debris.
It is not always possible to diagnose a pathology easily, therefore a special apparatus for the diagnosis of caries fissure. At home, the slight darkening of the grooves on the chewing surface is often left unattended. As a result, going to the dentist too late may result in the need for depulpation and even tooth loss. Therefore, all blackouts in the fissure area should be treated very carefully.
Symptoms and appearance of teeth affected by fissure caries
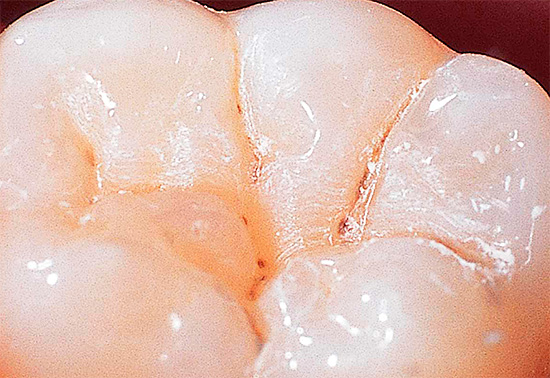
The photo below shows an example of fissure caries. In the deepest places of the fissures, dark areas of enamel are clearly visible, under which the main areas of tooth damage are located:
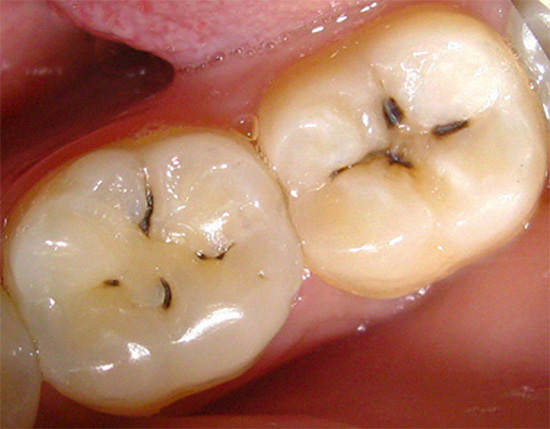
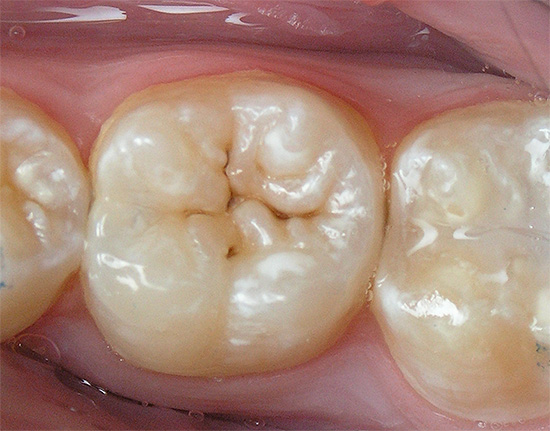
Fissure caries can develop within a short time after a teething, and the likelihood of pathology depends on several factors, which include:
- great depth and specific form of fissures;
- low resistance of tooth enamel;
- the constant presence in the oral cavity of easily digestible carbohydrates and cariogenic bacteria.
Fissure caries affects mainly the weakest areas on the chewing surface of the posterior teeth. Most often, pathology develops in children on the first permanent molars (on sixth teeth).
On a note
The development of fissure caries in the first permanent molars is due to the fact that these teeth erupt in a child as early as 6 years old. Their teething often remains unnoticed by parents and is sometimes mistakenly regarded as the appearance of milk (temporary teeth), which will still fall out.
Most often, the lower sixth teeth erupt at first, and the upper teeth only after a while, so self-cleaning does not occur when chewing, since there are no contacting areas. A child cannot ensure proper hygiene of such distant posterior sites himself, as a result, a kind of "biological garbage" arises. Fissures that are constantly contaminated with carbohydrate residues begin to darken, because under the action of organic acids, demineralization zones (a reduced content of minerals in the enamel crystal lattice) arise under the surface layers of enamel.
The following photo clearly shows that fissure caries is localized mainly in the central part of the chewing surface of the tooth. If the disease is not started, then the root and neck are not affected:
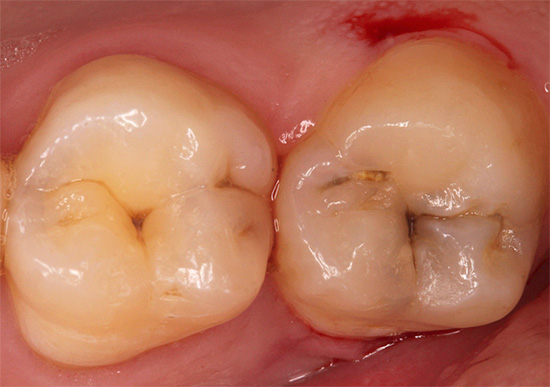
The clinical picture of nosology consists precisely in staining and further destruction of enamel in the fissure area.
Depending on the depth of the cavity, fissure caries may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Short-term pain from chemical irritants (sweet, salty, sour) and temperature (cold, hot) with superficial, medium and deep caries.
- Short-term pain from mechanical stimuli (when ingested in the cavity of the food) mainly with deep damage to the fissures.
- It is important that with caries the pains go away quickly, right after the elimination of the irritant.
In the early stages, fissure caries often develops asymptomatically (initial and superficial stages), which leads to late treatment of the patient: when the fissures are combined into a full carious cavity with softened infected tissues and vivid symptoms appear.
At the terminal stage, the lesion reaches the pulp. In this case, the pains acquire a completely different character: even after elimination of the irritant, they last for a long time, spontaneous pains appear (for no apparent reason), night, radiating or shooting (giving into any zone of the maxillofacial region), long aching, throbbing, tearing, intolerable etc.
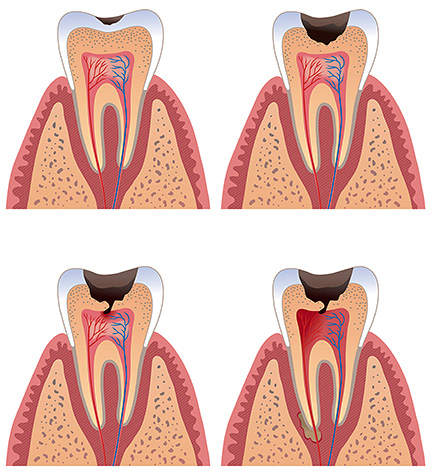
All these are complications of caries, called pulpitis or periodontitis, depending on the stage of damage to the "nerve" in the channels of the tooth. At this stage, the patient is forced to consult a doctor for emergency care, and treatment is carried out according to the diagnosis. It is characterized by technically more complex manipulations than in the treatment of caries and more often passes through several important stages before the filling itself. In terms of time and financial component - this is a costly undertaking.
The sooner fissure caries is diagnosed, the faster, cheaper and easier the treatment will be.
Diagnosis of the disease: means, devices and methods
Diagnosis of fissure caries in many cases is quite simple, since enamel lesions are clearly visible to the naked eye. But sometimes, especially in deep fissures, they turn out to be completely invisible, and the dental probe does not even stop in them with this instrumental diagnosis.

On a note
The fissures themselves have a darker shade than the rest of the tooth enamel surface. This is due to the fact that they are filled with plaque, dental plaques that cannot be completely removed with a toothbrush, and are simply located in recesses in the shadow of the tubercles of the tooth. All this often disguises fissure caries and makes it difficult to detect.
In general, the diagnosis of the disease is carried out in the following ways:
- visual inspection;
- radiography;
- use of caries markers;
- laser diagnostics;
- fissurotomy.
Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, which are manifested in the diagnosis of caries of different stages.
Visual inspection
The simplest technique for detecting fissure caries is a visual inspection.
A dental probe and a mirror are used to examine the oral cavity. But if the fissures are closed or the diameter of the lesion is less than the diameter of the tip of the probe, it is impossible to establish the presence of the disease in this way.
Roentgenography
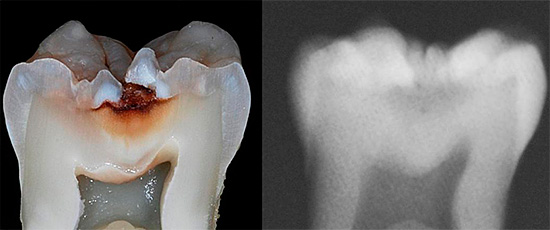
X-ray allows you to detect hidden caries fissure, even if there are no symptoms. The picture well reveals the lesion sites and their sizes, however, the doctor will not prescribe it without suspicion, and often before the appearance of pain in the tooth, radiography is not prescribed.
In addition, using X-rays, caries fissures cannot be detected in the early stages, before tissue damage under the enamel surface.
Laser diagnostics
Diagnosis, in which caries is "highlighted" by a laser beam, is an almost 100% method for detecting fissure caries (laser fluorescence method). Using this method, caries can be diagnosed at almost any stage of its development.
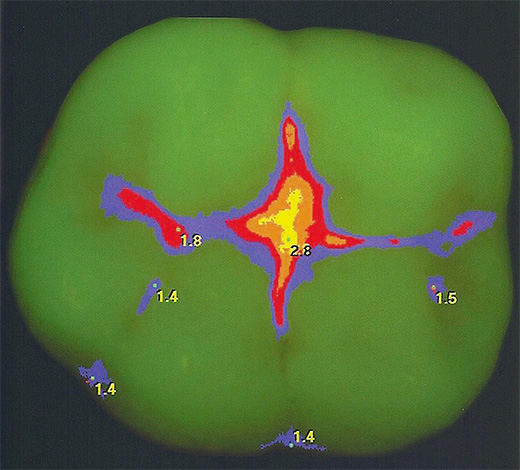
Although the price of the apparatus for diagnosing fissure caries is quite high, it is in all good dental offices. This is due to the fact that laser diagnostics reveals caries even in the initial stages. And with fissures of the "capsule" type, this option is optimal.
Fissurotomy
When lesions of the fissures are detected, but their size is not known, an additional method is used to determine the degree and depth of the carious zones - fissurotomy.A set of burs has been developed for this procedure, with the help of which a minimally invasive intervention is carried out in the tooth structure.
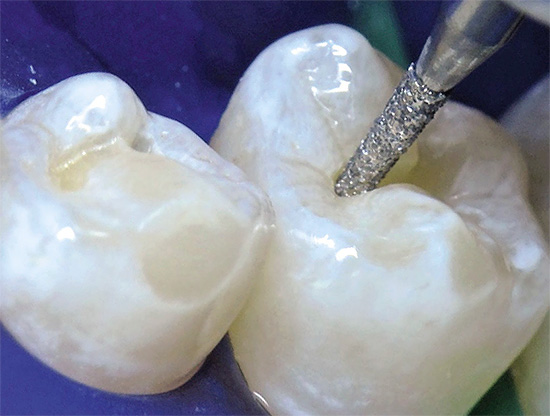
With the help of carbide boron, the darkened fissure opens approximately 0.6-1.1 mm. According to the opened picture, the dentist decides which treatment of fissure caries will be most effective.
Features of the treatment of fissure caries
Treatment of fissure caries is carried out in several stages:
- removal of affected areas;
- installation of a seal or restoration tab.
Removal of affected areas is carried out using a drill. Using modern filling materials, the treated cavities are filled.
If there is a complication of caries (pulpitis), then the "nerve" is removed. Then the channels are sealed, and depending on the clinical situation (the size of the cavity, area, position of the tooth, the load on it, interactions in the bite, etc.), either a seal is placed, or a set of measures is carried out, which may include options such as:
- seal + crown;
- installation by a dentist-therapist of a pin (anchor, fiberglass, titanium, etc.) + seal (or else setting the crown on top);
- recovery tab;
- Stump tab + crown.
The choice depends on the professionalism of the doctor, his tactics regarding the clinical situation in the oral cavity, since the tooth is considered not as a single organ with its inherent functions, but in the system of its interaction with other teeth and surrounding tissues.
An alternative to the well-known filling is the restoration tab - a micro prosthesis made according to the shape of the patient’s tooth. It is created in a dental laboratory from polymer materials, medical alloys, sometimes from silver, gold or platinum. To make a tab, a preliminary impression of the tooth is made. Its fixation is carried out using medical cement.
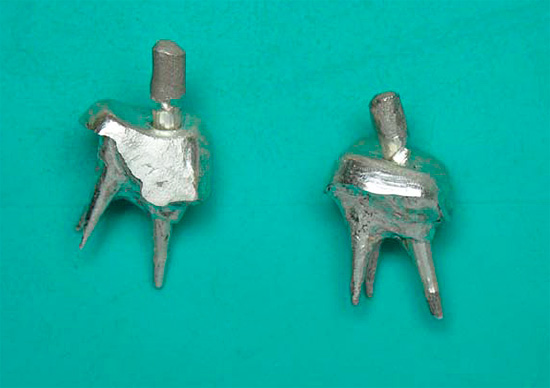
When fissure caries is diagnosed, treatment with a restorative insert is more promising than a filling, since its service life is longer. If it is made of polymers, it looks more aesthetically and outwardly similar to a healthy tooth.
How to prevent the development of caries on fissures?
Caries prevention, including fissure, is the best way to maintain healthy teeth.
The following areas of prevention are distinguished:
- adherence to oral hygiene;
- tooth fluoridation;
- timely sealing of fissures;
- regular dental checkups.
Thorough toothbrushing allows you to maintain a normal pH level in the oral cavity, removes plaque and bacteria, whose vital products destroy enamel.
But even with regular brushing, if the mineralization of tooth tissues is reduced, the risk of fissure caries increases. To strengthen the enamel, it is recommended to use fluoride toothpastes or undergo a remineralization procedure in the dental office.
A good method of prevention is sealing the fissures - they are filled with a liquid composite, which then hardens and prevents bacteria from accessing the tooth enamel. Active substances are added to the material, which additionally remineralize and strengthen the enamel.
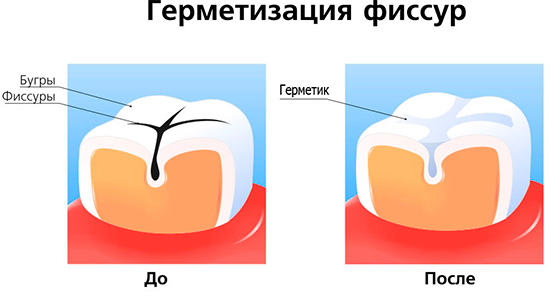
And, of course, it’s important to regularly visit the dentist’s office. A planned trip to the doctor and timely rehabilitation will allow us to detect caries at the very early stages of development and take effective measures to eliminate it.
From the practice of the dentist
As mentioned above, at the age of six, the first molars erupt - the teeth that are most prone to fissure caries, rapid decay, up to serious complications, and removal. This cannot be allowed in any way, as orthodontists (doctors correcting malocclusion) rely on sixth teeth, calling them the “occlusion key”.It is the ratio of these teeth that directly affects the formation of the correct bite. Removal of the sixth tooth entails serious consequences for the development of the jaw and bite. Therefore, early detection of fissure caries by pediatric dentists and hygienists is important to prevent future complications.
Useful video: what is important to know about fissure caries - expert comments
An example of the preparation of fissure caries