The simplicity or, conversely, the complexity of the diagnosis of caries directly depends on its location on the teeth and stage of development. Therefore, the methods for diagnosing caries also depend on the stage at which the disease is located.
So, at the spot stage, the carious process is sometimes barely noticeable and can only be recognized by special means.
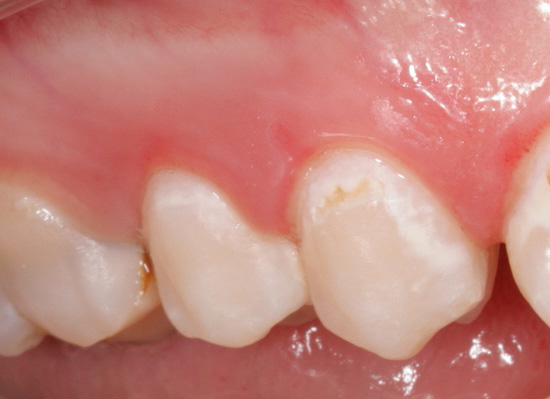
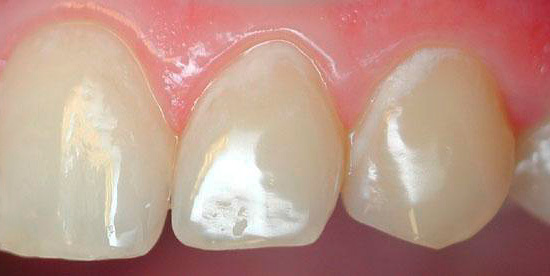
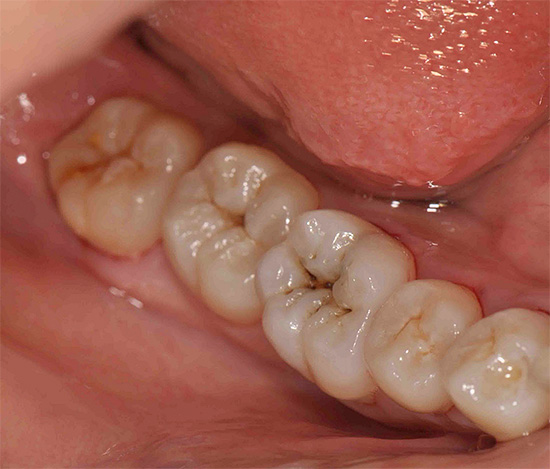
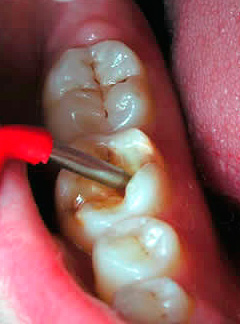
And already medium and deep caries can be recognized using a standard dental mirror and probe. Moreover, diagnosis is quite possible at home: multiple caries itself striking when examining the oral cavity in the mirror, and even at the stage of the spot (initial caries) causes discomfort when hot or cold products get on the tooth, and sometimes even when inhaling cold air.
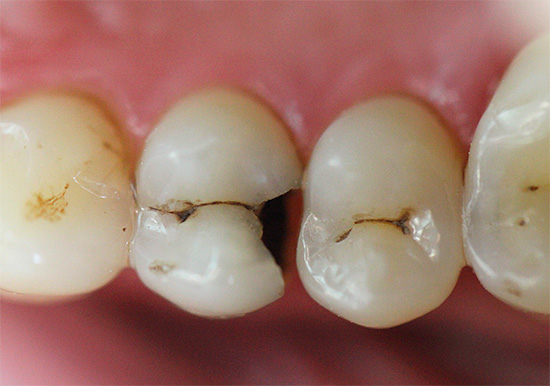
Nevertheless, caries is quite insidious, and in some cases can develop asymptomatically to stages where removal of a significant part of the dentin, and sometimes depulpation (removal of the nerve), will be required. That is why the definition of pathology in dental clinics is often carried out using modern equipment, and deep hidden injuries in the teeth are detected using high-tech methods.
Visual diagnosis of caries and cariogenic situation
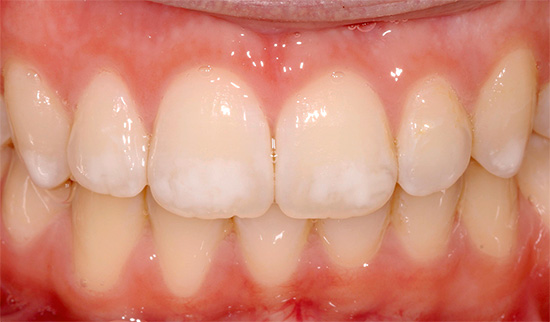
Visual inspection of teeth is the main way to identify a cariogenic situation in the oral cavity. Caries is characterized by the fact that at almost all stages of its course, it changes the color of tooth enamel. Even at the stain stage, when dentin is still not affected, the enamel ceases to be smooth and shiny, and the attentive dentist can easily notice such a change.
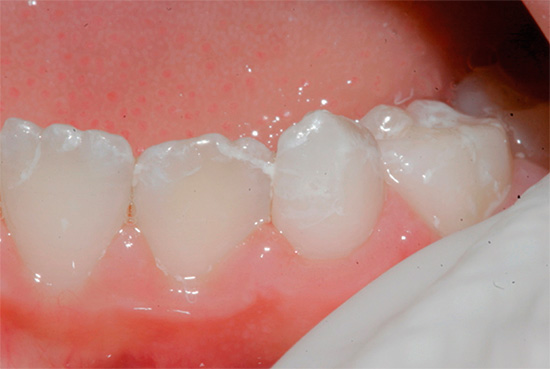
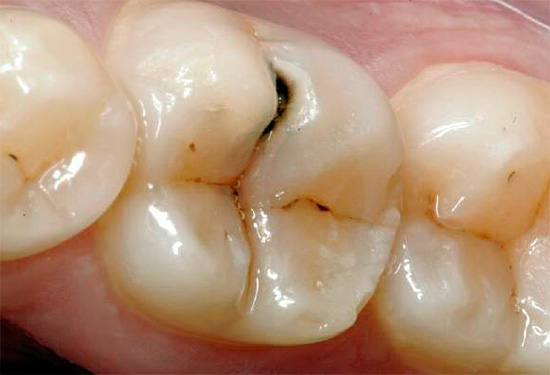
At later stages, determining caries with a simple examination is even easier: it either leads to the appearance of black and dark brown dots on the teeth, or when dentin is damaged, dark cavities are visible under the enamel.
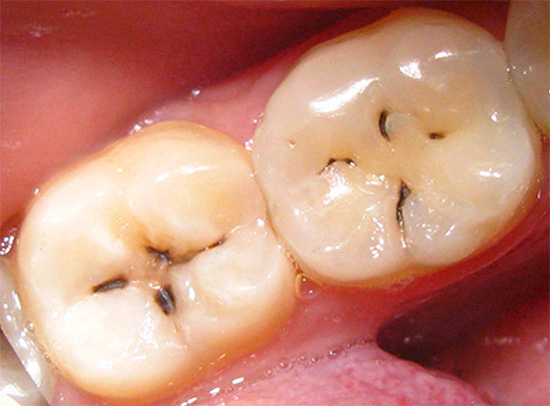
Not surprisingly, in most cases, visual diagnosis of dental caries can reveal most of the affected areas. With her, the dentist carefully examines the teeth from different sides with a mirror. In addition, the doctor can carry out a probe probe - in places of the early development of the carious process, the roughness of the enamel surface is clearly felt.
On a note
It is the visual diagnosis that is most available at home and allows you to recognize the pathology on the teeth yourself. It is enough just to carefully examine your teeth in the mirror. It is worthwhile not only to look for frankly black areas, but also to pay attention to all the places that stand out against the background of pure white teeth. Remember: black and brown areas indicate a sufficiently deep damage to the tooth (in the best case, only enamel will be pigmented). Such a tooth will probably have to be drilled, perhaps even a nerve will be removed from it. Therefore, the dentist should be consulted even before the appearance of significant visible damage.
There are times when visual diagnosis is not enough. For example, the affected areas located on the wall of the teeth in the places of their contact are not always visible. Sometimes the carious process develops under old fillings and crowns, under the gum (root caries), and you cannot see it with the naked eye. Here, more accurate diagnostic methods come to the aid of the dentist.
Tooth staining, or use of caries markers
The principle of using caries markers is that some substances are delayed precisely in the areas affected by caries. The most common such marker is methylene blue.When it enters the tooth from a healthy surface of the enamel, it simply drains off, and on the carious, in simple terms, remains (diffuses into the pores of the demineralized enamel). As a result, the doctor can not only determine the caries on the teeth, but also reliably identify the shape and boundary of the damage.
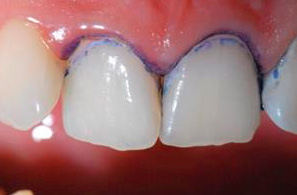
Most modern caries markers (sometimes also called caries detectors or indicators) use fuchsin to stain the affected areas pink. Markers are applied to the teeth with special swabs, and then washed off. The clinics use both imported products (VOCO, Pulpdent), as well as domestic preparations of the Color-test type.
X-ray of teeth
This method of diagnosing tooth decay is especially good in situations where it is necessary to identify deep caries that does not have noticeable external manifestations. For example, if the place of enamel integrity violation is hidden by the wall of another tooth or gum. On the radiograph, all internal damaged cavities are well recognized, but in most cases it does not allow to recognize caries in the early stages of development.
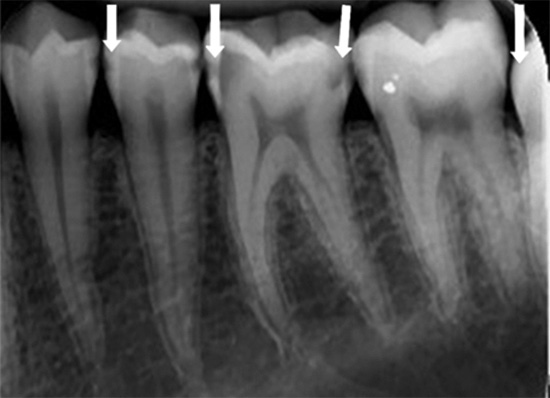
The decision to prescribe an X-ray is always made only by a doctor, and not all clinics have the appropriate devices. Usually they are quite large and expensive, and small cabinets do not have the opportunity to purchase even the simplest device. Patients of such rooms undergo diagnostics in third-party clinics. It is clear that only for the diagnosis of caries such devices are not purchased - their functional purpose is much wider.
Thermal diagnosis of caries
Diagnosis of dental caries using low and high temperatures is usually done to detect damaged areas on proximal surfaces. In this case, the tooth is simply treated with cold or hot (up to 60 ° C) water, and according to the patient's pain or lack thereof, they conclude that there is carious damage.
Typically, thermal diagnostics are used as an auxiliary method to confirm a previously established diagnosis. Using this method, caries are also diagnosed differently: if the pain passes quickly after contact with water, this indicates only caries. If the pain persists for a long time and is more acute, then we can talk about pulpitis.
Electrodontometry
Doctors also do not often resort to electroodontometry (EOM) to diagnose caries. Basically, this method is used to detect pulp lesion, and therefore it is used to differential diagnosis of caries in case of suspected pulpitis.
The principle of EOM is to expose the pulp to an electric current of different strengths. Depending on the strength of the current, pain appears, the doctor makes a conclusion about the degree of pulp involvement in the pathological process.
On a note
You should not be afraid of electroodontometry. Exposure to electric current does not mean that the tooth will be “hit” by electric discharges. Usually, the effect is stopped when the first tingling occurs. This is already enough for the doctor to determine the pathology. If there is only caries on the tooth, then EOM does not cause pain.
Fibrooptical transillumination (transluminescence)
Close to each other, transluminescence and luminescent diagnostics are quite rarely used in medical practice methods for diagnosing caries. Usually they are used for other purposes.
- Fibrooptical transillumination is based on illuminating the tooth with bright light. At the same time, the areas affected by caries turn out to be darker and create a clearly visible hemisphere against a background of healthy enamel. Such an examination is carried out in a dark room and cold light is used.
- Luminescent diagnosis consists in illuminating the tooth with ultraviolet light. Usually a ray of light is passed through a special filter (Wood filter).In this light, the tongue appears orange, healthy teeth have a snowy white hue, and carious teeth are darker. The borders of the affected areas are very clearly visible and therefore easily recognized.
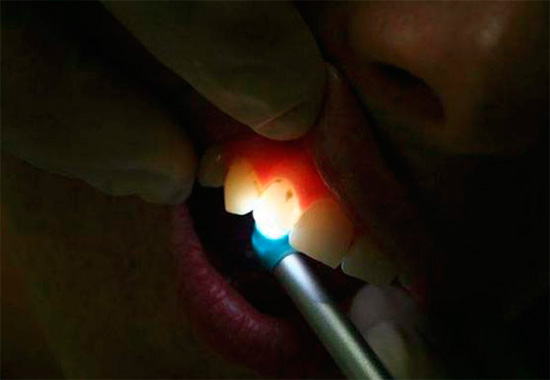
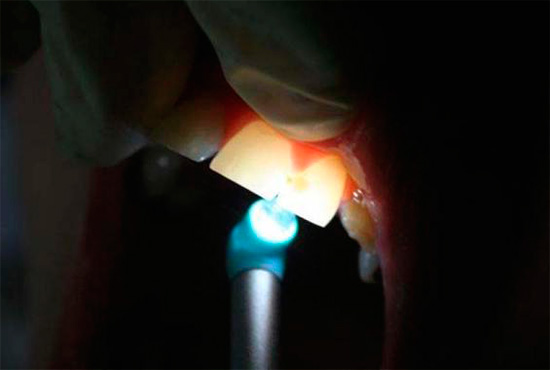
Both of these procedures are completely painless. Devices for caries diagnosis using this method are produced by the domestic industry (OLD-41) and many foreign manufacturers.
There is also a method of laser-induced fluorescence. In it, the tooth is illuminated by a laser beam, and the integrity of the tooth enamel is inferred from the spectrum of its own radiation. Devices for such diagnostics are small and are a good help in studying the cariogenic situation in the oral cavity.
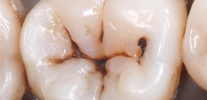
Fissurotomy caries diagnosis
Fissurotomy consists in opening the enamel in the area of the tooth fissures to determine the areas damaged by caries under it. Of course, in standard situations, such a procedure for diagnosis is not performed: it is simply impossible to drill a tooth to make sure that it is healthy. As a rule, this method is used to confirm a doctor’s suspicion of tooth decay, as well as to assess the extent of damage to a carious tooth.
In general, this method is mainly an assessment of the lesion, but not the detection of caries itself.
From dental practice
Often, a contact wall with gray enamel is found in patients on a particular tooth. Although caries is not clearly visible, an unknown formation is visible under the most intact enamel. In all cases, after processing with a fissure or a simple spherical bur, the enamel falls through and a hidden vast cavity in the tooth opens. Very often, under such a seemingly intact wall, chronic pulpitis develops.
Differential diagnosis: what dental diseases can be mixed up with caries?
Differential diagnosis of dental caries is carried out by almost all the methods described above. Wherein:
- Staining with caries markers allows you to distinguish caries from hypoplasia and fluorosis. Only caries will remain marked after applying the detector and flushing it with water.

- EOM and thermodiagnostics make it possible to distinguish caries from pulpitis and periodontitis.
- Based on an X-ray, deep caries can be distinguished from non-carious lesions of enamel and complications of caries (pulpitis and periodontitis).
It is almost impossible to carry out differential diagnostics by visual methods. Therefore, for example, to distinguish at home deep caries from pulpitis is possible only according to the sensations and nature of the pain.
In general, you can independently diagnose caries in yourself by noticing any abnormalities in the natural pure white color of the tooth enamel. Especially carefully should be inspected areas near fillings, chips, above the gums. It is also necessary to pay attention to the sensitivity of the teeth. Sometimes enamel is chipped on the front teeth, which leads to pain in breathing. Places of such chips are the “gateway” for the defeat of the exposed areas by cariogenic bacteria.
An additional, although not very unambiguous method of self-diagnosis of caries can be the use of dental floss. With their help, you can find damage to the enamel even on those sides of the teeth where caries is not noticeable. You just need to rub this side of the tooth with a thread, evaluate your feelings and check the thread itself. If pain is felt during the procedure, or the thread is severely scratched, then the enamel is damaged. It’s clear that caries or not, only a doctor can, but such a violation is already a reason to go to the clinic.
In any case, with any suspicion of caries, you should go to the dentist. If there are still no obvious signs of enamel destruction, but the teeth do not look completely healthy, then, perhaps, the treatment will not even require opening the enamel. And most importantly - do not be afraid to visit the dentist again.The sooner caries is determined, the easier, cheaper and more effective the treatment will be.
Interesting video: early diagnosis of caries
Caries in the most vulnerable areas of the teeth - in the fissure area