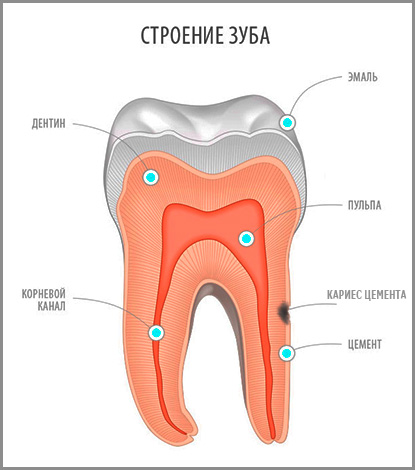
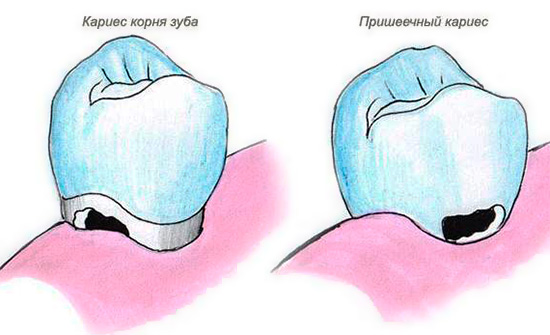
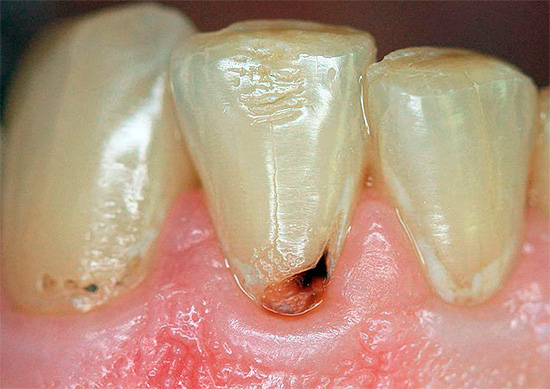
Compared to carious lesions of enamel and dentin, caries of cement or, alternatively, “subgingival caries” (root caries) is much less common, but in contrast to them it is more aggressive and dangerous for a tooth. Since the root of the tooth has a small wall thickness, its destruction by caries often takes place in a fairly short time, until the development of pulpitis or periodontitis, leading, in turn, sometimes even to the extraction of the tooth.
Since caries of cement is often combined with cervical caries, for the front teeth, in addition to the risks mentioned, this is also fraught with aesthetics. Dark spots or carious cavities on the front teeth, especially if they are not eliminated for several years, they often provoke psychological complexes, problems at work and in communication with the opposite sex.
To avoid all this, it is necessary, as they say, to know the “enemy” in person: that is why it is already possible and necessary to obtain understandable and accessible information on how to recognize cement caries in your home, what symptoms it may accompany and how to treat with maximum result for tooth preservation. This and much more will be discussed later.
Risk Factors for Caries Cement
Most often (in about 60-90% of cases) tooth cement decay develops in elderly people due to gum disease of various origins. Moreover, in most cases, a pathological pocket forms between the gum and the tooth - a place of accumulation of various microorganisms that not only provoke the destruction of the gingival attachment, which leads to loosening of the tooth, but also cause the dissolution of the root cement with a deepening in the root dentin (streptococcus).
On a note
According to the international classification of diseases, caries of cement occurs after carious lesions of enamel and dentin, and is not so common at a dentist's appointment. The classification of carious cavities according to Black (Black) makes it possible to conditionally attribute cement caries to class V - to cervical defects of all groups of teeth. Conventionality is determined by the fact that a cervical defect is not always combined with development caries under the gum; just like subgingival caries does not always extend beyond the gingival margin to the visible surface of the tooth.
The result of the destruction of cement and dentin by caries is the first formation of a small carious cavity, which sooner or later leads to the penetration of infection into the tooth with the involvement of pulp tissue (“nerve”) in the inflammation.
Additional risk factors for caries in cement:
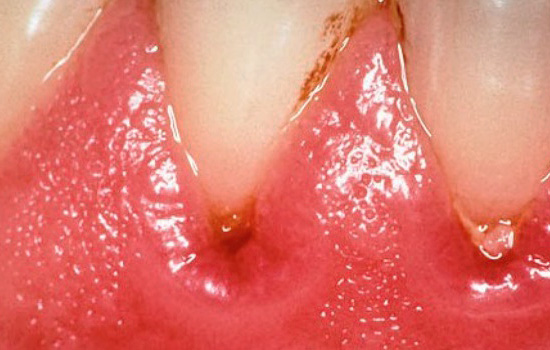
- Cervical or circular caries. If the carious process in the gingival region gains access to the cement of the tooth root, then a kind of “double” caries with two types of localization is formed: above the gum and under the gum. Here, either a violation of the fit of the gum, covering the neck of the tooth, or exposure of the root for any reason plays a role.

- Incorrectly installed crown or violation of the limitation period of its fixation. In case of errors in prosthetics with crowns, excessive introduction of its edges under the gum is possible, or shortening to the gingival margins established by the norms. The result of this is either a gum injury with the formation of local gum disease, or a constant delay in food in the place where the crown does not reach the gingival margin, which also leads to inflammation. As a result of this, cariogenic microorganisms can easily penetrate under the gum with the involvement of root cement.


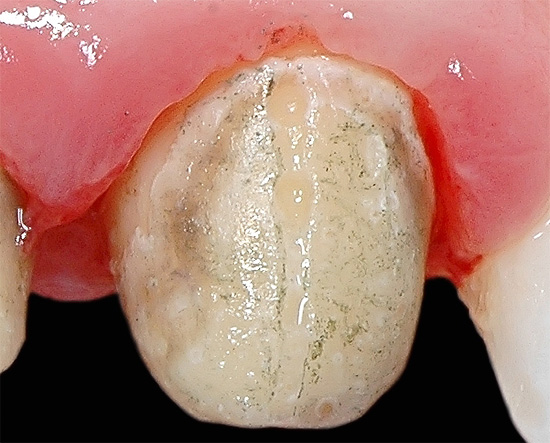
- Violation of oral hygiene.The constant accumulation of plaque in the cervical region of the tooth or crown of poor quality without proper and regular hygiene often leads to subgingival and subgingival caries due to cariogenic factors in the dissolution of tooth enamel and root cement.
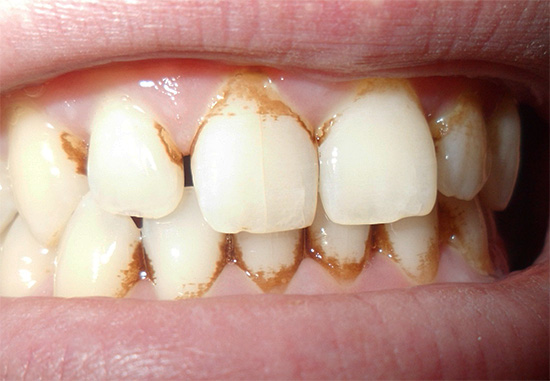
Clinical signs
Depending on the location of the carious lesion under the gum, a clinic characteristic of dental caries is also determined. So, with the localization of caries in the gingival pocket, when the inflamed gum closes the root from external stimuli, we are talking about a closed location. In such cases, the caries clinic of root cement is not bright. As a rule, a person does not have any pain or they are slightly expressed.
With the open location of cement caries, in addition to the root, the cervical region is also involved in the destruction process. Depending on the depth of the carious lesion, there may be complaints about:
- violation of aesthetics (especially on the front teeth)
- discomfort when eating
- the onset of pain from chemical (sweet, sour), thermal (cold and hot) and mechanical (with the penetration of food under the gums) irritants.
Feedback
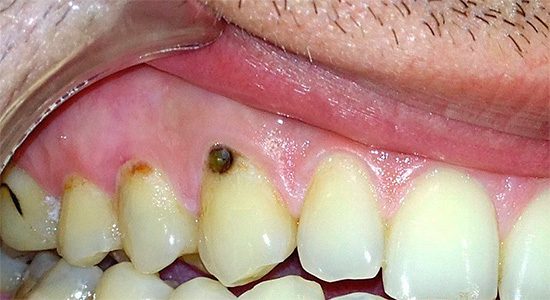
Not so long ago, I had a blackness near the gums of the upper tooth and he began to hurt. At first it was not even blackness, but some kind of brown stain, which I could not brush off with toothpaste, but then the gums began to bleed, and the stain began to increase every month. As a result, it hurt me to drink cold water and brush my teeth because of a sore gum. Since I work as a sales consultant, I have to communicate with people, and the front tooth with blackness catches my eye, all the more - it also hurts. The dentist said that this is already beginning caries of the root, which must be urgently treated before it injures the nerve. First, the plaque and stone were removed from all my teeth, and after 3 days a beautiful seal was placed. Now nothing hurts.
Yaroslav, city of Reutov
Diagnosis of caries cement without leaving home
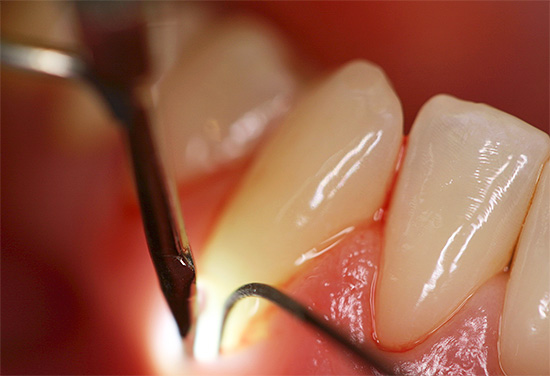
With a closed location of cement caries, it can be very difficult to independently detect a defect. In such cases, it is usually detected only during the procedure of curettage (curettage) of pathological gingival pockets, or during gum repair at the dentist-surgeon or dentist-periodontist. Since the boundaries of the defect do not go beyond the gingival margin, it is only with the occurrence of pulpitis and pulpitic pain that you can independently understand that this tooth has a hidden problem.
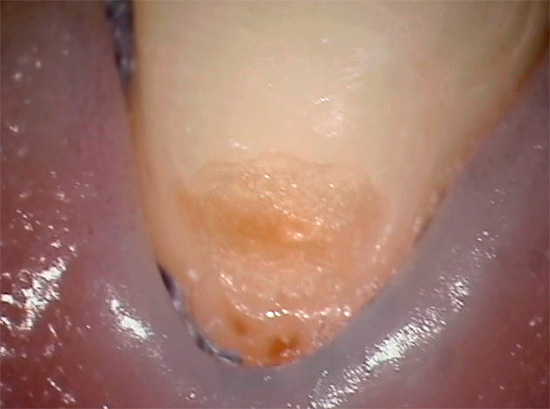
It's important to know
The acute form of pulpitis is characterized by severe spontaneous pain that occurs even without external stimuli. Depending on the stage of inflammation of the "nerve" and the protective mechanisms of the body, the duration of pain is determined: from several minutes to 1-2 hours. Most often, the pain intensifies in the evening and at night.
Chronic forms of pulpitis can develop, bypassing the acute stage, and manifest themselves as prolonged aching pains, which can be aggravated by food irritants (more often from hot). The chronic course of pulpitis can last up to 2-3 months or more, until the transition either to an exacerbation of pulpitis with a clinic of acute spontaneous pain, or periodontitis - inflammation of the tissues surrounding the root of the tooth, which often leads to its removal.
With the open location of cement caries on the front teeth in combination with cervical caries, as a rule, already at the stage of a carious spot without a carious cavity and any symptoms, serious problems can be suspected and a doctor should be consulted. Moreover, in this case we are talking about the comfort of communicating with loved ones, friends, colleagues and other people. The appearance of dark dots, a chalky shade of enamel, its cracks and spalls at the border with the gum allows you to determine the caries of cement at the initial stage of development, when it may still just “break through” into the subgingival area.
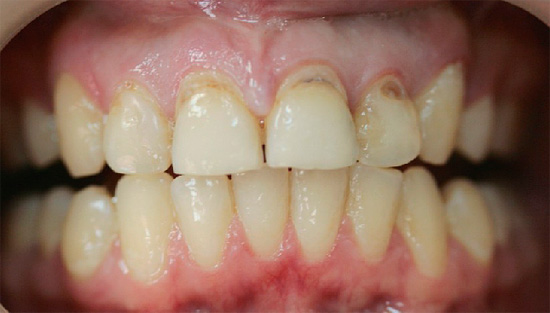
With extensive carious cavities extending from the outer surface of the tooth deeper into the gums, reactions to cold, hot, sweet, sour, as well as a feeling of soreness, pain during eating usually occur. Often the gum moves away from the tooth so much that under it is visible the affected area of the root cement and the root itself. In such cases, you must immediately consult a specialist for additional studies and confirmation of the diagnosis.
Professional diagnostic methods
When the root cement caries is closed, additional manipulations are required to make a diagnosis using instrumental and hardware methods. In the framework of differential diagnosis, the following approaches can be applied:
- Removal of supra- and subgingival dental deposits: cleaning plaque and stone from all surfaces of the teeth. Since gum disease is most often triggered by tartar and plaque, in order to make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the inspection area from deposits. For this, manual methods are used (scalers, chisels, curettes, etc.), ultrasonic tips and devices for ultrasonic cleaning of teeth (tip for the dental unit Scaler, Piezon-master, etc.), as well as dental treatment with Air Flow.

- Careful isolation of the examined root from saliva. Cofferdam is used for this - as the best option for protection against saliva and the convenience of root research, but you can do with ordinary cotton rolls.

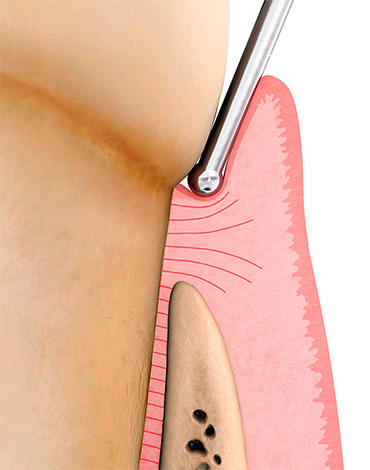
- Sounding of the root surface. In this case, only a sharp probe is used, which makes it possible to distinguish healthy tissue from caries affected by the characteristic surface roughness.

- X-ray examination. It allows not only to detect subgingival cavities in a suspicious tooth or under a crown, but also to reveal the slightest gingival defects in the area of contact walls that are tightly adjacent to each other. At the same time, even a slight “darkening” can be seen in the X-ray of the tooth, which indicates that the X-rays easily pass through the caries-affected tissue, which means that the carious process has already affected at least the cement, and at most the dentin of the root. To detect the caries hidden under the gum, a visiograph is widely used - an apparatus that transfers data to a computer and allows you to identify a defect and view it in an enlarged image or at different angles.
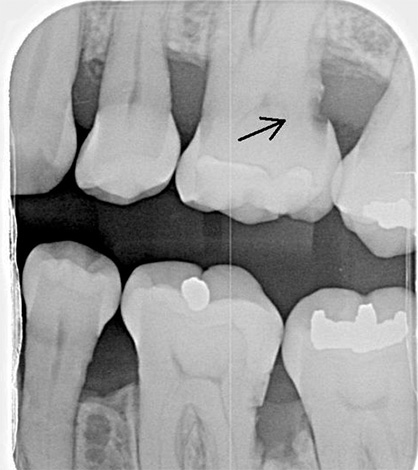
The ideal option is a set of diagnostic measures that combine the data obtained by the patient during self-diagnosis with a description of characteristic complaints, as well as the consistent use of professional diagnostic methods - from removing tartar and plaque from all surfaces of the teeth to X-ray diagnostics. This approach in the future allows us to conduct a number of additional studies for differential diagnosis of caries cement from pulpitis or periodontitis in case of difficulty. Namely: thermometry (the reaction of a tooth to cold water or a heated instrument), EDI (the reaction of a “nerve” of a tooth to a specific current strength, characteristic of a particular diagnosis, using electroodontometry devices), etc.
Modern approaches to treatment and the specifics of the choice of filling material
Modern approaches to the treatment of root caries allow the procedure to be performed in one or several visits - this largely depends on the clinical situation. If the gum closes the carious cavity, bleeds or is a serious obstacle to a successful filling, then on the first visit, gum correction (excision) is often performed.
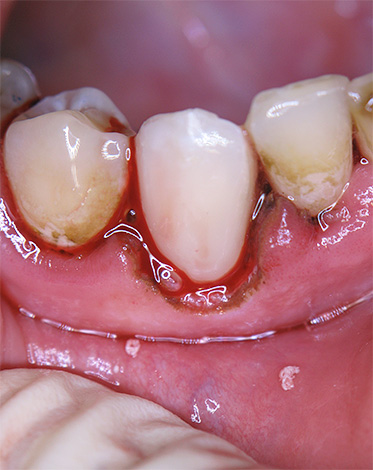
After removing the interfering area of the soft tissue, the carious cavity after treatment (or without it) is closed with a temporary filling made of glass ionomer cement or ordinary oil dentin. After healing of the gums, the patient is invited to a second appointment and fillings are performed.
The basic principles of carious cavity treatment:
- Mandatory anesthesia, as root tissues are the most sensitive area for machining.
- Maximum excision of discolored and softened tissues on the root surface using modern techniques.
- Preservation of intact root surface areas.
- The formation of a rounded cavity.
To treat cement decay, materials resistant to the effects of gingival fluid, saliva and blood during tooth filling are used. Such materials are glass ionomer cements and compomers.
From the observations of the dentist
For patients who neglect oral hygiene, it is recommended to use glass-ionomer cements, which provide long-term fluorination of tooth tissues after filling. Most modern glass ionomer materials have acceptable aesthetic characteristics that, in certain clinical cases, allow them to be installed even on the front teeth.
Light curing composites can be used in combination with combined techniques, for example, with the open sandwich technique, when glass ionomer cement or compomer is first introduced and distributed in the subgingival cavity, and a filling from a composite with improved aesthetic qualities is modeled in the subgingival region (in the smile zone). Thus, the positive properties of each of the materials used are maximally used to achieve long-term fixation of the future seal, its strength and external perfection.
To control the quality of treatment, it is necessary to come for a second appointment after filling after 2-3 days (with artistic restoration) and be sure to - after six months for a routine examination to exclude fillings defects and relapse of caries.
How much can the treatment cost?
As a rule, private clinics set prices for services based on the complexity of treatment and the cost of the materials used. In addition to the status of the clinic, its level of equipment, training, etc. cement caries treatment is included in the price list as the most difficult in technical implementation. At the same time, the price for the use of certain devices and preparations during treatment (for example, for excision of the gum that has grown into the carious cavity), as well as materials for fillings: glass-ionomer cements, compomers, composites, etc., is separately fixed.

Combined techniques using a cofferdam to isolate the working area, 4-handed work with a dental assistant, treatment of dental caries in 2-3 visits cost, of course, more than a simple filling.
And the use of orthopedic methods of dentistry (crowns, tabs) in conjunction with therapeutic measures (fillings) or without them cost several times more.
An attempt to diagnose and treat tooth decay of root cement for free (by compulsory medical insurance) can end in failure - do not forget that this is a difficult case. Due to the workload and poor equipment of most dental departments (especially rural) and polyclinics, there is a high risk of getting a free or cheap seal, which, in violation of the filling technique, will fall out after a few months. In the worst case, an incorrect diagnosis by the doctor may lead to the appearance of pulpitis pain under the established filling, thereby losing the time for retreatment of the tooth or even the tooth itself due to complications.
Dentist's advice
In order for cement caries treatment to be effective, you can choose any dentistry (even state), but it is important to find out from relatives, friends or acquaintances about the level of equipment of the clinic, reviews about specialists, treatment approaches, long-term results, materials used, etc. If you want to save money, then you should think about comfort and service last, as well-developed companies charge up to 30-40% of the cost of treatment for this particular category of services.
Useful video about cervical caries and its characteristic features
About gum diseases and what they can lead to (about periodontitis)

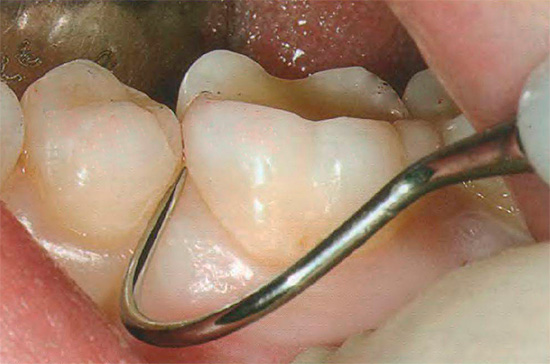
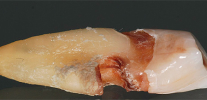
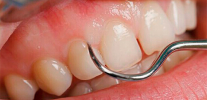
Is it possible to treat cement caries from the inside before setting a permanent filling (pulp removed, canals treated, temporary filling)?
Hello! If you mean treatment through the tooth cavity, where there is the possibility of deep penetration to the damaged wall, then sometimes this can be done, but there is a chance of leaving carious areas on the outer surface of the tooth, where access is difficult. Ideally, the view of this part of the tooth should be favorable, better from the outside through gum retraction, so that through this access a complete excision of the carious tissues is performed. And already inside the "dead" tooth, this process can be controlled.