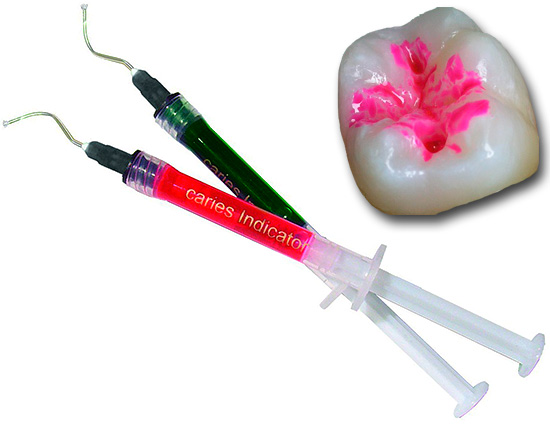
A caries marker is a special substance that, when applied to caries-affected tissues (demineralized enamel, dentin), is fixed on them and, thanks to its bright noticeable color, allows the doctor to detect the carious zone or clearly indicate its boundaries. In this case, on healthy tooth tissues, the caries marker does not linger and is easily washed off when washed with water.
Simply put, a caries marker paints denatured tooth areas damaged by caries in bright contrasting colors and increases their ease of detection.
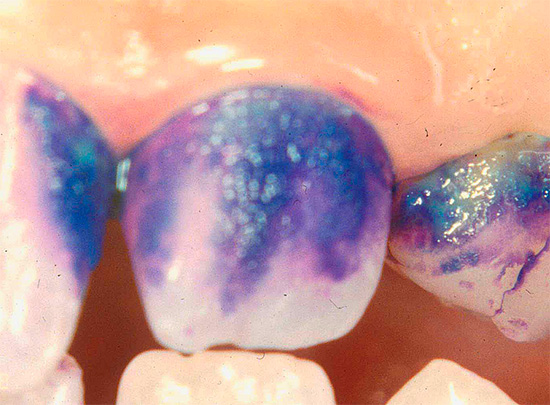
In this case, the terms “caries-detector” and “caries-marker” should be distinguished. Caries marker is just one type of caries detector, although some reputable authors believe that these are absolute synonyms.
Caries-detector is a broader concept, it denotes not only chemicals that help visually highlight carious areas, but also special devices and technologies that can detect caries in other ways.
But the caries indicator and caries marker are synonyms. However, in dentistry, the second version of the name turned out to be more popular. Some authors use the term “caries indicator” as a separate component of the caries marker, which is responsible for binding the drug to the affected surface, but there are about the same number of authors as those who call the caries indicator the drug as a whole.
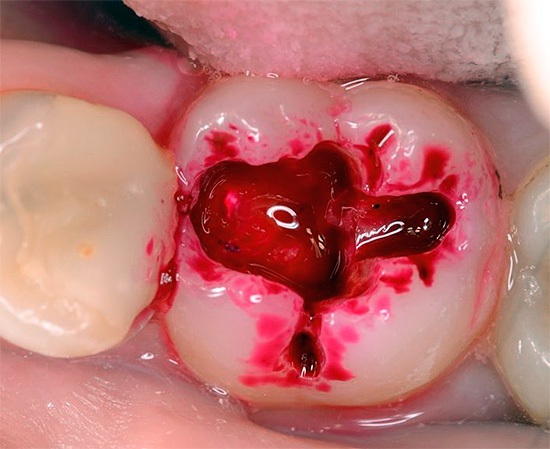
So, a caries marker significantly increases the reliability of caries diagnostics. It effectively stains carious areas at any stage of the development of the disease, including the stage of the stain, while it penetrates to a certain depth of the affected tissue and helps the doctor also at the stage of removing necrotic areas of the tooth.
After treatment with a staining solution of the carious cavity, it is enough for the doctor to clean the tissues colored with the indicator with a drill, and after each removal, treat the cavity walls with a new portion of the marker. This procedure is repeated until the walls of the cavity cease to stain at all, which will indicate complete removal of the tissues affected by caries.
On a note
Sometimes a caries marker is used for the differential diagnosis of caries. For example, enamel areas with spots from fluorosis or with hypoplasia, the marker does not stain.
The caries indicator has proven itself very well in order to educate young doctors and students, as well as to demonstrate the affected areas to the patient. Often it is also used to monitor the condition of enamel areas near crowns and fillings (it helps in violation of the marginal fit of fillings, cracks, improper placement), in fissures, where it is very difficult to notice developing caries in the early stages.
The use of markers somewhat reduces the speed of tooth treatment, but eliminates the element of doubt when cleaning affected dentin, thereby making the therapy more qualitative and reliable.
Classification of caries detectors and their constituent components
Today in the world dental practice several types of caries-detectors are actively used:
- Chemical detectors are precisely the same markers whose principle of operation is based on the interaction of a brightly colored substance with a surface affected by a carious process.
- Optical detectors in which a light beam with a wavelength of 405 nm is used to detect pathological changes in the tooth. According to the degree of its refraction, a special analyzing program displays different colors on each computer site on the computer screen, thereby forming a clear multi-colored image of the tooth, where damaged areas are clearly visible in the presence of caries.
- Laser detectors, the principle of which is similar to optical, but a laser beam works as a sensitive element in them.
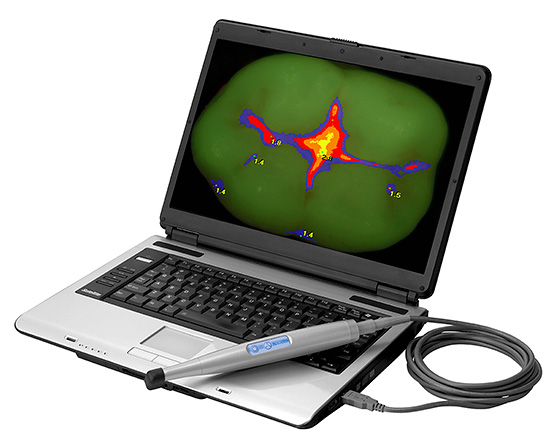
Optical and laser detectors are very convenient for diagnosing caries, but with their help it is more difficult to control the quality and completeness of cleaning of damaged areas of the tooth. In addition, they are expensive to acquire and today are the property of only elite clinics.
Caries-markers are much more accessible than laser and optical devices, and therefore they are used in most clinics, including in fairly budget ones. Their use does not lead to an increase in the cost of caries treatment, while significantly facilitating the work of the doctor.
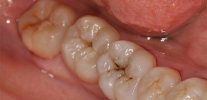
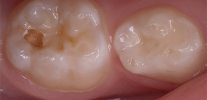
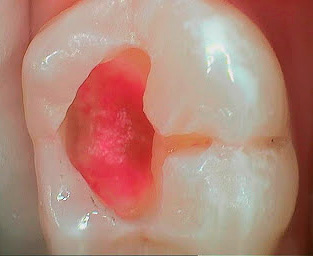
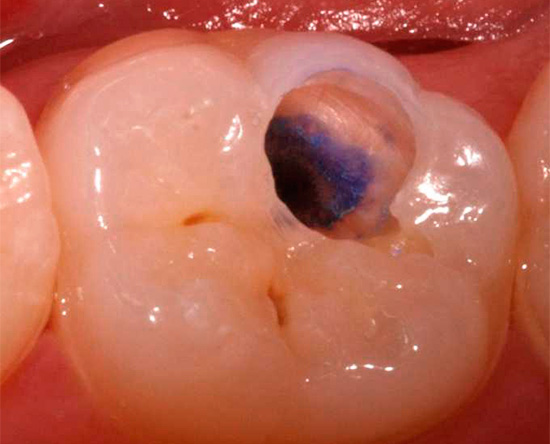
Of the active ingredients in caries markers, acid fuchsin is the most commonly used - a well-known synthetic dye that has an intense red color in aqueous solutions. The photo shows how well the carious sections of the tooth are stained with it:
Less commonly, methylene blue is used to detect caries, which works similarly to fuchsin, but stains the affected areas blue.
Instructions for the use of markers
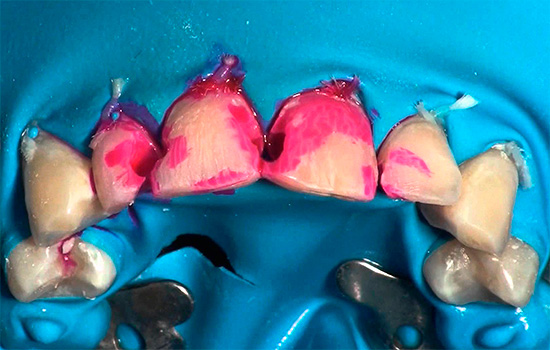
The instructions for using the caries marker are simple. To diagnose caries with markers (for example, in the stage of a white spot), the teeth are washed with water, dried and a preparation is applied to the enamel surface. You can squeeze the marker directly from the syringe, but you can also use special foam balls for this.
The drug is left on the enamel for 5-10 seconds, after which the tooth is washed with water. Caries-affected areas remain stained with an indicator.
The drier the tooth surface before applying the marker on it and the higher the microporosity of its tissues, the more intense the color of the painted surfaces will be.
During treatment using a drill, all tissues dyed in the color of the indicator are removed using boron. After that, the walls of the cavity are again treated with a marker for 5-10 seconds and again rinsed with water. When new stained areas appear, they are again removed. The procedure is repeated until the staining with the marker stops when processing all the walls of the cavity.
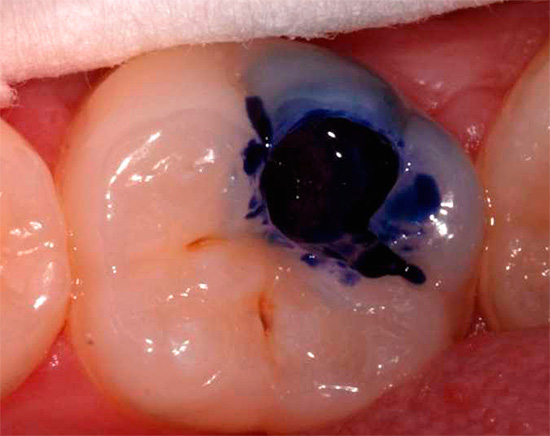
Such an instruction is universal for all standard caries indicators, including methylene blue.
Important:
Caries marker stains not only carious surfaces, but also plaque on teeth and tartar. Therefore, it is important not to confuse them with areas of carious lesions.
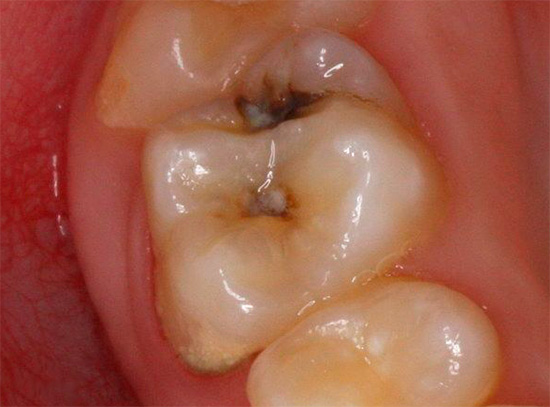
Caries markers are not intended for home use. These are exclusively professional tools that only a doctor uses, and more than half of the cases of using such tools are not associated with the diagnosis of caries, but with their use to increase the efficiency of cleaning carious cavities during therapy.
Marker staining is especially helpful when removing necrotic, infected dentin, which often leads to caries complications. It is the remains of necrotic dentin that were not mistakenly removed by the doctor that can lead to the development of caries under crowns and fillings (secondary caries). With strict adherence to the instructions, the caries marker allows you to completely clean the cavity from infected tissues.
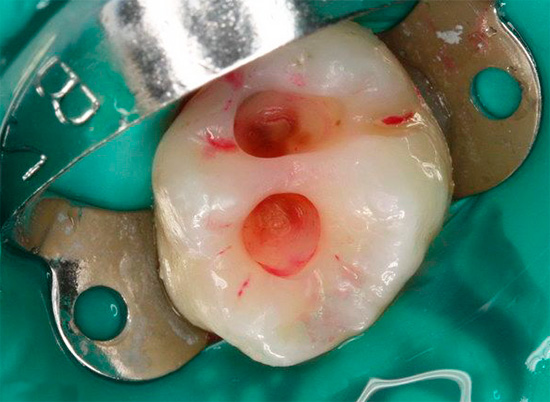
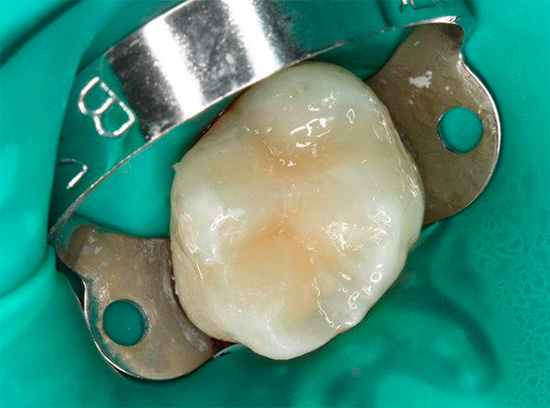
On a note
Caries-markers are used at a dental appointment, where there is no hard time limit, as in most budgetary institutions. To use these tools as an additional diagnostic method, treatment is required for at least 30-60 minutes. Saving time at this stage, especially with deep caries, can lead to serious damage to the pulp (“nerve”).
The point is that only a complete excision of the affected, non-viable carious dentin can reduce the risks of “postoperative sensitivity”, recurrent caries and infectious pulp inflammation. Caries marker (detector), when all diagnostic conditions are met, is recommended to practicing dentists to guarantee the quality of the treatment.
Cautions and safety measures
The main danger that must be avoided when working with a caries marker is the possibility of staining with a healthy, not damaged indicator dentin caries. This situation occurs when the marker on the tooth is too long - more than 10 seconds. Therefore, the optimal tooth processing time is about 7 seconds.
For this reason, it is not recommended to treat many teeth at once. This reduces the efficiency of work, and by the time the first teeth are already washed, the marker may already begin to stain healthy tissues on the remaining ones.
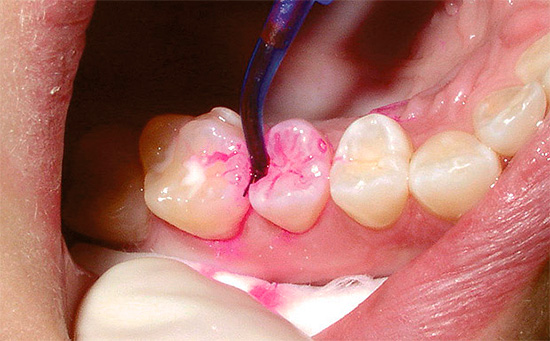
Also, with a significant deepening inside the tooth, it is necessary to correctly distinguish the areas colored with red indicators from the pink dentin near the pulp.
Caries markers are harmless to human health. However, some of them contain propylene glycol and can cause allergies in especially sensitive patients when they enter the mucous membranes. Unpleasant symptoms quickly disappear after washing the mucous membranes with water.
On a note
Due to the rich color of caries, markers are able to leave permanent marks on clothing and the surface of the skin. You can wash them off with a cotton swab dipped in vinegar, but you need to do this immediately after the marker has hit the skin or tissue, since subsequently the stain will be more difficult to remove.
Prices for caries markers from different manufacturers
The most famous and often used in clinics are caries markers of the following manufacturers:
- Voco, a German-made drug. The price of 1 g of caries marker Voco is approximately 400 rubles, and 3 grams - about 1000 rubles.

- Kuraray, a Japanese remedy - the price of this caries indicator is approximately 2500 rubles per 6 ml.

- Color test of the Russian company VladMiVa. Perhaps this is the most affordable drug: a 20 ml bottle costs about 100 rubles.
These prices vary greatly, depending on the city, as well as on the clinic, which includes them in the calculation of the cost of treatment. Nevertheless, the figures given reflect the difference between the cost of different drugs correctly.
In this case, there is no fundamental difference in the operation and use of different markers. Usually, the dentist tries to work with several of them, and eventually stops on the drug that is most convenient for him to work with.
Interesting video: an example of using a caries marker in practice
The use of a caries detector during tooth preparation