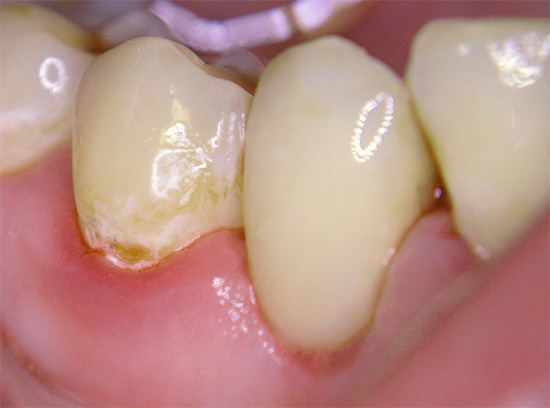
Three parts are distinguished in a tooth: root, neck and crown. The anatomical crown is normally located above the gum, and the neck and root are covered by surrounding tissues. That is why caries, which is located on the border with the gum and near the neck of the tooth, is called cervical (otherwise - cervical).
Below are some photos with examples of cervical caries:
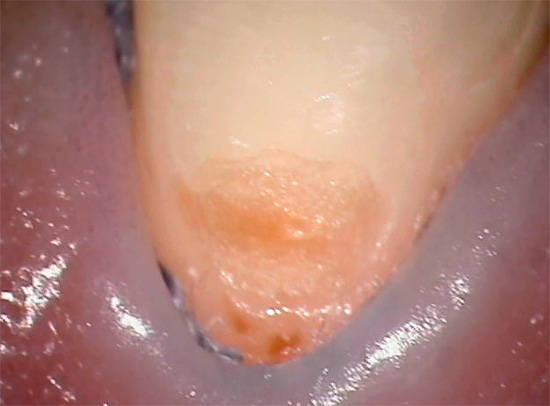
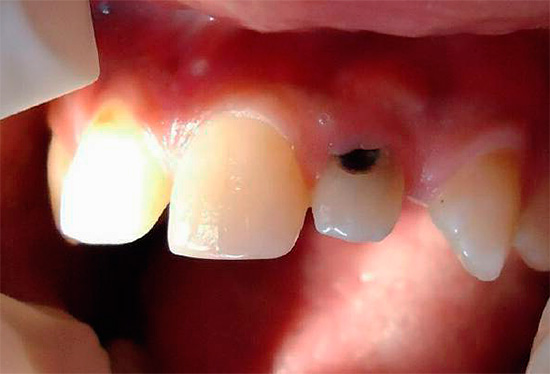
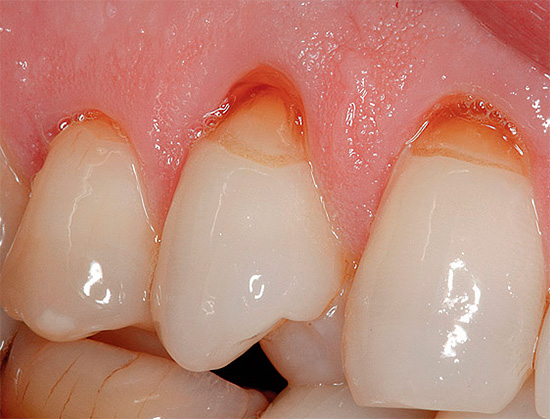
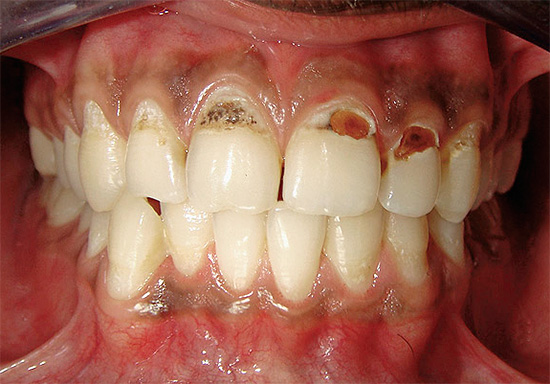
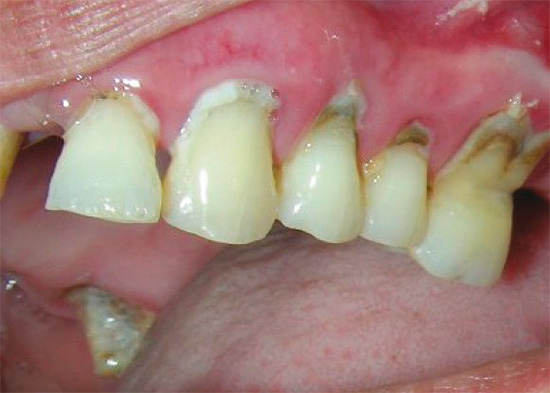
Many people begin to take cervical caries seriously and the reasons that cause it only when the problem is clearly evident in the reflection in the mirror and causes natural aesthetic inconveniences. The smile zone for people who need communication to implement certain tasks is of particular value. And since cervical caries is often localized precisely on the front teeth, there is an urgent need to return the aesthetic component.
The photo below shows a typical example of cervical caries on the front teeth:
At the same time, many questions arise regarding the causes of such problems and, of course, regarding possible methods for eliminating cervical caries, which we will discuss further.
The main causes of cervical caries
The main reasons for the development of cervical caries in general do not differ much from the causes that cause other forms of carious tooth damage. They are related:
- With the nature and diet: the amount and frequency of consumption of foods containing easily fermentable carbohydrates.
- With a microbial factor: activity under plaque and in its volume is predominantly bacteria of the Streptococcus mutans species. In this case, bacteria ferment carbohydrates with the formation of organic acids, which act on the surface and subsurface layers of enamel with the formation of foci of demineralization. As a result, calcium, phosphorus, fluorine are washed out, the enamel mineral crystal lattice is broken with the gradual formation of a carious spot.
- A very common cause of carious lesions is also the lack of adequate oral hygiene (properly formed manual skills for cleaning tooth surfaces, the mode and frequency of this procedure).
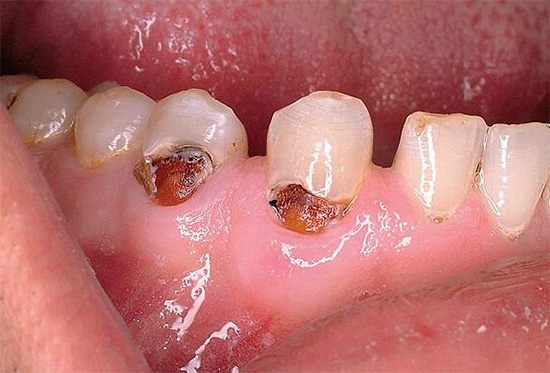
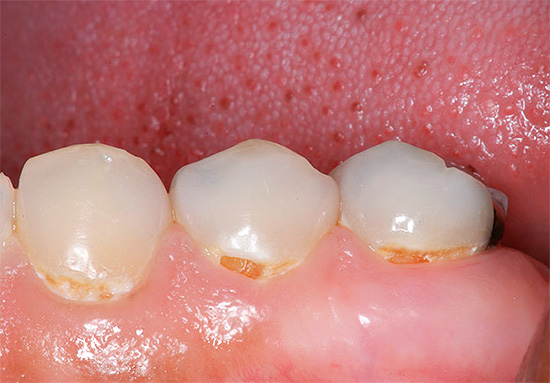
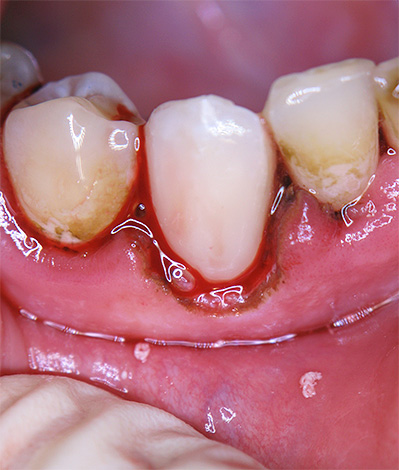
The photo primary caries in the cervical area of the tooth:
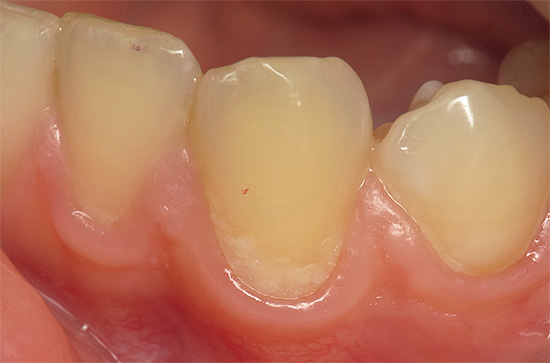
From the experience of the dentist
Often people ask me questions like: “Why, then, does my brother eat as much sweet as he wants and when he wants for many years, and he doesn’t even brush his teeth, but they are still intact, and I have solid fillings?”
The fact is that although the causes of caries are the same for everyone, they affect everyone differently. A significant role in the prevention of caries is played by the composition and amount of saliva, its remineralizing properties, the functional state of the body, environmental influences, caries sensitivity of the tooth surface, the individual structure of tooth tissues, determined by genetics and heredity.
However, the cervical region of the tooth also has a number of features that contribute to the fact that the carious process here can pass very quickly from the stage of initial caries to deep ...
Variety of clinical presentation
In its development, cervical caries goes through all the same stages as any other:
- Caries in the spot stage;
- Surface;
- Average;
- Deep.
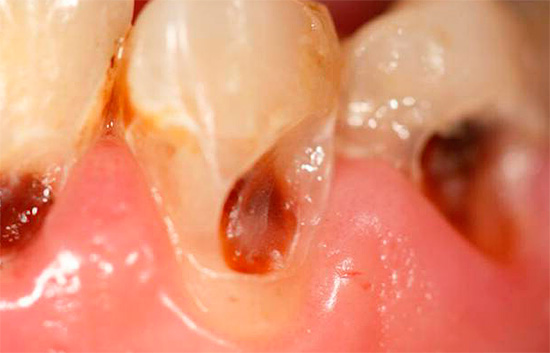
A peculiarity of cervical (cervical) caries is that it is often difficult to determine at what stage of destruction enamel and (or) dentin are. It is especially difficult to distinguish between caries in the spot stage and superficial caries, as well as between medium and deep.
This is due to the fact that at the border of the transition of the crown of the tooth into its neck there is a thin and often weakly mineralized enamel. As a result, the cervical region has a tendency to excessive abrasion due to improper brushing techniques, excessive brushing and the use of highly abrasive toothpastes (usually called whitening).
As a result, over the years, the thickness of the enamel in the cervical area becomes less and less. And as soon as this zone ceases to experience a cleansing factor, then with the combination of several cariogenic mechanisms, cervical caries quickly develops.

On a note
Many patients mistakenly call cervical defects as cervical tooth decay. From the point of view of the classification of caries, such forms do not exist, but the doctor, when asking the patient to cure “cervical caries of the anterior tooth,” easily understands what help is needed from him (and often it’s not even about caries, but about wedge-shaped defects that we we’ll talk later).
Gingival caries is a synonym for cervical. It is only important to distinguish between subgingival and subgingival. The first develops directly above the gum, and the second - in those areas of the tooth that are below the gum.
Most people with carious spots on their teeth in the cervical region (the initial stage) may already experience discomfort: discomfort, soreness and even certain pains characteristic of hypersensitive teeth, but this is less common. Basically, caries in the spot stage is asymptomatic and is determined only visually as a white or pigmented spot.
Below is a photo of cervical caries in the spot stage:
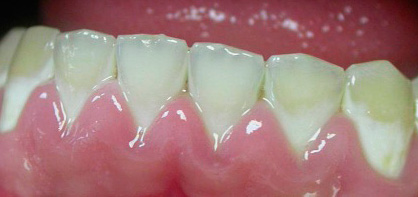
With superficial caries, pain often occurs from chemical irritants (salty, sweet) and from temperature (cold). Outwardly at this stage, the disease resembles caries in the spot stage, but when probing with a dentist with a special sharp instrument (probe), a roughness zone is detected in the center of the vast spot.
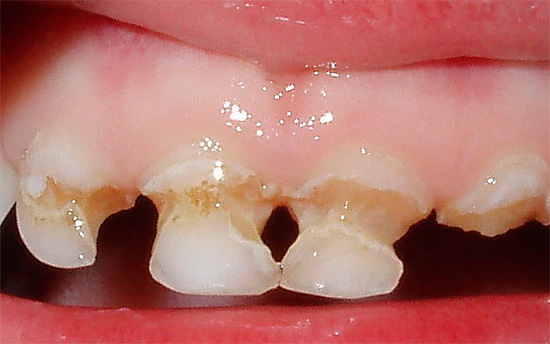
Medium and deep cervical caries are often characterized by a whole palette of pain symptoms from all types of irritants. Sometimes they can be joined by pain from mechanical influences, when hard food gets in, but this is rare due to the shape of the teeth, which protects the cervical zones from food falling under the edge of the gums.
Cervical decay of anterior teeth often causes pain when inhaling cold air.
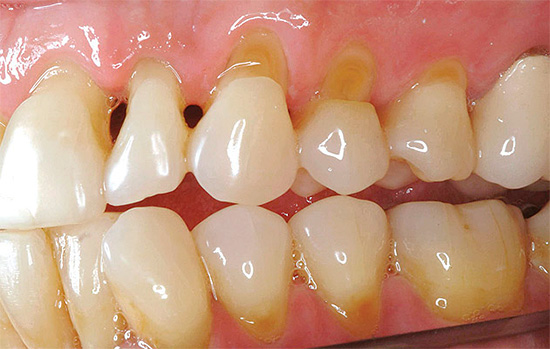
Feedback
A month ago, he was forced to consult a dentist, as his front teeth fell. First, the front ones were slightly darkened near the gums, and then the fangs also. This did not end there. Just a few days before visiting the dentist, I began to feel severe pain in my front teeth from cold water and sometimes from sweets. I tried to drink warm water and eat less, but could not continue this way. I went to the clinic, where for 5 visits my front teeth were repaired, and then my fangs. They said that this is a neglected cervical caries. The color, however, was not perfectly matched, but it saved the money.
Maxim, Tolyatti
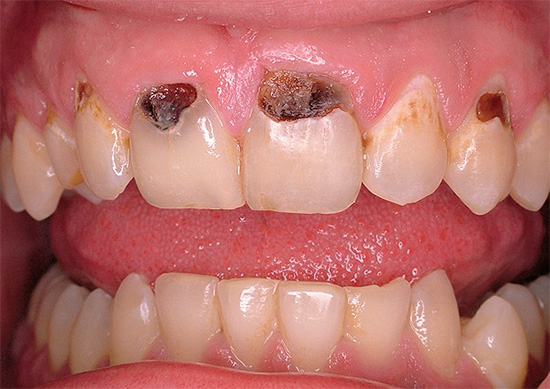
The following photo clearly shows deep caries in the cervical region:
Cervical caries and circular: similarities and differences
The following lesion zone is characteristic of cervical caries: the subgingival areas of the vestibular (buccal) and lingual (palatine) surfaces of the lateral and front teeth.
If the causes of the pathology are not eliminated, then there is an increase in the boundaries of caries in the cervical region to the contact surfaces with the coverage of the tooth in the form of a ring - in this case we are talking about circular caries. That is, circular caries can conditionally be called a "complication of the cervical."
To a greater extent, circular caries affects milk teeth, especially in weakened children.It is also called "annular" or "anular."
In the photo below you can see an example of circular caries on the baby’s baby teeth:
It is easy to guess that circular caries, as more aggressive, often proceeds with severe clinical symptoms, and even sometimes leads to fracture or spallation of the crown of the affected tooth. However, in some cases, even such serious defects may not cause severe pain, since they produce replacement dentin that protects the pulp from irritation.
Possibilities of differential diagnosis of cervical caries
At home, it is difficult to determine exactly what kind of education on the tooth spoils the aesthetics or causes pain. Spots, strokes, defects, indentations in the cervical region - all this can characterize the following types of pathologies:
- Actually cervical caries.
- Dental diseases of non-carious origin (fluorosis, hypoplasia, erosion, a wedge-shaped defect, etc.).
- Various options for pigmented (colored) plaque, up to the so-called “smoker's plaque”.
Below the photo shows the spots on the teeth with fluorosis:
Of all these options, cervical caries ranks first in the number of visits by people to the dentist. Other types of pathologies are less common.
Only a doctor can correctly make a final diagnosis, but you can correctly orient yourself even before visiting a dentist yourself. Most often, difficulties arise when comparing caries with fluorosis and enamel hypoplasia.
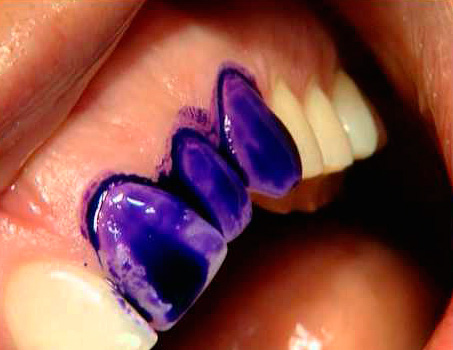
The age of existence of spots or spots on the enamel, as well as their location on different parts of the tooth crown, may indicate hypoplasia (its cause is underdevelopment of tooth enamel, which is caused even at the stage of development of the fetus in the mother's body). To confirm the diagnosis, the dentist stains the stain with a 2% solution of methylene blue. If the spot does not stain, it is enamel hypoplasia, and not cervical caries in the stage of a white spot.
Fluorosis is more difficult to distinguish from caries and other non-carious lesions. It is important to know the level of fluoride in drinking water in this area or in the area of early residence. If it is elevated, then the multiple nature of the spots located on the teeth of the same name at the same time indicates fluorosis. Cervical caries most often develops as a single carious spot.
It is important to distinguish between a wedge-shaped defect and cervical caries: they differ in that the former is in the form of a wedge or V-shaped. With a wedge-shaped defect, the walls of the cavity are dense, smooth and shiny, which cannot be said about carious tooth decay in the cervical region.
Despite the fact that the localization of these diseases is the same, the appearance of the cavity always tells the doctor the correct diagnosis. In addition, the initial forms of caries and a wedge-shaped defect can be recognized when stained with special caries indicators.
There is no such thing as a wedge-shaped caries of a tooth. This is the commonplace name for a wedge-shaped defect.
In the photo you can compare the wedge-shaped defect and cervical caries:
Feedback
I went to the dentist about the strange destruction of the front and rear teeth on the left. I’m already over 50 years old, almost all of my teeth, I did not suffer from caries, unlike my relatives, but recently I felt pain from cold water and began to examine my teeth in front of the mirror. I found some holes near the gums on the canine and on other teeth only on the left side.
The doctor said at the reception that these are wedge-shaped defects on three teeth on the left, and not caries at all. The possible reason was that I was right-handed, and I always brushed my teeth hard and for a long time, so I erased the enamel on the left side, since it is more convenient to brush there. The dentist showed me that there are also beginning wedge-shaped defects on the right, but they are not yet expressed.
Sergey, Volokolamsk
Modern treatment methods and the specifics of the choice of materials for fillings
Depending on the depth of the lesion, the appropriate treatment tactic is chosen.
Home treatment for cervical caries may be a supplement to spot stage caries therapy. In this case, apply:
- toothpastes and gels containing high concentrations of fluorides, as well as calcium and phosphorus compounds;
- dental floss (flosses) soaked in fluorides;
- rinses again with fluorides (since this particular element very effectively promotes the mineralization of tooth enamel).
To use fluoride-containing complexes on your own, without prior consultation with the dentist, can be hazardous to health. Any prescription of drugs or additional funds is based on the diagnosis, activity of the carious process, lesion area, long-term results and possible risks.

Cervical caries in the spot stage is most often amenable to conservative treatment, that is, without the use of a drill. However, due to the close proximity to the gum tissue, constant leakage of gingival fluid into the work area and a thin layer of enamel, certain difficulties are created for the application of some new techniques.
For example, the modern minimally invasive ICON technology (Aikon), due to the close location of dentin in the cervical region, is limited to use, since the substances used can not affect dentin. It is difficult to determine how thin enamel is in the cervical region of a particular person, therefore this technique is rarely used for cervical caries.
Chemicals related to remineralizing therapy and deep enamel fluorination are widely used.
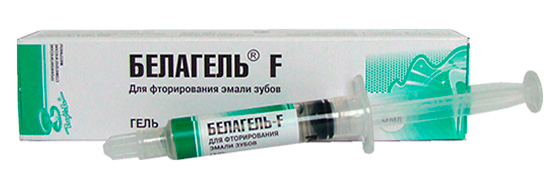
In adult and pediatric dentistry, the following drugs are currently actively used to treat initial cervical caries:
- Glufthored;
- Enamel-sealing liquid;
- Belagel Ca / P, Belagel F.
- Remodent.
Treatment of superficial, middle and deep cervical caries with the impossibility of conservative therapy is carried out in the following sequence:
- Anesthesia (anesthesia) to ensure painless manipulation.
- Cleansing a carious tooth from dental plaque to reduce the infectious load.
- Preparation (machining) of the tooth to remove carious and pigmented tissues.
- Drug treatment of the cavity with weak solutions of antiseptics.
- The formation of the cavity according to the selected material for a permanent seal.
- Filling a formed cavity.
The complexity of the choice of material for the filling is determined by the direct location of the formed cavity near the gingival margin. The closer the cavity to the gum, the more difficult it is to establish the material in a quality manner. The reason for this is the possibility of moisture, gingival fluid and blood getting on the work surface.
Dentist Opinion
The most difficult for high-quality fillings are not even subgingival carious cavities, but their combination with subgingival cavities. Combined forms are not so rare and are associated with the activity of the carious process in a particular tooth. Often, cervical caries of the anterior teeth is complicated by subgingival defects, which, as a result of preparation, can be difficult to isolate from the fluid (blood) even using cofferdam. In this case, the doctor chooses a material that can be inferior in strength and aesthetics, but hardens reliably in a humid environment.
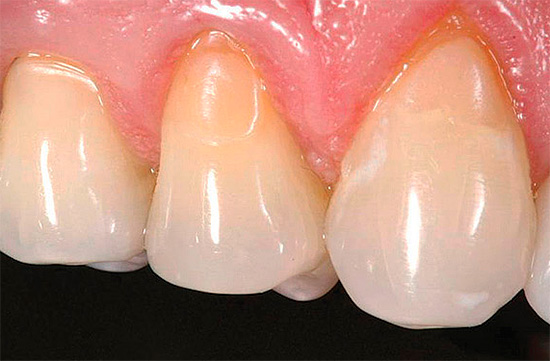
Due to the specifics of localization of carious cavities, the choice of dentists is reduced to the use of glass ionomer cements (CIC), which are more resistant to moisture compared to aesthetic composite materials of light curing. Of particular interest are hybrid JRCs.
On a note
One of the most widely used glass ionomer cements for filling cavities in cervical caries is VITREMER (Vitremer). This is one of the few SICs with a wide color gamut, a triple curing mechanism and high strength.In the treatment of cervical caries, this material competes with aesthetic light-cured composite materials.
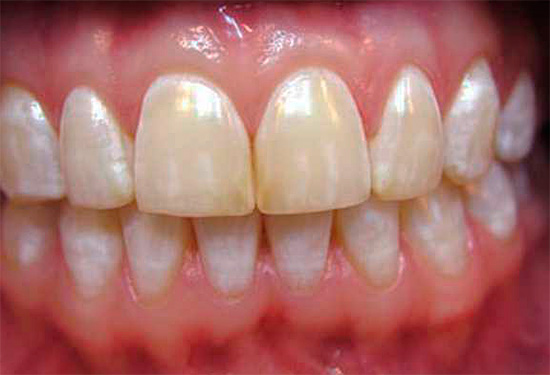
Modern techniques and technologies make it possible to combine glass ionomer cements with composites to achieve maximum effect. Proper implementation of the instructions for the materials used makes it possible to advantageously use the positive properties of each subsequent material when introduced into the formed cavity, creating a seal with reliable fixation, increased retention time, strength and aesthetics.
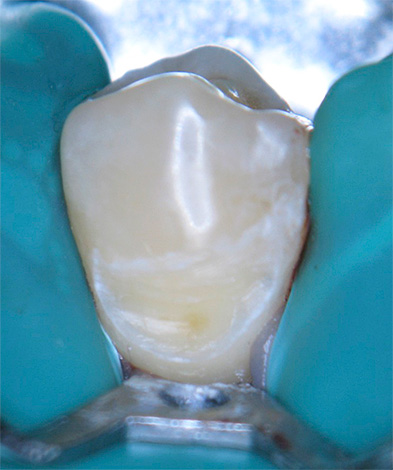
An example of filled teeth after cervical caries treatment is shown below in the photo:
Unfortunately, many budget organizations cannot boast of the possibility of using modern technologies and materials. The equipment of hospitals and clinics is often limited only to materials on compulsory medical insurance, where there is no cofferdam, saliva ejector, modern and convenient for working with cervical defects of the test center, light curing composites - all that is required for high-quality work for the long term.
Feedback
A week ago, standing in front of a mirror, I found in my front upper tooth a dark spot near the gums. There were no pains, but the fear of the prospect of walking with a black tooth seemed to me, as a physics teacher at school, stronger than the dentist’s fear from childhood. They advised a good doctor in a small private office, where after examining the stain, the doctor said that it was cervical caries, which had already destroyed all the enamel and went a little under the gum. It turned out that fear had big eyes: they made a good import injection, drilled a little, put a seal at a time, and even the color of the seal, one can say almost like a real one, cannot be distinguished from the outside.
Alexander, Omsk
Features of early diagnosis and prevention of cervical caries
Among the common diagnostic methods for cervical caries are the following:
- Visual methods. They are actively used by both the doctor and the patient. When tooth decay occurs on the front teeth, it is not so difficult to recognize defects (especially in a neglected form). In this case, the doctor only needs a dental mirror and a probe.

- Laser diagnostics. No less popular technique, especially when it comes to hidden caries or root caries zone. One of the devices - “Diagnodent” - uses the principle of changing the characteristics of a laser beam reflected from tooth tissues affected by caries. As soon as cervical caries or root caries is found, the device emits a sound signal.
- The method of vital staining of carious spots. Ideal for doubts of the doctor in the diagnosis of caries. The easiest and most reliable way is to stain the stain with a special caries marker (indicator), which, for example, is used, for example, a 2% dye solution of methylene blue. If staining occurs - this is the initial caries. Other well-known chemical dyestuffs can also be used: 0.1% methylene red solution, carmine, congorot, tropeolin, silver nitrate solution.
- Transillumination The technique, which is used much less often, but allows you to identify the initial forms of cervical caries when teeth are exposed to a bright ray of light. In this case, shadow formation is assessed as the beam passes through healthy and caries-affected tissues.
Modern caries prevention is aimed at eliminating the causes of its development:
- First, you need to break the chain “carbohydrates - a microbial factor” (which will stop the development of not only cervical caries, but also generally improve the cariogenic situation in the oral cavity).
- Secondly, it is necessary to strengthen the mineral structure of enamel.
To implement the first direction, the following steps must be taken:
- Observe the dietary regimen and nature, emphasize solid and moderately rough food, increase the amount of fruits and vegetables (especially after the main meal), limit the consumption of easily fermentable carbohydrates in any form (cakes, cookies, sweets, sweet rolls, etc.) .).
- Stick to important hygiene rules: brush all accessible tooth surfaces with brushes, toothpastes and flosses at least twice a day, and rinse your mouth immediately after each meal. It is important to understand that brushing your teeth before eating does not give a good result, since a dental plaque seeded with germs forms in a matter of hours after a snack.
On a note
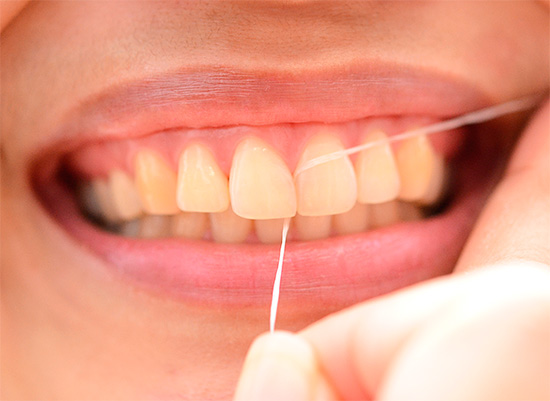
Flosses (dental flosses) are by no means a waste of time, but a thorough cleaning of the most inaccessible contact surfaces, especially in the cervical region, where caries most often begins to form.
The photo shows an example of the use of dental floss:
To strengthen the mineral structure of enamel, it is enough to combine the above methods with various forms of drugs for remineralization and fluorination at home. The range of products containing mineral components (fluorine, calcium, phosphorus) in their various combinations is huge. To find out what is better for the health of your teeth, and also has fewer risks when used independently, the dentist will help.
The most popular for home prophylaxis of cervical caries are: toothpastes with fluoride and calcium, rinses (with fluoride), and dental floss soaked in fluorides.
The correct and safe combination of methods and means of prevention is usually selected at a dentist's appointment. Within 20-40 minutes, the doctor can talk about the pros and cons of each of them, determine the most suitable option for you, taking into account individual parameters (dental car susceptibility, hygiene level and condition of the cervical region).
An interesting video about the features of cervical caries
An example of the treatment of deep cervical caries using a drill

Very informative, thanks!
Scary, but it is necessary to treat.
Very interesting. I didn’t even know that there are different types of caries. We will treat a little. Although now a dentist is not a cheap pleasure.
Very interesting, I learned a lot. When my teeth ached, I was advised in the pharmacy to rinse with mummy and sensodyn paste. And after 2 days the pain subsided. But, of course, I didn’t recover to the end, I’m looking for an experienced dentist.
A very good article. One tooth was already filled. Only when they drill painfully, and so - nothing.
Until 2012, she treated her teeth by VHI. At the very least, there were teeth, I could eat, drink, smile. Then, having lost VHI, she applied for compulsory health insurance to the district polyclinic, where they drilled me without having anesthetized enough tooth. Paid it was not possible to treat. 6 years have passed.I am now 50 ... And I have both cervical caries and half the teeth. 21st century ... You need to either swear in clinics, or rot alive. This situation is in dentistry, and in other medical fields.