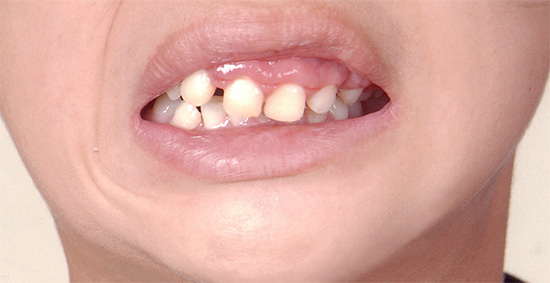
In young children, the development of decay of milk teeth usually proceeds much more rapidly than in adults, and often the destruction affects several teeth at once. In such situations, prolonged inaction of the child's parents can lead to very serious consequences.
Do not think that "these are just milk teeth, and they will fall out anyway." The infectious carious process is not limited only to the hard tissues of the tooth, rather quickly going beyond the root with purulent fusion of the surrounding soft tissues. In such cases, the best emergency care option for the child’s health and normal life is premature extraction of a milk tooth, which, incidentally, by itself often traumatizes the psyche of a small child and causes persistent fears in the dentist's office.
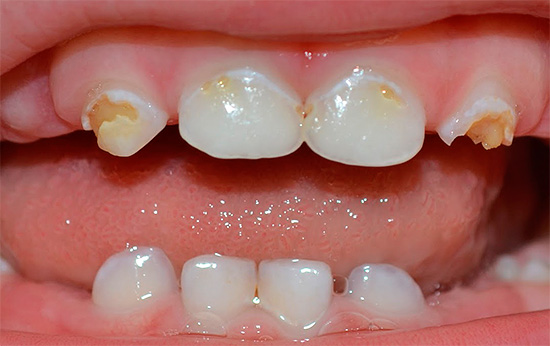
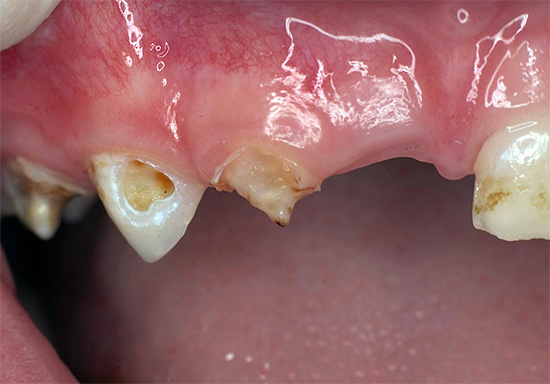
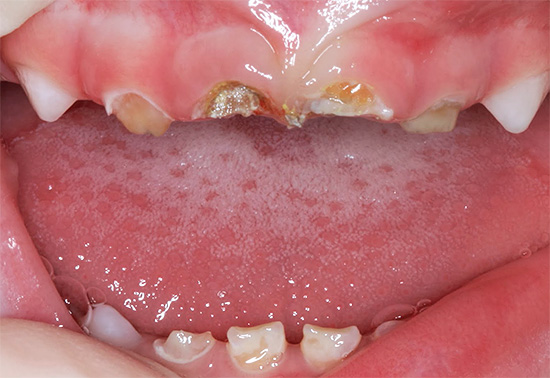
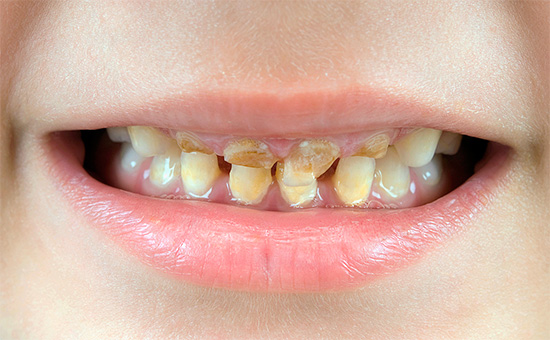
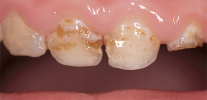
The photo below shows examples neglected caries deciduous teeth in children (including with a complication of periodontitis in the second example):
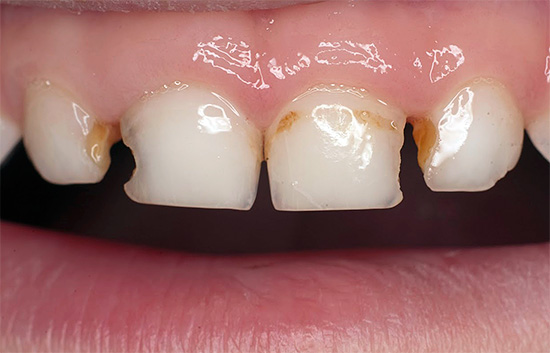
But the main result of such premature extraction of milk teeth is various violations of the bite, speech, appearance of the child (face shape), the possible emergence of inferiority complexes in the team (when the baby has been walking with rotten teeth for years or not at all). What will happen if we do not treat decay of deciduous teeth in young children, as well as about the most dangerous complications, we will talk even further in more detail, but first things first ...
According to statistics, decay of deciduous teeth occurs in 12% of infants up to one year of life, and at 5 years old dentists find this disease in about 73% of children. If you think about these statistics, it turns out that although milk teeth begin to erupt on average from 4-6 months of a child’s life and, it would seem, should be “fresh” and healthy, almost every tenth baby already has caries at 12 months of age at any stage on the baby tooth. Most clearly, these data reflect the plight of babies in small villages and cities where there are no pediatric dentists or hygienists.
The carious cavity that forms in the not yet mature temporary teeth is a focal point of infection with numerous pathogenic microflora. This focus directly or indirectly affects the protective functions of the child's body. The problems arise not only in connection with pain in the teeth damaged by caries from various irritants (cold, sweet, sour), but can also turn into complications of caries, which often cast doubt on the continued existence of the deciduous tooth. At an early age, such complications often lead to serious conditions, including the need to save a child’s life when a purulent infection spreads to the soft tissues surrounding the tooth (abscess, phlegmon, sepsis, thrombosis of the cervical and other veins, meningitis, thrombophlebitis).
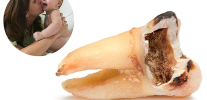
Look at a few more photos that clearly demonstrate the consequences of a lack of proper dental care for a child from a very young age:
I especially want to note the fact that an infection in the carious cavity often gives complications at the slightest shifts in the child’s immunity, for example, under hypothermia, severe stress:
- on the nose - constant runny nose, sinusitis;
- on the ears - otitis and ear pains;
- sore throats - sore throats;
- and even in the gastrointestinal tract - digestive disorders.
An attempt by parents to leave this problem unattended is a crime in relation to the health and life of a small person.
Why do deciduous teeth die from bacteria
Numerous studies have shown that the cause of decay of deciduous teeth is bacteria, which are usually transmitted from mother to baby.The main "destroyers" of teeth are Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguis. These microorganisms usually enter the child’s oral cavity when using common cutlery, when their parents lick spoons, nipples, and even kisses.
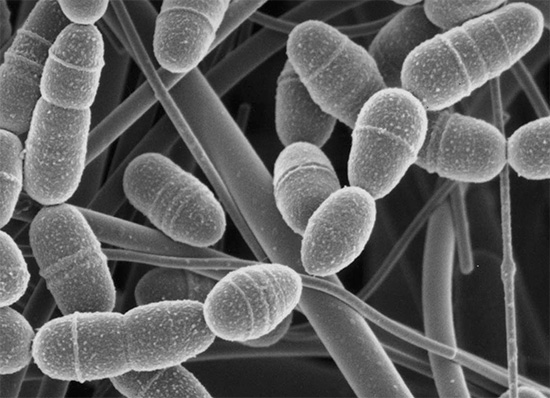
It is interesting
According to studies published in 2008 in Pediatric Dentistry, there is direct evidence that the mother is the primary source of Streptococcus mutans (streptococcus mutants) that can colonize the body of children. According to other studies, it turned out that fathers are potential sources of infection.

Thus, the cause of decay of deciduous teeth during caries is, in fact, a bacterial infection that can be transmitted from one person to another. This is especially important at the teething stage, because it is at a very early age that the baby’s baby teeth are especially vulnerable to the cariogenic effect of microorganisms.
But not everything is as sad as it might seem at first. The presence of cariogenic bacteria in the saliva of a child is only a kind of puzzle element, which in itself does not yet cause decay of deciduous teeth. In fact, the destruction is caused by a whole range of factors: the presence of cariogenic microorganisms, oral hygiene, eating habits, their modes, frequency and duration, characteristics of the baby's saliva (buffer capacity, the presence of protective immunoglobulins, mineralizing properties), and the heredity of the baby.
As practice shows, the constant sucking of a feeding bottle filled with juice, milk or another sugar-containing liquid is particularly strong. Bacteria use sucrose and some other carbohydrates for nutrition and reproduction, while releasing organic acids that demineralize tooth enamel. Early decay of deciduous teeth forms in the subsurface enamel layer and gradually captures the entire enamel with the formation of a small cavity at first and then deep - with the transition of carious decay to dentin (in this case, the teeth can become very painful).

On a note
According to the American doctor Jane Soxman, if the reproduction of cariogenic bacteria is not actively restrained, they will soon populate the entire oral cavity and will actively attack already permanent teeth after they appear.
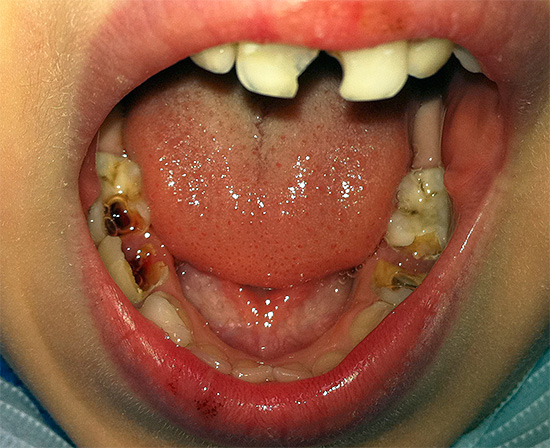
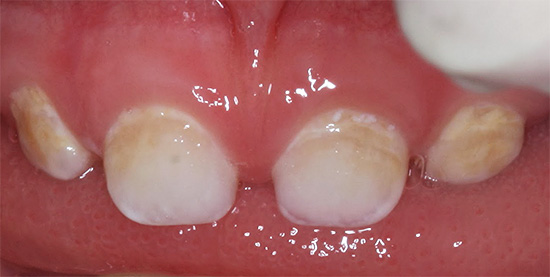
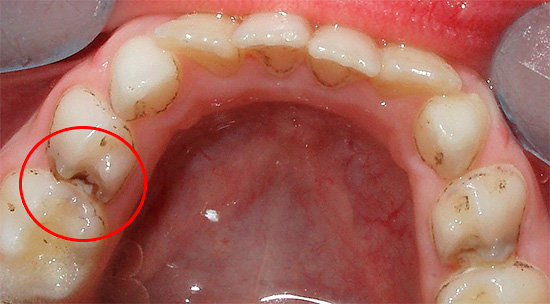
The photo below shows the initial decay of deciduous teeth:
How to recognize caries on baby’s milk teeth in time
Most often, caries first appears on the front milk teeth and manifests itself as spots of various shades (white, yellow, brown, black) or carious cavities (cavities) visible to the naked eye. Lesions can be located in the cervical (basal) region of primary teeth, on one or two contact (interdental) walls, and also capture half or most of the tooth crown.
This photo shows the earliest signs of decay of baby teeth in a child - the enamel has become white due to demineralization:
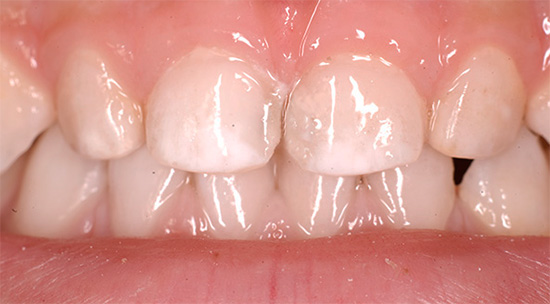
If cavities on the molar teeth are affected by caries, then these areas become dark brown or even black. Further progression of caries leads to the fact that the integrity of the enamel in the fissure is broken and a cavity is clearly visible with the naked eye or, more simply, a “hole” in the milk tooth.
So, the main signs of decay of deciduous teeth:
- Visuals. The appearance of suspicious stains on the teeth (especially in a short time).
- Painful. Often during caries, a child begins to complain of painful reactions from cold, sweet, hot, etc. Sometimes the teeth hurt very badly, and sometimes they practically do not bother.
- The appearance of odor from the baby's mouth. Under the influence of cariogenic microorganisms, food particles in the oral cavity actually rot. In this case, a specific smell is formed, which should prompt thoughts about decay of deciduous teeth.
- The multiplicity of manifestation.Due to the slight mineralization of enamel of deciduous teeth, caries begins to develop with almost the same intensity on several teeth at once, which is the reason for the appearance of multiple lesions. The accumulation of carbohydrate residues in the areas of retention (food retention): near the gums, in the spaces between the teeth, in the fossa (fissures) creates a favorable environment for the active nutrition of bacteria that provoke the dissolution of enamel.
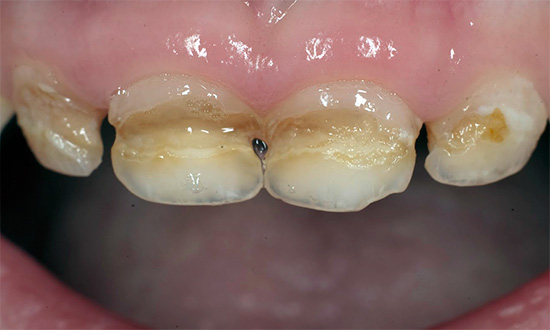
Is there a connection between caries and breastfeeding?
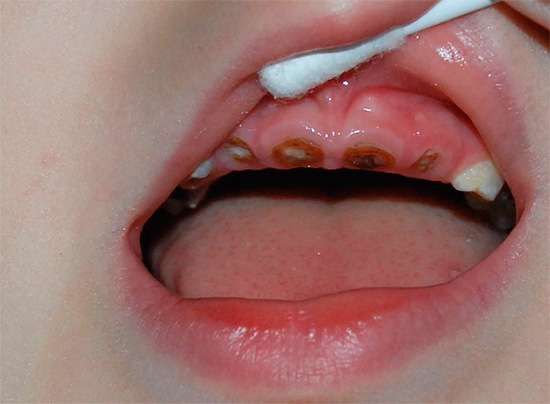
The so-called “bottle” caries develops in children from zero to four years old and destroys milk teeth after they erupt for a certain period of time. Most often, bottle caries develops on the front teeth in the cervical region with a partial or full coverage of the crown around the circumference - in this case it is also called circular caries.
Often, you can also observe white or black spots in the gum zone, extending to the boundaries of the gaps between the teeth. Sometimes there is a full coverage of the crown of a milk tooth with circular caries - in such a situation, the entire crown part can easily break off.
Pictures of deciduous teeth with circular caries:
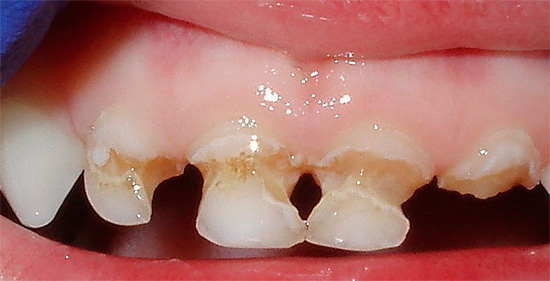
Breastfeeding does not directly provoke bottle caries. According to experts, only frequent and prolonged night feeding without hygienic procedures after it can provoke and accelerate the formation of caries on milk teeth.
In this case, it does not matter what they feed: breast or bottle, milk or juice. The main thing to start the formation of plaque on milk teeth and the cariogenic activity of microbes is frequent feeding of the child, especially in sleep, feeding sweets between main meals, as well as the lack of hygiene measures after eating.
An attempt not to treat circular decay of deciduous teeth can result in serious multiple defects of crowns, up to splitting and breaking. Often this is accompanied by pain when eating or even spontaneous acute pain. Loss of function of a large number of teeth entails malocclusion, chewing, digestion, general well-being of the child.
On a note
For the treatment of bottle (circular) caries of deciduous teeth, fluoride-containing medicinal preparations are used, which can be applied both in the clinic and at home, if you follow the doctor’s instructions. Laser treatment of caries and ozone treatment at an early age are not used. In order to prevent childhood caries of milk teeth, dentists recommend brushing the baby’s teeth after each meal, and parents of young children should follow the processing steps and sterilize the nipples and bottles.
Are deciduous teeth sore from caries
Caries on milk teeth can occur both asymptomatically and with pain characteristic of it. As a rule, a tooth hurts only from exposure to any irritants (as noted above, it can be hot or cold food, something salty, sweet or sour). While the action of an external factor lasts, a pain attack lasts.
Depending on the stage of tooth decay, pain reactions are distinguished with:
- Superficial caries - in this case, children usually complain of pain from sweet and sour foods;
- With moderate caries - short-term pain from cold and hot food, sweet and sour;
- With deep caries - in this case, the pain symptom is more often expressed from all the listed stimuli, as well as from the meal itself (mechanical irritation).
At initial caries milk teeth (at the stage of a white spot) pain symptoms do not exist yet, so it is easier to start treatment at this stage.
The possibilities of modern treatment
Modern pediatric dentistry has various methods of treating caries in babies, even at a very young age.Moreover, such approaches to treatment are selected that are highly reliable, safe and least traumatic for the psyche of the baby.
The main ways for treating early decay of deciduous teeth - these are non-invasive or minimally invasive technologies:
- remineralization of enamel and dentin (restoration of the lost mineral structure);
- deep fluoridation;
- manual processing of the cavity without the use of a drill;
- delayed filling;
and etc.
Particularly in great demand in the treatment of decay of deciduous teeth is the latest development - ICON technology (Aikon). At the same time, long courses of treatment with remineralizing compounds and fluorine preparations are not required, since almost a visit is almost always enough for a carious stain to disappear from the tooth surface.
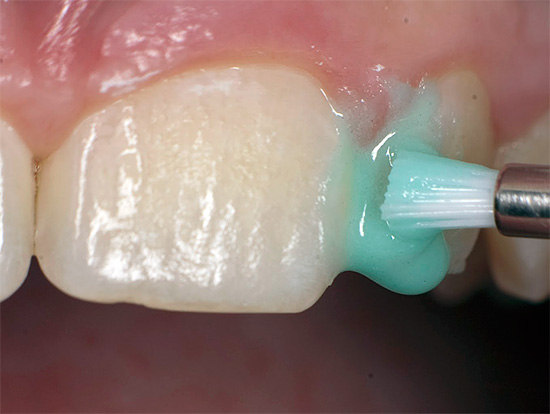
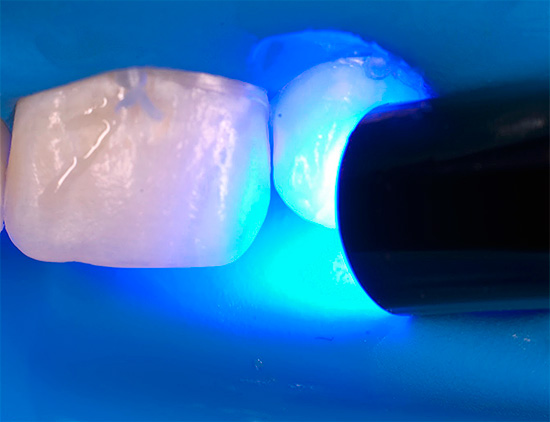
The meaning of the procedure is that after cleansing the enamel from plaque, a gel with a weak acid is applied to the carious stain, which removes the enamel surface layer, and then a highly fluid polymer material cured by the light of a special lamp is introduced into the caries lesion. In this case, the polymer resin fills the pores of the enamel and hardens in them, creating a new strong and reliable structure.
It is interesting
ICON treatment is somewhat similar to tooth filling, but without the participation of standard equipment. This technology is actively used in orthodontic treatment after removal of braces, as well as in the treatment of caries in the spot stage, located on the vestibular (external) and contact surfaces, that is, in between the teeth. ICON technology is suitable for the treatment of early decay of deciduous teeth in babies from 3 years old.
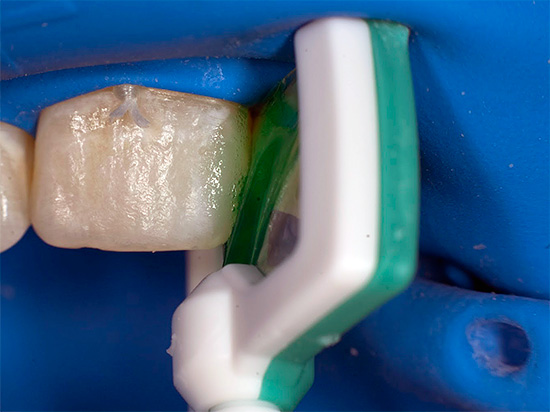
If ICON technology is used to treat initial caries, when there is still no cavity, then what if the decay of the deciduous tooth has already crossed the enamel and reached dentin? In the event that the child has an increased fear of traditional methods of treatment based on the preparation of the carious cavity with a drill, then the ART method (atraumatic rehabilitation treatment) is used.
The photo below shows some of the tools used when using the ART-method for the treatment of caries - in fact, they replace the drill:
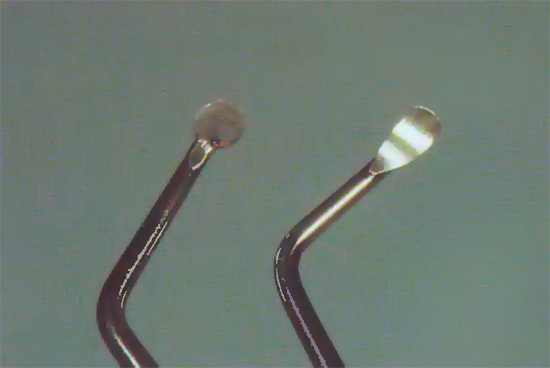
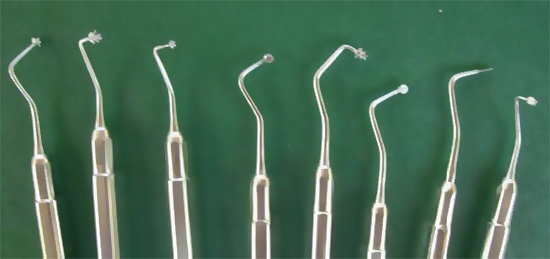
The meaning of the technique is simple: special sets of hand excavators and some other tools are used, which clean the carious cavity from softened and infected tissues, after which it is treated medically with weak solutions of antiseptics and filled with glass-ionomer cements - materials that can saturate tooth tissues with fluorides for a long time.
Despite the significant drawback of the technique, which often remains pigmented (dark) uncleaned dentin on the bottom and walls of the cavity, nevertheless, it is possible to stop the progression of the decay of the milk tooth due to caries, make up for the defect and return the tooth to normal chewing processes and also eliminate pain symptoms from external irritants. And if this technology is not always suitable for permanent teeth, then for the treatment of carious foci of temporary teeth - this is sometimes the most successful option so as not to injure the baby's psyche.
Where to go for treatment
In the event of decay of deciduous teeth or its complications, unprepared parents always have a problem: where to lead your child to treat their teeth? Often, “adult” dentists carry out a mixed reception, that is, they also treat children.
However, pediatric dentistry is significantly different from "adult", so you should choose specially equipped dental institutions for children. The choice between public and private institutions rests on the financial component. It should be borne in mind that any savings on child health often make themselves felt in the future.
Of course, not in all public institutions with free admission, treatment will be of poor quality, but the frequent uneven distribution of small patients between several pediatric doctors admitting in a large hospital or clinic leads to various paradoxes. Professional doctors who are ready to help the child in a quality manner are forced to serve from 15 to 25-30 and even more children a day, but not quite conscientious and not capable doctors often have a lot of free time, but no one wants to bring the child to them.
It must be understood that in those and other cases, you may not receive quality and guarantee assistance. Moreover, conditionally “free” institutions most often use outdated methods and approaches to the treatment of caries, “ancient” equipment and far from the most modern materials.

A large flow of patients excludes an individual approach, which cannot be said about private clinics and centers where an individual plan of prevention and treatment is drawn up not for one day (as is most often the case in state institutions), but for years to come. The clinic’s task in this case is mutually beneficial cooperation with parents in order to preserve the baby’s baby teeth until their physiological shift, given the age and psychological status of the baby. At the same time, experienced pediatric dentists establish a form of interaction in the form of a game.
From the observations of the dentist
One of the most effective ways in modern private dental clinics to arouse a child’s interest in treatment is through colored fillings installed on milk teeth in the treatment of caries. Popular sets of colored fillings from the German company Twinky Star allow the child to choose the color of the future fillings himself. The set includes 7 colors: blue, orange, pink, yellow, green, etc. As a rule, the strongest motivation of the child in this case is to boast a beautiful new seal in front of his peers.
If the baby is panicky afraid of doctors
To lure a child to a dentist appointment, sometimes there is little persuasion, motivation with colored fillings or buying a new toy. For many children, the fear of a white coat is an almost insurmountable barrier to the preservation of milk, and subsequently permanent teeth. Often in such cases, you have to resort to the most risky method of treatment itself - this is the use of anesthesia, when the child is put into sleep for a while.
No matter how clinics and individual doctors present anesthesia as a safe method of treatment, all the same, there are facts of possible complications during and after anesthesia and a percentage of failures (albeit small), it exists, as warned by parents who sign papers on possible negative consequences application of general anesthesia.
In this regard, of particular interest are drugs that have a sedative effect (suppression of consciousness), allowing manipulations when the patient is conscious, but does not feel fear. Almost all such drugs (tranquilizers) are available on prescription.
For example, in modern pediatric dentistry a convenient over-the-counter drug Tenoten for children is used, which is available in lozenges. The use of the pill 20 minutes before visiting the dentist can significantly reduce the anxiety of the child, eliminates fear, increases the pain threshold, improves mood.
From all of the above, it is important to understand that only mutually beneficial cooperation and the full interaction of parents and a pediatric dentist will create a truly comfortable environment for the prevention and treatment of young children. This, in turn, will provide a real perspective for the preservation of primary teeth until their natural change, and to preserve future permanent teeth will create the necessary positive attitude of the baby to any dental interventions.

Create all the conditions for this, and your children’s teeth will always be healthy!
How prevention saves baby teeth
For effective prevention of decay of deciduous teeth A comprehensive approach is of paramount importance. At the same time, systemic and local methods of preventing carious processes are distinguished.
For a better understanding: systemic measures are the use of special products or drugs inside. Local methods of caries prevention include, first of all, applying various active mineralizing enamel components to the teeth.
What each parent needs to understand about systemic measures:
- Limit carbohydrates and increase consumption of “hard” foods (fruits, vegetables). In many sources, you can find the phrase: "exclude sweets from the diet of the child." Unfortunately, such an ideal option does not fit our realities, but it is quite possible to somewhat limit the intake of sweets by a young child. The big problem of parents is that not only mothers and fathers themselves, but also numerous relatives feed the child with cookies and sweets in between meals. In this case, it is not worth wondering why, already at the age of 2-3 years, small dentist patients in the dental office feel at home. Fruits and vegetables are great for completing a baby’s meal, as the best option for self-cleaning the surface of the teeth.

- Systemic use of calcium-containing products can have a very positive effect on the baby’s milk teeth resistance to caries. It's no secret that this useful element necessary for our bones and teeth is best absorbed from the following foods: milk, cheeses, kefir, parsley, spinach, cream, cottage cheese, dried apricots, and others. Preparations containing calcium are prescribed according to coordination with the pediatrician with the expectation of an individual age-specific dosage of the child in a course of 2-4 weeks. In winter, it is recommended to combine such preparations with vitamin D supplements. Multivitamin complexes for children with mineral components, including calcium, are especially relevant.

- Systemic use of fluorides. Generally speaking, most of the fluoride, as one of the most important components of the enamel mineral lattice, must come with water - this is how its maximum absorption in the body occurs. Unfortunately, in many regions of Russia there is a serious shortage of fluoride content in drinking water, without which the baby’s baby teeth can quickly become affected by caries. Based on the data on the fluorine content in the water supply system, a systemic prevention base is being formed related to the introduction of fluorinated milk, salt, as well as the appointment of fluoride tablets, rinses, gels for application to the teeth in a clinic or for home use. Since fluoride in inept hands is poison and can cause harm to the health and even life of a child, a mandatory doctor consultation is required before such a serious fluoride prophylaxis.
What you need to know about local preventive measures to protect milk teeth from caries at an early age:
- High-quality cleaning by the parents of the baby of the surface of milk and permanent teeth with a toothbrush and toothpaste. Such hygiene should be started already after the appearance of the first milk tooth, for which special napkins are suitable, for example Spiffies with special impregnation for better cleaning from plaque. You can even use simple gauze moistened with warm boiled water. It is important to understand that such treatment should be carried out precisely after the child has eaten food. It is enough to clean the surface of the teeth 2-3 times a day to significantly reduce the risk of bottle caries on milk teeth.

It's important to know
Begin to accustom a child to a toothbrush should be from 1.5-2 years in the form of a game. You can not force a child to force, as this creates a persistent negative attitude to hygiene.Parents of babies should remember that their example of proper and effective brushing can easily motivate the child to obtain the same manual skills.
First, a toothpaste that does not contain fluoride is used together with a toothbrush, and with each year the necessary concentration of fluorides recommended for a given age should appear in it. It has now become quite simple to navigate: almost every paste for kids has a recommended age for its use.

- Professional and home (under the supervision of the attending physician) application of deep fluoridation. Most often it is an enamel- or dentin-sealing liquid. The alternate application of preparations for deep fluorination allows you to quickly strengthen the enamel of milk teeth and create a barrier to the action of acids of microorganisms from plaque. The advantage of the local use of fluorine-containing drugs is a point effect on the tooth tissue, bypassing the processes of long-term absorption of fluorides from water or food. Moreover, a correctly conducted technique of deep fluorination completely eliminates the likelihood of toxic effects of fluorine on the body.
As mentioned above, only an integrated approach with a competent combination of systemic and local prophylaxis will strengthen enamel of milk and permanent teeth and protect the child from caries for a long time.
Useful video: why is it important to treat milk teeth?
How to properly care for the oral cavity in young children



The child is 1 year 10 months old. The upper incisors are partially destroyed. What to do and where to go? The problem is that in our region no one undertakes to do any procedures with such a small child.
We have the same problem. At the daughter in 1.4 months. the front teeth began to crumble sharply. In just two weeks, 3 teeth flew! Also, no one wanted to take a cure. In the city dental clinic silver plated for free. Now the daughter is 1.10 months. and I see that the teeth are further destroyed. I found a private clinic in Kiev, they treat such little children there.
My child’s teeth are also destroyed, 2 upper. We went to the doctor, they said only to clean. Cleaned. Now almost all of the upper teeth look like gnawed. Doctors do nothing ... But it’s a pity to snatch. We are just starting to speak almost normally (2 years already, the teeth began to deteriorate at 1.6 years).
Daughter's teeth began to deteriorate rapidly with 1.5 years. The doctor advised 2 solutions: either treatment and removal under general anesthesia, or sitting around waiting for new ones to grow. My daughter is now 4 years old. All the lower ones in the seals, the upper ones are partially sealed and removed. Black teeth are very ugly. Treat teeth to your children in time.
What anesthesia did?
Stop sucking nipples, bottles on time, breasts - it's 12 months.Do not eat or drink sweets and begin to care for your baby’s teeth! We, pediatric dentists, have early caries, like a bone in a sore throat! Take care of the children, dear parents, and we are pediatric dentists, we will always tell you, but we are not magicians, caries (“holes”) are not overgrown by pills and kind words.
Breastfeeding cannot provoke tooth decay - this is a myth, and very harmful! But sweet teas from a bottle at night - yes. Well, in general, the later the sweet will become part of the child’s diet, the better for him. And, of course, accustoming to hygiene and preventive examinations at the dentist should be the norm.
Today we were at the dentist's appointment, the child is 1 year old, a plaque on all front teeth. The doctor said it was from overnight breastfeeding. We don’t give anything sweet, we clean our teeth 2 times. And still deteriorate.
This is far from a myth ... My child does not perceive any bottles and nipples, much less sweet tea at night. We are only at the GV, and nightly feeding. Here you go!
Yes, we are to blame, no doubt ... But then the question is: we came to the pediatric dentist at almost 2 years old, bottle caries, 4 teeth damaged. The "doctor" told us that at this age they did not treat him at all. "Brush your teeth and water overnight instead of milk." As far as I can judge by myself - if there is caries, then it’s definitely not treatable by brushing your teeth. It came to pain, the child cannot sleep ... What to do? Where to run? Which doctors? And what should I say at the meeting to the woman who misled us ?!
Hello Marina! You should contact a pediatric dentist in a private clinic: it is better to choose a private pediatric dentistry that has a maximum of positive reviews, not paying attention to the expensive price - high-quality treatment is expensive. It is clear that with a certain psychological status of a child, a dentist can sometimes not be able to cope with the work in full, although it is best to act in this direction rather than letting go of the situation and waiting for the "flux" - purulent inflammation in the area of diseased teeth to join the child's crying.
If a child gives an opportunity to treat teeth, then they are treated with practically the same methods as in adult dentistry: there is a set of materials that, after treating teeth from caries, can be qualitatively filled (restored) so that the child not only does not suffer from pain, but in the kindergarten was not an outcast - the object of ridicule (because of decayed teeth or because of a toothless mouth).
If the child does not allow the teeth to be treated by either the first wonderful dentist or the second professional, then the choice is small: either remove the teeth by force, but this may be a psychological trauma for life and fear of a white coat, or resort to sedation and (or) anesthesia. There are many pediatric dentistry clinics that practice sedation (anesthesia) in the treatment of aggressive or non-contact children, it is effective, but also expensive. It is clear that anesthesia is certain risks and possible side effects, superficial sedation is already closer to a safe option for the full treatment of the child, while he is relaxed and indifferent to everything for a short time.
As for the woman who misled you: of course, I do not know all the nuances of the work of this dentist in this institution. Maybe she has a “burnout” syndrome, and she is not going to be “bitten” by an offended child for such a small salary, and she does not have time to persuade (play with a child a doctor) with such a stream of small patients. There is an option that she does not have experience with such young children.
I don’t know for sure what prevents this woman from eliminating carious lesions in small patients on time, but I’ll suggest a replica for the dentist - it may come in handy:
“If you are not professionally prepared to work with children 1.5-3 years old, then maybe instead of giving empty and harmful advice to parents, is it better to take advanced training courses, or even change the scope of activity? In private clinics they can treat caries and pulpitis even at such a young age. ”
Dear doctor! We would love to go to the "private children's dentistry", but in our city there are simply none. But in our state they are able to torture children well. First, the queues are four hours long, then the doctors scream and scare the baby, but it's just a child and it hurts and is scared!
Very nice article! I learned a lot. Thank you) Take a note and be careful.
My son 1.7. The top 4 teeth crumble steel. Let's go to the doctor, the doctor said: constantly clean. Now I’ll try to find a pediatric dentist.
The teeth began to deteriorate rapidly from 2 years old, from the same age we clean in the mornings and evenings. We went to the children's dentist, healed and covered with silver, but the teeth are destroyed further and even turned black ((What should I do ?!
Hello! It's not about cleaning, but in the multiplicity of sweets in the oral cavity. The most damaged teeth, according to statistics, are in children who stick between sweets between meals and after it (especially lollipops, toffee, chocolates). As a parent of a baby, I myself was confronted with the fact that I “beat” the hands of strangers from the street who popped sweets (from sellers to grandparents from the entrance). Moreover, these strangers tried to assure me, the dentist, that without chocolates (such sweet snacks) the child would grow up stupid: “After all, a child needs chocolate for his mind and development.”
Fortunately, relatives and friends were aware that it was definitely impossible to feed lollipops up to 2.5-3 years, and later it was undesirable, but already a little bearable. I will not explain why. To the questions of my clients: “My son has already destroyed several teeth with caries already at 2 years old, and he is not given a chance to heal, how can you treat your son’s teeth?”, I say that at 4 years old he has no teeth with caries, I he had not yet been treated in a chair.
Naturally, in addition to “shaking hands”, oral hygiene was somewhat different than many parents imagine: the first teeth began to erupt in a year (this is a slight delay), the child cleaned them himself after training for a minute, then the game began: how the bumblebee flies in and buzzing in the mouth, a rabid Shyrk-Shyrk brush, tooth brushing by the parent outside and inside, especially the front group of upper teeth (most often caries).
We still continue to clean the child after his 1-2 minute “game”. Moreover, the best effect is achieved when cleaning follows after breakfast, and not before it. Since milk teeth almost always have gaps between teeth, floss is not required, only controlled oral hygiene and the absence of sweet foods: plugging a child’s tantrum with sweets is a vicious practice, at least for dental health.
By the way, brushing starts with the first erupted tooth. We are lucky that everything began already with a brush, but for anyone who has teeth clutching for 4-5 months, you will have to choose a fingertips or a banal toilet of the oral cavity and teeth with a gauze napkin. I do not think that there is any transcendental philosophy in this.
"Ignorance of the law is not an excuse". Now one missed problem gives rise to new ones. Of course, silvering teeth is a vicious practice. Many dentists will agree with me now: this is either a very "temporary measure", or generally ineffective. It is clear that it is easier for a child to anoint his teeth than to undergo treatment using the ICON system (from 2 years old it is possible), filling the teeth with the classical method of glass-resin cement after preparation, etc.As for the choice of methods, only a qualified pediatric dentist can tell. I don’t think it’s worth it to go back to the doctor who suggested a not modern and controversial silvering technique. Good luck in finding a professional and health for you and your baby!
See: from toothpastes, so expensive, also depends. Some pastes make the teeth very weak - as if they were porcelain, and gradually fall out in particles.
Dear Svyatoslav Gennadevich. Tell me please! The child is 1 year 3 months old. The first tooth got out in 3 months. The second in 4. Almost immediately, yellow spots appeared on the teeth. Naturally, sweets at this age cannot be discussed, moreover, he did not suck a pacifier or a bottle, only breasts, complementary foods from a spoon that was previously treated with boiling water. I asked the pediatrician for the cause of the stains, she said that there was nothing to worry about. In the year they were examined by the dentist (mixed reception leads), at that time there were already deepenings on the teeth. She also said that it’s not scary. Now I noticed that the depression on one tooth has become larger and, as it were, covers the tooth. I climbed on the Internet, found this article and realized that I need to do something! But what? The child is small and will not allow to heal. Tell me, please, a way out! Is everything so scary, or with constant hygiene can you reach the permanent teeth? Thanks in advance!
Hello! I think that the weak mineralization of your teeth, which is characteristic of your child, allowed even in the presence of minor factors (breast milk + night feeding) to create a situation of development of cervical caries on these teeth. If there were no night feedings, then caries could develop as a result of daytime. The problem is that from caries in the spot stage, it smoothly passes into superficial or medium caries, which already requires filling. This is ideal.
I think that it is premature to judge whether the child will give a cure or not. You need to go to a normal clinic, where there are specialists - children's dentists. Often they find an approach to the child even in the most difficult cases.
This is me (since I rarely work with children) and this age may surprise you, but pediatric dentists who take 10 or more children from 0 to 17 years a day are unlikely. Without examining the child’s teeth and checking the caries (the depth of the lesion), it is impossible to draw up a treatment plan, and even more so to say: will the teeth reach the permanent without treatment. In general, the last question is extremely philosophical, and a pediatric dentist is unlikely to answer it, since it all depends on the rate of tooth decay, which is not amenable to simple arithmetic. Thanks for the question.
In Central Asia, I didn’t know what toothpaste was until I was 7 years old, I didn’t know who a dentist was. After 7 years, I first tried toothpaste - for the sake of taste, but very rarely used it. At 19, she first visited a dentist!
I agree with my colleague in everything. I was very pleased that at last Aykon was noticed (it was too painful for me to “get” from my colleagues for my opinion on the benefits of this drug). This is an excellent material in the treatment of tooth decay in the enamel area. And not only in children. And, by the way, from my own practice, I note that they managed to save a girl of 16 years old who had fluorosis from the crowns. It was an experiment. And the result pleased both of us. Single case. I am a young doctor. But fact is fact.
But what I, in fact, wanted to say - yes, a lot is said about treatment, about prevention, about hygiene and diet. But they do not say a word that we can protect the teeth of our baby even during pregnancy. Enamel laying of temporary teeth occurs in the first trimester, permanent - in the last. At this time, future mothers are able to, observing a certain diet (eating well) and their own health (not doing feats, risking their health), to ensure the most favorable conditions for this process. There are special drugs for the prevention of weak enamel bookmarks in a baby.Although I am somewhat wary of any kind of dietary supplements, but if you live in such conditions where it is difficult to call good nutrition, for example, water has a low fluorine content, then you should not ignore such things. Of course, under the supervision of a gynecologist and your dentist (there are, by the way, fluorinated products), because an excess of fluoride is also not good. But it’s better to try to eat well, walk in the sun and not get sick. Yes, the main thing is not to get sick. Especially in the first trimester of pregnancy, when the laying of the main organs and the formation of the baby’s immune system are under way (poor immunity - weak saliva - caries).
I hope this information is at least “timely” for someone.
As for the nutrition of infants and babies. Any product containing sugar can cause caries. Even breast milk. Another question is that breast milk also contains antimicrobial substances and is drunk with proper breast uptake (and usually there are no problems with the appearance of teeth with moms), so that it almost doesn’t get on the teeth (an exception may be feeding a half-asleep baby, when he, falling asleep, "slides" onto the nipple). Therefore, caries is called “bottle” and not “breast” or, in general, “milk”. Because basically our enemy is a bottle. But hygiene and cleanliness of the female breast is very necessary. Rinse simply with water without soap after each feeding. I know that a rather large percentage of women do not do this, being mistaken, thinking that since milk has antimicrobial properties, it also “heals” and disinfects the nipple. This is not true! Milk is an organic protein product that quickly colonizes microbes. Antimicrobial properties are not enough. It is not an antiseptic!
With the introduction of complementary foods, the risk of developing caries in a baby increases dramatically. This is due to the fact that the supply of sugars increases dramatically. Juices, sweet teas are especially dangerous. I strongly recommend diluting the juices in half with water (believe me, the baby will be delicious!), And it is better to completely abandon them until 2-3 years of age. Replace them with mashed fruit. And it doesn’t matter if you pedantically brush your baby’s teeth after each feeding, if you have these teeth at all - teach your baby to drink plain water! I ate - they gave me some water. Better from the mug - at the same time it will rinse your teeth and quickly master this “profession”. I woke up at night - offer first some water. I asked for a drink - some water! By 2-3 years, when the baby "loves" the water and will be more conscious of the fact that the mouth needs to be rinsed after a meal, juices can also be introduced.
You need to start accustoming your baby to brushing your teeth as soon as possible. Usually, in a year and a half, children have a pronounced desire to repeat after adults. Set an example. Brush your teeth - take your baby with you, let him gnaw a brush. The main thing is to develop a habit! Then teach and movements.
If you have tooth decay, just brushing your teeth a little. At a minimum, it is worth revising what could cause tooth decay. Snacks or juices. Or something else. And eliminate them. And do not wait until 6-7 years, when the teeth begin to change themselves. Not all teeth change at 6 years old, there are those that change at 12.
Health to you!
My son is one year and two months old. The upper enamel began to crumble, while the tooth was whole, as if the bark had come down from the tree, and the color of the inner tooth was light dull yellow. The doctor in the clinic said that when I was pregnant, I didn’t get minerals, vitamins, or anything else (although I drank vitamins, iron, and magnesium B6). I’m very afraid for the condition of already bone teeth. Please advise, should they be pulled out, or wait? Thank you in advance.
Hello! The description is similar to the so-called bottle caries. Without a strong need, you should not remove milk teeth, as it depends on how correctly and timely permanent teeth erupt.But just waiting, doing nothing, also makes no sense: you need to make an accurate diagnosis and identify the causes of rapid tooth decay, and then eliminate these causes if possible.
Try to contact another pediatric dentist with your baby. Not all dentists are ready to help at such an early age, since it has a number of difficulties, but it is worth a try, because not only the health of future permanent teeth depends on this, but also the health of the baby as a whole. I hope that you will find a competent pediatric dentist who will not refuse you qualified help, despite such an early age of the baby.
Dear Parents. We can simplify trips to the doctor and not injure the child. This is to brush your teeth with the appearance of the first (in the morning after eating and in the evening as well). Up to 9 years old, parents should brush their teeth. The child himself only trains during this age period! Remove juices and sweets from food. In a child, I think, cutlery should be separate from adults. Every 1, 2, 3, 4 year, go to the doctor for a scheduled examination. I wish your kids not to get sick.
Svyatoslav Gennadievich, hello. Please tell my son two years and ten months. On the lower tooth, after the incisors, on the fang, I noticed a small dot, similar to the beginning caries. What can be done? We clean teeth with pleasure. The remaining teeth are in order. And another question: how often to give a child calcium gluconate?
Hello! I think it’s worth contacting a pediatric dentist and staining the stain with a special dye to understand: this is caries, pigmentation or just plaque at this point has accumulated, which is not removed when brushing your teeth. If it is caries, then you have to treat. The doctor chooses the tactics, depending on the behavior of the baby and the capabilities of the dentistry itself.
As for the need and frequency of taking the baby calcium gluconate in absentia, I can not tell you. It is important to examine the teeth: the appearance and condition of the enamel, in order to have an idea whether this drug can be useful and how generally it is justified. Often, this is also controlled by the pediatrician together with the pediatric dentist. That is why I recommend a personal visit to the doctor with the baby.
Now his son is 3 years old. Milk caries began in the year, went to the doctor - they said that we can’t do anything, they are milk ... As a result, the upper 4 teeth collapsed, and now a bump is digging on the gum over one tooth and blood was released from the rest of the tooth, like with pus. Recently we were in dentistry, a doctor on sick leave, tomorrow we'll go again. Tell me what to do? Remove clove remnants?
Hello! It is necessary to find out the scale of the problem: how much these teeth are damaged. Maybe some of them can still be saved. Those that are in the purulent phase (exacerbation of chronic periodontitis) will have to be removed. Removal and treatment at this age is often performed under general anesthesia. There is also superficial sedation as an alternative to anesthesia. These options are selected only by a specialist (pediatric dentist, it is better in an institution specifically for children), evaluating the presence of contraindications and conducting diagnostics, external and in the oral cavity. So your first step is to find a professional pediatric dentist.
It is better not to pull with a purulent tooth (or teeth), as this is often a direct threat not only to dental health (for future permanent teeth), but even to the baby’s life.
Hello, we got out the first tooth in a month, and at 6 months we had almost all our teeth. And they immediately began to wear off on the gums. We went to the doctors, they told us that they could not help, since we are small. I do not know what to do.We are now 1.9, our front teeth have almost all been erased, and so far only holes have appeared on the back. Tell me, please, what can be done?
Hello! I am sure that the so-called bottle caries made a significant contribution to the erasure of the front teeth: this is a common problem today, especially with temporary teeth that erupt early. Try as much as possible to improve the hygiene of the child's oral cavity so that in the future the teeth no longer decay so quickly.
To clarify the situation and determine which teeth can and should be restored and whether there is an urgent need to remove the remains of damaged teeth - you need to contact pediatric dentistry (preferably a high level, since your case is not simple). Even the smallest patients can be helped there, using, for example, sedation or anesthesia. It is possible that a consultation of several doctors (surgeon, general practitioner, orthopedist, orthodontist) will be required. And most importantly - do not delay the visit to the doctor, as the consequences of procrastination can be very serious.
Thank you for the article! I learned a lot of useful information, especially about the prevention and hygiene of milk teeth. And I agree with the comment above, it is better to start following them from the very first children's tooth, so that later there are no serious problems.
Svyatoslav Gennadievich! Good day! My daughter is 1.5 years old, milk caries of four front upper teeth. In private dentistry, the doctor offered to drill a couple of teeth, about anesthesia, of course, there was no question. And silvering, according to many, does not give the desired result. Explain what is still a more effective treatment? Is it worth it to fill your teeth at such an early age, is it painfully sorry for the baby ?! Thank you in advance for your response!
Hello, Tatyana! The silvering method is really not an effective treatment. Rather, it can be called a variant of “glossing over the problem” and turning it into a chronic process, often with negative consequences for milk teeth.
Often at this age, not only anesthesia is used, but also superficial sedation, which carries fewer risks and allows a pediatric dentist to do his job qualitatively. As a result, the child does not interfere with the doctor's work, and the doctor heals correctly.
The fact that the doctor offers you, as I understand it, without anesthesia and without sedation to “drill” the teeth of the baby, on the one hand, is normal, but usually not many children in this age category sit quietly, are not afraid and follow the doctor’s instructions, that is do not interfere. There are some doctors who not only perform caries treatment in a quality manner, but also skillfully entertain the child so that he then asks the parents to come again to this office. You can interest a baby in many ways - from watching cartoons and small gifts to color fillings and delicious polishing pastes. But the risk that the child does not get to such a nice doctor is great enough, and the possible consequences are the fear of a white coat because of pain during treatment.
Be that as it may, it is important for you to act quickly enough until the teeth have collapsed and caries has gone into its complications with the risk of losing teeth or even disrupting the eruption of permanent teeth.
Hello. My son is 4 years old. At 2.5, he knocked out the front tooth, after which all the teeth of the upper jaw began to decay ... Only “stumps” of the upper teeth remained! Doctors shrug their hands from the very beginning, without specifying the exact causes of destruction and what to do next, assure that this will not affect permanent teeth. Is it so?
Hello! The fact is that this is not just about a knocked out tooth, but about fast-moving caries (most often in the cervical zone), the so-called "bottle caries". It is he who is the main cause of tooth decay in your baby. The processes occurring in decayed teeth can affect permanent teeth, and the severity depends on the infectious component. If a purulent-necrotic process develops inside the canal, the infection quickly penetrates deep into the bone and the rudiment of a permanent tooth often suffers.In some cases, the primordium can be severely damaged, up to its "resorption".
I think that your attending physicians cannot provide assistance to the child for a number of reasons, which is why they make such strange sayings, to put it mildly. I am sure that you need to find pediatric dentists who can adequately assess the situation in order to begin treatment or urgently remove damaged teeth (hemp) in order to avoid the development of a purulent infection.
Caries is the most obvious sign of vitamin K2 deficiency. It is K2, not to be confused with K1.
Hello. We are soon a year old, the other day I noticed that there were brown spots on the fangs, and today I saw that spots appeared on the front teeth, and as if holes were starting. Is it really impossible to do anything? I’m very worried, tomorrow I’m sure to see a doctor.
Hello! Fortunately, much can be done. There are different methods for the prevention and treatment of caries at this age: from the outdated method of silvering teeth to their modern restoration using Icon technology. In any case, it is important to contact the pediatric dentist in time to plan treatment. So do not worry and treat decay of deciduous teeth as soon as possible so that the health of the child and the rudiments of permanent teeth are not affected. Health to your baby!
Good evening! Toddler 1.7. 4 front teeth are destroyed. On chewing sixes there is so far a white coating. As I understand it - this is the initial stage of caries. In a private clinic, they recommended filling all the upper teeth, including those with a white coating. Of course, I would not want to mess with anesthesia. You wrote above about sedation at that age. Somewhere they wrote that it is permissible from 3 years. It is scary to imagine even filling a tooth with such a baby when he screams, cries and twitches. Huge stress for the baby. Question: Do you use sedation at an age like ours? And is it really necessary to fill in caries at the stage of a white spot?
And one more question. Is there any way to delay or stop tooth decay for a while? Until the age when it is possible to agree with a child and treat tooth decay even with nitrous oxide? I read about the silvering of the affected areas of the tooth. Will this help stop the destruction?
Hello, Rose. Caries in the stage of a white spot can be left under observation, subject to careful hygiene (at the same time, you need to watch so that there is no worsening of the situation). If the child has already destroyed some teeth (there are carious cavities), then they must be treated, since these are foci of chronic infection that affect the overall health of the child and lead to further tooth decay. At an early age, high-quality treatment can only be done under general anesthesia - sedation, unfortunately, will not work. Prior consultation with an anesthetist is required.
It is not necessary to delay the solution of the problem with decayed teeth, because the carious process will spread further, and can lead to complications, it is very problematic to suspend this process. Silvering of the affected areas of the tooth is applied until a certain stage of destruction, however, a number of specialists consider the procedure ineffective. Therefore, I do not recommend counting on silvering alone.
Thanks!
Well, pictures, tin) My husband and I tamed a daughter from childhood on eating only on weekends, because it affects teeth especially. Baby drink calcium bear formula. We pay special attention to nutrition. The husband is a fitness trainer, so we also try to feed the baby correctly. There are no problems with this.