We all want to have beautiful and healthy teeth. In order for them to remain so, it is important to be able to recognize the signs of initial caries in time, in order to take adequate measures to prevent its further development.
Even if you go to the dentist every six months, it’s far from the fact that during this time the carious process from its initial form, for example from the white spot stage, will not have time to develop further by touching the dentin of the tooth. Then dental treatment without the use of a drill is unlikely to be avoided.
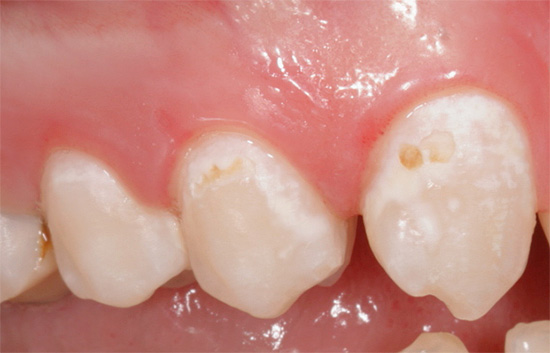
So, if you notice suspicious white spots on your teeth, and even more so brownish or even almost black, and you periodically feel a soreness in your mouth (a feeling of astringency or an astringent aftertaste) - it is highly likely that caries has already begun its destructive work on the enamel of your teeth.
What is the initial caries and its causes
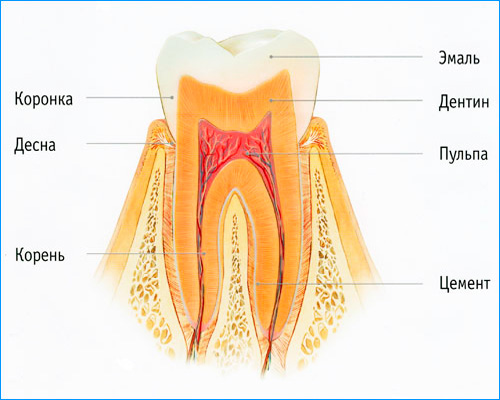
For a better understanding of what initial caries is and why it occurs, let's recall the structure of the tooth. Namely - that the top and most durable part of it is enamel. If hygiene behind the oral cavity is unsatisfactory, as a result of the vital activity of microorganisms in the mouth, organic acids are formed from carbohydrates (primarily from sugar), and plaque is formed on the surface of the enamel.

The tooth enamel consists of compounds of calcium, phosphorus and fluorine, as well as a protein matrix, which, like a mesh, permeates the entire structure. With prolonged exposure to acids on the enamel, mineral components are washed out of it - this process is called enamel demineralization and is the main cause of initial caries.
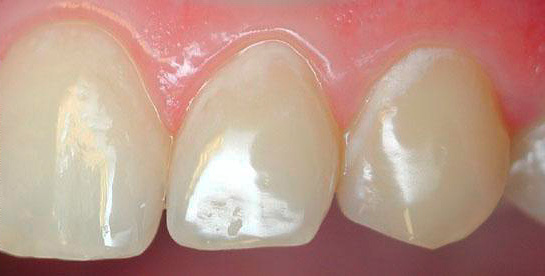
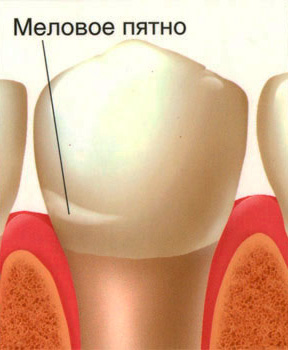
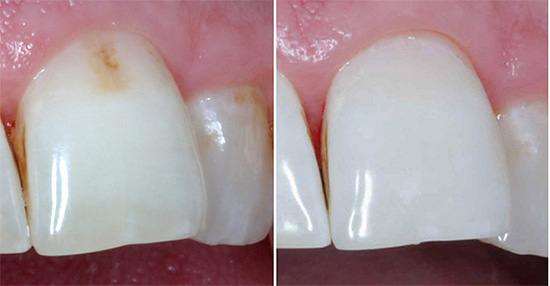
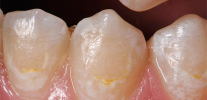
As a result, white chalky spots appear on the surface of the teeth - areas of demineralization. Initial caries at this stage is also called white spot caries. At the same time, the tooth enamel still looks smooth, but already loses its luster, its hardness in such areas decreases slightly, it becomes more porous (see photo):
It is interesting
The enamel demineralization in the initial stages of the carious process is reversible. Numerous experimental and clinical studies have shown that the crystalline structure of enamel can be successfully restored due to mineral components coming from outside - primarily calcium, phosphorus and fluorine compounds. However, such remineralization is possible only with a certain degree of destruction of hard tissues.
The limit determining the possibility of such remineralizing treatment is the preservation of the enamel protein matrix. If the protein matrix has not yet had time to break down during the initial caries, due to its inherent features, it is able to absorb calcium ions and phosphate ions from the outside, which eventually crystallize in its structure with the restoration of the protective properties and hardness of the enamel.
Initial caries in the stage of a white spot is especially noticeable on the front upper and lower teeth: just stand in front of the mirror and slightly dry the surface of the tooth. The areas of demineralization in this case appear as white spots (the so-called white caries). However, it is obvious that the pathological process is far from limited in its localization by the front teeth, it can occur on almost any tooth and any surface.
Dentist tells:
“It should be noted that white spots on the enamel may also indicate a non-carious lesion (for example, enamel hypoplasia). Is it worth it while worrying, looking at such areas? I don’t know, but I personally have a white spot on one tooth, which I noticed about 5-7 years ago in front of a mirror.I had not noticed before, but for the first time I really panicked, looking at the change site in the upper lateral incisor. He didn’t do anything, but after the lapse of time he realized that this was hypoplasia - underdevelopment of enamel since childhood.
So, as I acted, it is better not to act. Then I clearly imagined that such spots could not be caries and was not reinsured in the dentist's chair. Having initial knowledge on this issue, I made the correct preliminary diagnosis in absentia and was not mistaken. ”
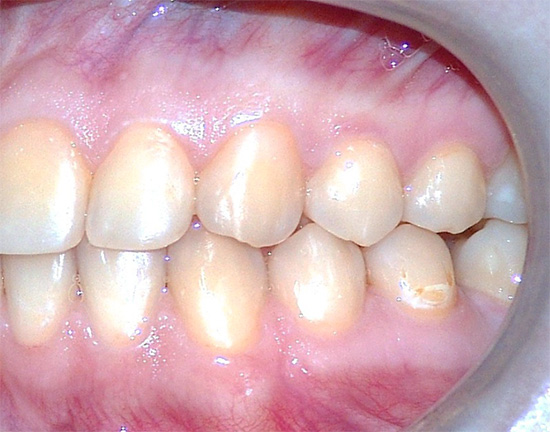
The increased porosity of the demineralized enamel areas leads to the fact that the initial caries from the stage of the white spot rather quickly passes into the stage of the dark spot. In this case, carious tissues are pigmented by various dyes and acquire shades from light brown to dark brown, almost black.
However, let's talk about the clinical manifestations of initial caries in more detail, since it is important to be able to recognize the problem at the initial stages of its appearance in order to take action in time.
Clinical manifestations of pathology
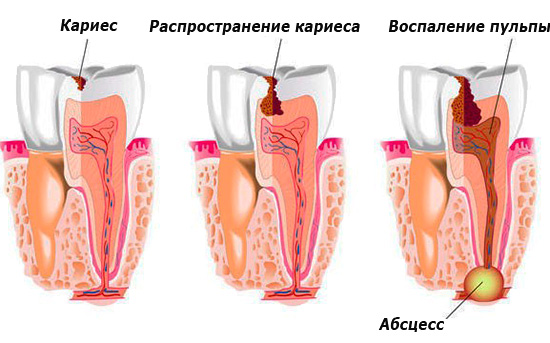
It is believed that with initial caries, the standard symptom is a person’s periodic sensation of a sore mouth that occurs when sour, sweet, or salty foods get on your teeth. At the same time, there is no strong pain, such as in the case of dentin caries (the main tooth tissue under the enamel), which is the peculiar cunning of initial caries - a person can walk with it for a long time, not even suspecting that the enamel his teeth are gradually decaying.
However, in practice, patients do not always complain of a feeling of soreness, especially in the early stages of initial caries.
On a note
Tooth enamel is devoid of nerve endings and consists of almost 97% of inorganic substances. The thickness of the enamel in different parts of the tooth varies significantly, almost vanishing at the neck of the tooth. Accordingly, strong pain during caries will be felt only when the carious process gets through the enamel below, to the dentin penetrated by microscopic tubules with nerve endings.
However, tooth sensitivity can be caused not only by the appearance of demineralization zones, but also by increased enamel abrasion (when brushing the teeth and pressing the brush in the cervical areas), as well as a banal violation of the enamel density (or structure), when the process of “conductivity occurs without the appearance of initial caries »Cold and hot from enamel to the underlying tissue.
The enamel itself, of course, does not have nerve endings, and its structure changes constantly even without initial carious zones. However, for some people, it is enough for a couple of days to excessively press on the cervical areas with a toothbrush, so that for the next 2-3 days they are afraid to even touch sensitive areas.
Clinical manifestations of initial caries include a change in tooth color, as discussed above. In this case, the following shades are observed as the pathological process develops:
- natural shade of the tooth, but matte;
- white;
- beige;
- light brown;
- dark brown;
- the black.
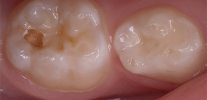
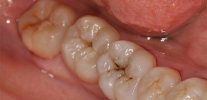
You may be surprised, but the black dots or stripes on the teeth in the fissure area (the natural relief of the tooth surface) do not mean that the tooth has irreparably rotted and everything is very bad with it. He really has problems, but this condition may well be one of the clinical manifestations of initial caries. And he, as you remember, can in some cases be completely reversible.
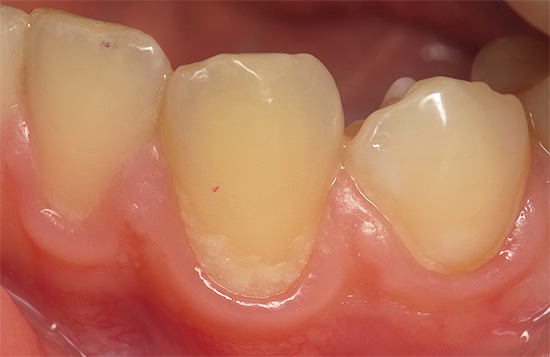
The photo below shows approximately the initial caries in the fissure area of the tooth:
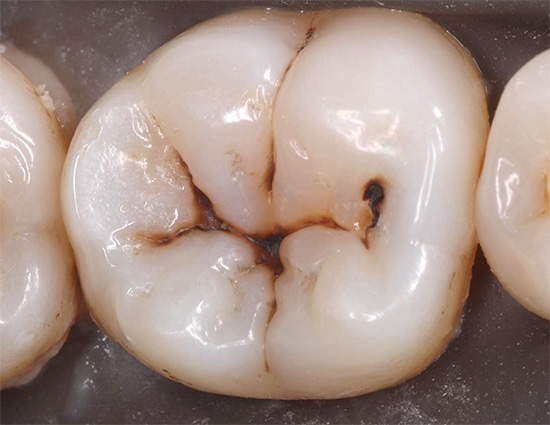
From the point of view of a professional dentist, the clinical picture of initial caries is supplemented by a number of significant nuances.So, for example, the doctor will definitely check the condition of the enamel with a dental probe - with the initial caries in the stage of a white spot, the tip should slide on the surface, since the enamel still retains a fairly high hardness.
With a deeper process of demineralization, sounding can reveal some roughness and reduced hardness. The patient may feel slight soreness.
Diagnosis methods for initial caries
There are several widely used methods for diagnosing initial caries, which make it possible to reliably differentiate it with other pathological conditions of the teeth. The simplest of them is the drying of tooth enamel mentioned above. At the same time, the sites of demineralization look dull, often whitish (loss of gloss of enamel is a characteristic sign of initial caries).
With the location of dark spots in the fissures, it can be quite difficult for the doctor to identify whether this is really initial caries, or is it a more deeply entered form. Diagnosis in such cases in children is especially problematic, since tooth enamel in the fissure area is often insufficiently mineralized, and pain during probing can occur even on intact (not involved in the carious process) surfaces of the teeth. Many reputable children's dentists generally prohibit the use of sharp probes (and probes in general) for diagnosis fissure caries in children with unformed enamel due to the fact that:
- The probe injures the enamel;
- The probe can begin to get stuck even in a normal fissure, creating artificial foci of "roughness" of enamel.
A very effective method for diagnosing initial caries is the use of various dyes, which, due to the increased permeability of demineralized enamel, are able to penetrate into its depth and firmly fix in the pores. The most commonly used organic dyes are:
- methylene blue (2% solution in water);
- methylene red (0.1% solution in water);
- tropeolin;
- carmine;
etc. The diagnostic procedure begins with the isolation of the tooth from saliva using cotton rolls and its subsequent drying. Then, a little dye solution is applied to the enamel surface with a cotton ball and wait a few minutes so that the dye can fix in the enamel pores, if any. Then the stained areas of the tooth are washed with water. A sign of initial caries is persistent staining of the enamel in the color of the dye used.
The photo clearly shows the dyed areas of demineralized enamel:
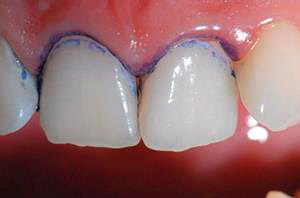
A method is also proposed for staining demineralization sites with an aqueous solution of silver nitrate. Silver ions are reduced in the pores to metallic silver, which gives the enamel a black color. The disadvantage of this method is the irreversibility of such a color.
On a note
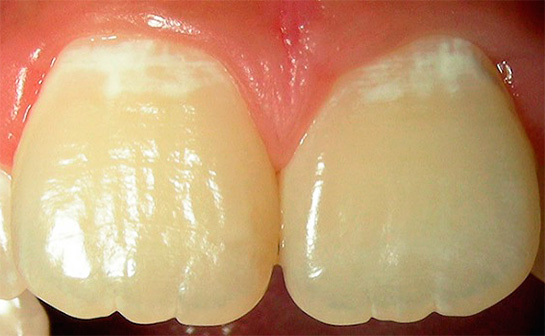
During differential diagnosis of initial caries the dentist must also ensure that white spots on the teeth are not signs of endemic fluorosis associated with excess fluoride in the body. A carious spot is usually single, and fluorous spots are usually multiple and are often symmetrically located on the teeth of the same name on the left and right sides. It is also taken into account that initial caries is usually localized on the approximate surfaces of the tooth crowns, in the area of the necks and fissures, while occurring in people who are generally prone to caries and have other symptoms. Fluorous spots are often formed on fangs, as well as on incisors - that is, on teeth that are most resistant to caries.
The doctor also takes into account the endemicity of the area according to the disease. This means that in areas with a high fluorine content in drinking water, endemic fluorosis is common and, accordingly, to the doctor is a hint.Most areas (perhaps more than 90%) in Russia are low in fluorine in drinking water, so sometimes it’s enough to look at the medical records to see if a patient has arrived who has multiple stains on his teeth.
Diagnosis in case of suspected fluorosis can be carried out using a dye solution, since only carious sections will be stained.
The following photo shows examples of fluorosis:
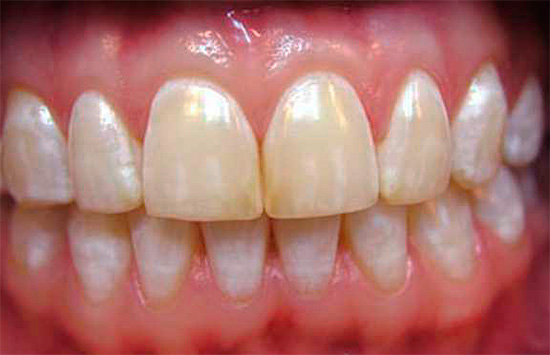
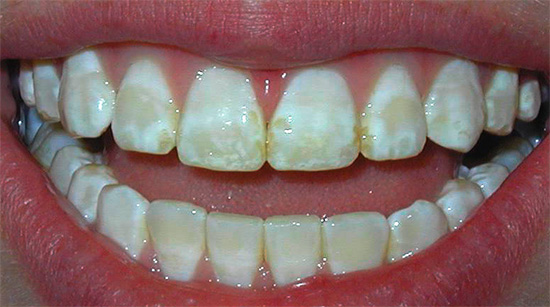
It should also be borne in mind that the presence of whitish spots on the teeth in children can be a sign of enamel hypoplasia, that is, its insufficient development, usually associated with metabolic disorders at the fetal stage. With hypoplasia, the enamel is generally thinned, there are glassy white spots, which in the form of paths encircle the crown of the tooth. Such spots are not stained with dye, which allows us to reliably distinguish them from white spots characteristic of initial caries.
Dental treatment of initial caries
The main approach in the treatment of initial caries is to try to restore the properties of tooth enamel by remineralizing it with calcium, phosphorus and fluorine preparations. In other words, it is necessary to saturate the enamel with those minerals that it lost during the carious process, and such treatment can be carried out using conservative methods, without using a drill and drilling affected areas of the tooth.
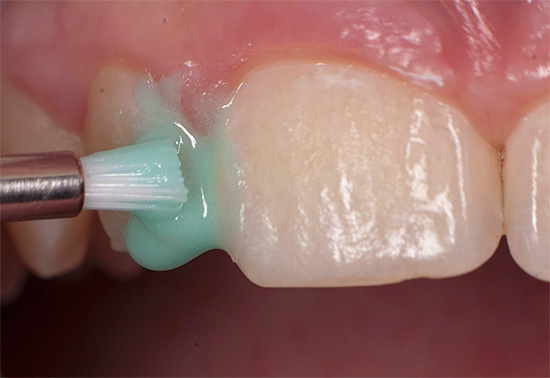
Given that dental deposits, soft plaque and plaque prevent minerals from entering the enamel, the doctor will first conduct professional oral hygiene. In addition to plaque and stone removal, grinding of the surfaces of all teeth, fillings and orthopedic structures will also be carried out.
This is followed by the stage of the actual remineralizing therapy, during which initial caries is treated with calcium, phosphorus and fluorine preparations. With their help, a higher concentration of the necessary chemical elements is achieved tens and hundreds of times compared with their content in saliva. As a result of this, the processes of diffusion of substances into caries-affected tissues proceed much faster, which allows completing treatment in just 10-20 procedures.
It is interesting
Often, the composition of the funds used for remineralizing therapy in the treatment of initial caries includes fluoride. It was established that this microelement significantly accelerates the precipitation of calcium in the protein matrix of tooth enamel, generally increasing its resistance to acids. This becomes quite understandable if we recall that the basis of enamel is the chemically very inert mineral fluorapatite.
The following options are available enamel recovery techniques:
- the surface of the teeth is mechanically cleaned from plaque with abrasive toothpaste. Then it is treated with a weak solution of hydrogen peroxide, dried, the affected areas are treated for 20 minutes with a 10% solution of calcium gluconate, after which lotions are made with a 2-4% solution of sodium fluoride for about 5 minutes. To get rid of white or weakly pigmented carious spots, usually 15-20 such procedures are usually carried out every other day or once a day. With initial changes, the therapeutic effect becomes noticeable almost immediately. However, today Borowski-Leus method is increasingly being abandoned due to the toxicity of the solutions used: working with such concentrations of fluorides is risky.
- Another option is possible, when a special slightly warmed gel containing about 2% sodium fluoride and 3% agar-agar is applied to the teeth after they are pre-brushed with toothpaste. The gel quickly hardens on the teeth with the formation of a film. Usually 5 applications are enough for treatment. The disadvantage of the technique, as in the previously described, is the use of high concentration fluorides.
- Sometimes the drugs used to treat initial caries may not contain fluoride at all, based only on calcium salts and phosphates (for example, the drug Remodent, calcium phosphate-containing gels, etc.)
In some cases, the course of treatment ends with the coating of all teeth with a special fluorine-containing varnish (fluoride). In addition, the doctor teaches the patient the rules of oral hygiene, explaining how to carefully monitor their teeth so that tooth decay does not appear.
In pediatric dentistry today, for example, the following drugs are used to treat initial caries:
- Glufthored;
- Enamel-sealing liquid;
- Belagel Ca / P, Belagel F.
Periodic monitoring of the condition of teeth treated from initial caries is also important. It is recommended to visit the dentist no later than 3 months after the course of remineralizing therapy.
Turning to the dentist for treatment at a stage when caries is already characterized by the presence of almost black pigmented areas on the teeth, it is important to understand that in such cases remineralization will not always help. As a result, the affected surface will either be drilled and filled, or, in a favorable case, sanded with subsequent remineralizing therapy.
From the practice of the dentist
Most often, enamel lesions in the form of caries in the spot stage are found in children. This is due to the weak mineralization of enamel and its incomplete formation at one age or another. It is noticed that in children with multiple white spots on the teeth, the intensity of caries is higher. This is a rapidly ongoing form of demineralization, which requires the immediate start of remineralizing therapy to prevent the carious process from moving to another stage.
According to some authors, pigmented carious spots found in large quantities in a child require planned treatment (with a favorable prognosis for the effectiveness of remineralizing drugs).
How to treat tooth decay at home
If there are signs of initial caries, the best option would be to contact a dentist who will conduct the treatment effectively and efficiently. However, at home, a certain positive effect with the right approach can also be obtained.
In fact, the task is to independently conduct remineralizing therapy using available drugs. For this, you can, for example, use:
- Remineralizing gel ROCS Medical Minerals (Rox Medical Minerals) based on compounds of calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. The gel does not contain fluorine, therefore it is safe to swallow. It relieves tooth sensitivity and is effective for the treatment of caries in the stage of a white spot. When applied to teeth, mineral components gradually penetrate the enamel, thereby restoring its structure.

- Gel Elmex (Elmex, Germany). A sufficiently effective fluoride-containing gel for treating teeth with a fluoride-ion concentration of 12500 ppm (1.25%). This is a fairly high concentration, so swallowing the gel should be avoided, especially for children. For a pronounced remineralizing effect, it is enough to apply the gel on the teeth (brush their teeth) at least 2 times a week for 2 minutes.

- Amazing White Minerals Teeth Remineralization Gel. A particularly good effect is achieved after professional oral hygiene, but even without it, the gel is quite suitable for stopping the development of caries in the stage of a white spot.
There are a number of other means for the treatment and prevention of initial caries, and this includes toothpastes containing fluoride. A particularly pronounced therapeutic effect can be obtained with a competent combination of calcium and phosphorus-containing preparations (for example, in the morning) with fluorine-containing preparations (in the evening). However, to conduct the treatment procedure at home as efficiently and safely as possible, be sure to consult your doctor.
Prevention of Initial Caries
Well aware of the reasons that lead to the appearance of initial caries (enamel demineralization under the influence of acids), the preventive measures that will avoid it are also quite obvious.
Perhaps the most effective way to prevent tooth decay is regular and proper oral hygiene. If you brush your teeth 2 times a day and think that this is enough, then you are mistaken.
Important
Carious microorganisms are able to lower the pH in the oral cavity within 10-20 minutes after ingestion of sugar-containing food. So, if you do not rinse your mouth after eating, after 20 minutes the tooth enamel begins to undergo the destructive effect of acids.
The correct use of dental floss, chewing gum after eating, the competent choice of toothpaste and toothbrush - all this also requires attention in the prevention of carious processes.
In general, preventive measures are divided into exogenous, which we have already partially affected, and endogenous - these are general prevention methods associated with exposure to the body from the inside. This includes the general strengthening of immunity, the intake of a sufficient amount of vitamins, a balanced diet, reduction of exposure to stress factors, taking fluoride, calcium and other drugs.
We also note some exogenous methods of caries prevention:
- fissure sealing
- professional oral hygiene and training in proper dental care skills
- prophylactic remineralizing therapy
and etc.
Paying due attention to the prevention of caries can reduce the risk of its occurrence at any age. It's never too late to start, so start taking care of your teeth today.
Useful video: causes of initial caries and its treatment at the spot stage
How to brush your teeth correctly



Super article, no water, with precision!
Very useful article! The dentist often tells me about these fissures that there is nothing to worry about, and I told her: “No, look, I have terrible caries, I already gobbled up my whole tooth!” )) And this fluoride gel with a mint flavor, which covers the teeth after prof. cleaning - the most pleasant thing that can be at the dentist's appointment)