According to statistics, it is the average caries, as a diagnosis, is most often found in the practice of a dentist. Despite the seemingly, at first glance, insignificance of the pathology and its “medium” degree of severity, it can lead to very serious problems (if measures are not taken in time).
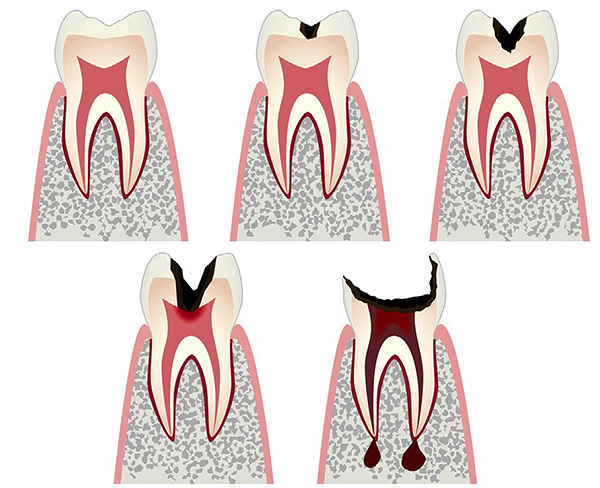
For a better understanding of the fact that the process is already quite running, it is useful to have an idea about the conditionally distinguished stages of caries, which happens:
- Initial (sometimes they say about the stage of a white or chalk spot - at this stage only some demineralization of tooth enamel occurs);
- Superficial (tooth enamel is destroyed);
- Medium (active dentin already under protective enamel already occurs on this);
- Deep (the pathological process comes close to the pulp chamber of the tooth).
If the first two forms are sometimes difficult to diagnose and often similar to normal congenital pigmentation on the teeth, which does not lead to any negative consequences, then average caries is almost always easy to identify.
On a note
Often caries in the initial stage can be in a compensated form (in a "sleeping" state) for more than 5-10 years, practically not developing further and not leading to problems. While average caries is usually not chronic: as a rule, the pathology progresses quite quickly, the carious cavity deepens and expands. As a result, as the first consequence (and not the most dangerous), tooth pulpitis develops, characterized by severe pain.
So it turns out that the patient often comes to the dentist only when clearly noticeable problems have already been outlined on the teeth. Fortunately, not everything is so bad - average caries, taking into account the specificity and depth of tissue damage, is exactly the form when you can:
- Accurately determine its localization (with the exception of specific situations). That is, in most cases, it is possible to correlate the symptoms that a patient has with a specific tooth during an examination by a dentist;
- To preserve tooth tissue as much as possible (preparation with a drill is carried out at a relatively shallow depth);
- To place a seal painlessly and with minimal time costs or to carry out high-quality artistic restoration of the front tooth in one visit;
- To conduct treatment with minimal financial costs on the part of the patient (in comparison with the complications of caries - pulpitis or periodontitis, the treatment of which can cost up to 10 times more). In addition, treatment of secondary caries, in contrast, for example, from deep, usually eliminates the use of medical pads, as well as unnecessary visits to the dentist.
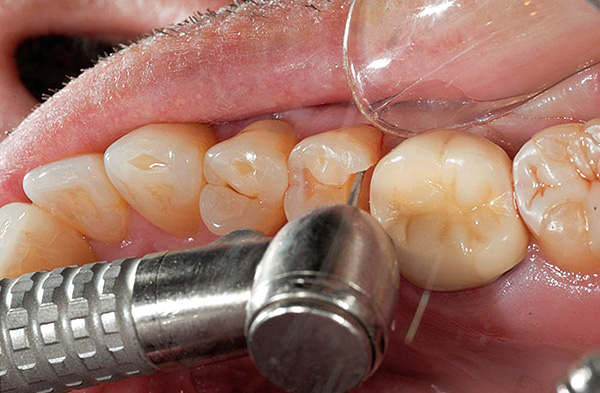
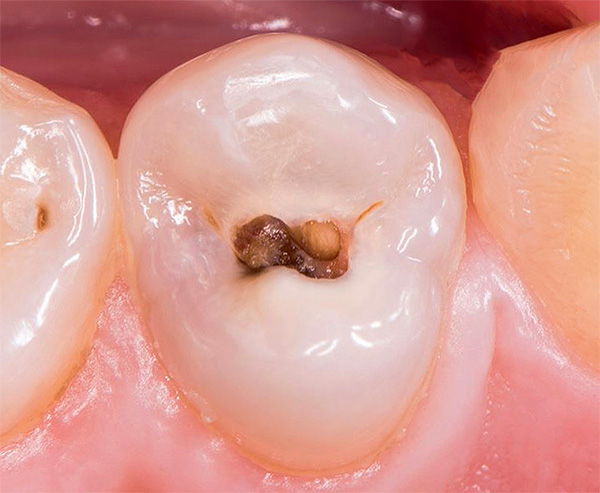
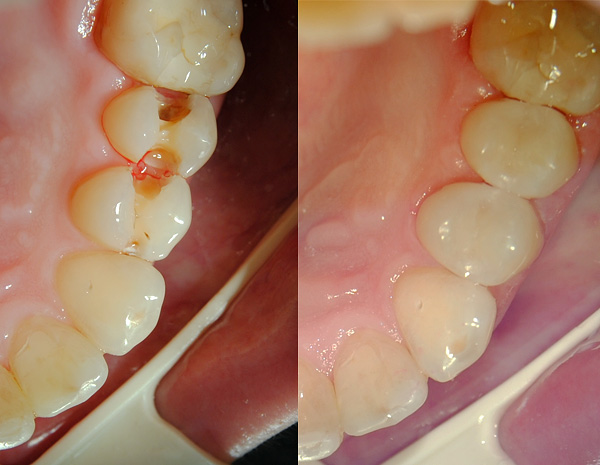
The photo below shows the average caries localized in the fissure (fossa) region of the molars:
On a note
When preparation of a tooth is required, the treatment of any degree of neglect of caries is accompanied by the use of air-water cooling, but not in all clinics its level is perfect. That is why the "drilling" of a tooth with deep caries is fraught with overheating of a nearby pulp (the so-called "nerve"). With moderate caries, the use of cooling is also necessary, but the risks of pulpitis after such treatment are practically reduced to zero due to the shallow cavity.
Preserving a tooth with a lively healthy pulp is the most preferable solution, in contrast to expensive intracanal treatment, which is almost always carried out in several visits. In addition, a “dead” tooth (without pulp) may darken over time, become brittle and significantly less resistant to stress.Therefore, it is better not to delay and carry out planned reorganization (complete elimination of carious foci) at the first signs of a carious process.
The main signs of secondary caries: how to identify the problem in time
If the initial and superficial forms of caries most often go unnoticed, then average caries can easily be detected even at home.
Here is an example of the beginning of a standard medical history:
“The patient complained of periodic pain from sweet and cold, which first appeared two days ago from the moment of treatment ...”
What diagnosis is the dentist suspected of first? Of course, average caries, as the most common pathology for such symptoms: any irritant, once exposed to dentin, can cause short-term pain. Irritation of the nerve endings of dentin can be chemical (salty, sweet, sour), mechanical (solid food) and temperature (cold, hot). Visually, a shallow carious defect, usually dark in color and irregular in shape, is determined on the tooth.
On a note
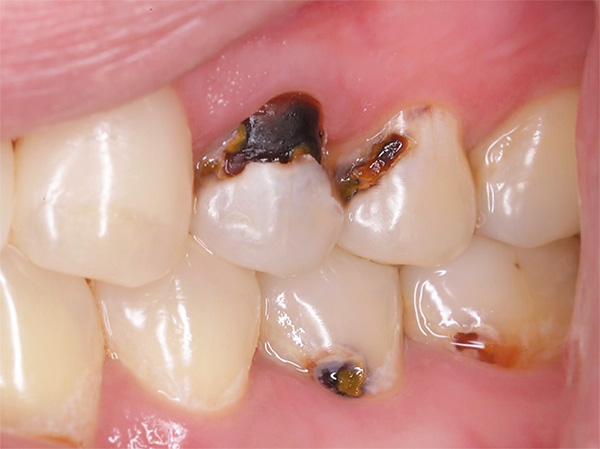
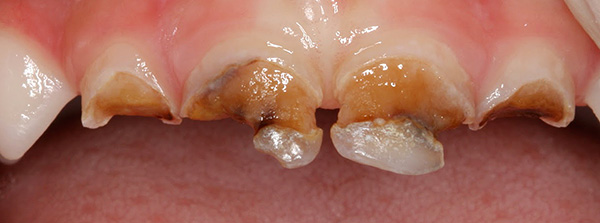
At home, such defects cannot always be correctly identified - they can look like grayish or brown spots, dots, grooves. If such a defect is in the interdental space, then it can be difficult to notice. Defects on the lower small and large molars are clearly visible (an example is given in the photograph below).
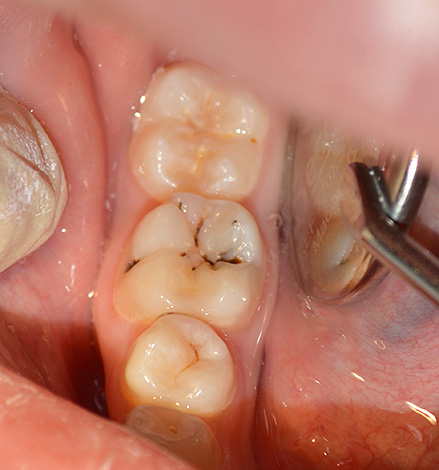
Sometimes complaints of pain may not be present at all, but the appearance of carious spots changes for the worse every month - and this is a 100% indicator of not acquired, but acquired defect, that is, caries. Only the dentist can clarify the stage of the carious process by collecting additional information: specifying the medical history, examining the oral cavity, and probing the carious tooth. Sometimes, instrumental research methods (X-ray diagnostics, EDI) can also be applied.
From the practice of the dentist
At the time of diagnosis, the coincidence of the patient’s symptoms with the clinical picture in the oral cavity is crucial. If the complaints relate to acute and (or) prolonged aching pains - spontaneous or long-term from the irritants listed above - then almost 100% we are talking about complications of caries (pulpitis or periodontitis). It doesn’t matter if there were such pains in the past, or they make you "climb the wall" at a given moment in time, and it’s not important anymore, a large carious cavity, or hardly noticeable.
On the contrary, if the patient focuses only on recently appeared minor and short-term pain from irritants, and the tooth has a well-defined “deep” carious cavity, then, despite the symptoms, the doctor treats not medium, but deep caries, or even (if necessary) intracanal tooth treatment.
Today, the main diagnostic methods are sounding, EDI (electroodontodiagnosis) and X-ray diagnostics. When probing secondary caries, a sharp probe is stuck in the carious cavity, and often the patient reports pain when the probe exposes the enamel-dentin border. The EDI values in this case are from 2 to 6 μA, and a carious cavity of small depth is determined on an x-ray.
And what, in fact, happens to a tooth during carious destruction?
Under certain conditions, long before the decay of the tooth becomes visually noticeable, the processes that trigger the mechanism of “decay” of the tooth begin. The speed of these processes depends on many factors.
In addition to the genetically determined enamel structure, there are also general and local factors that directly affect dental health.
Here is a simple example: a person’s teeth were all right all his life, but suddenly, for one reason or another, xerostomia develops (decreased salivation). And literally over the next few months, multiple caries develops on the teeth - from the initial to the middle and deep stages. The reason in this case is that saliva (which is often called “liquid tooth enamel”), which contains a complex of mineral components that are very important for dental health, has stopped flowing onto tooth enamel. In other words, the balance turned out to be upset, and the teeth quickly “sprinkled”.
As a rule, the development of caries is not complete without the main local cause of focal demineralization - this is caused by carbohydrates and plaque (this combination releases organic acids on the enamel surface that dissolve its crystal lattice). It is worth considering that plaque is formed within a few hours after brushing your teeth, and carbohydrates absorbed (especially in large doses) are the favorite food of bacteria, mainly from the Streptococcus mutans group. The biological transformation of sugars in plaque provokes the introduction of organic acids (lactic, pyruvic, etc.) into the surface layers of enamel with the formation of a site of focal demineralization.
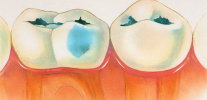
Focal demineralization of enamel - this is the initial caries, which visually begins to be determined as a matte, white or already slightly pigmented spot on the surface of the tooth.
The photo shows an example of caries in the stage of a white spot on the front teeth of a child:
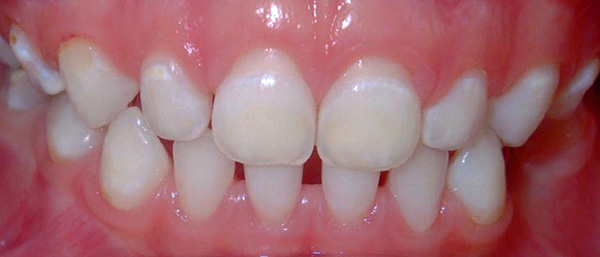
It is this stage of the carious process that can be reversed with a timely set of recovery procedures - remineralization and fluorination. With further softening of the enamel, its structure is irreversibly destroyed, surface caries is formed, and over time, bacteria also begin to destroy dentin.
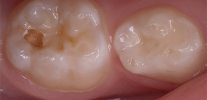
At the stage of secondary caries, as a rule, a rather rapid destruction of dentin is observed, the porous structure of which is filled with many carious bacteria. However, the most severe and neglected form of caries is the deep form, when a deep carious cavity forms against the background of the rapid destruction of the dentin structure. At the same time, only a few millimeters (often even fractions of a millimeter) remain to the pulp, and the bottom of the cavity is covered with softened, pigmented, decaying tooth tissues. Nominal deep caries is the most dangerous from the point of view of transition to a more serious disease - pulpitis.
This is how deep caries looks like:
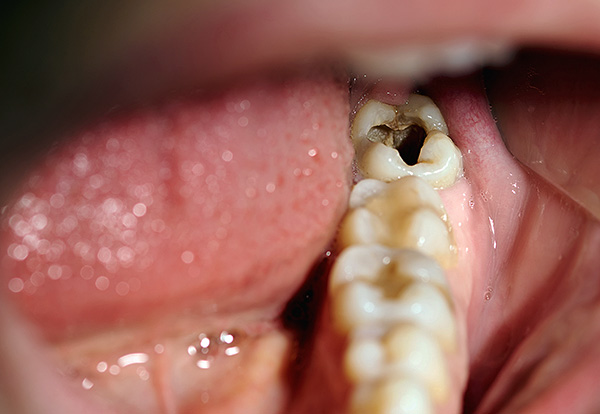
It is interesting
There is a myth that one bad tooth can “infect” with caries its neighboring neighbors. This erroneous thought is inspired by the fact that when treating one tooth in the adjacent one, a carious lesion is often also found.
In fact, caries is an exclusively local pathological process. During the use of easily fermentable carbohydrates, the spaces between the teeth are literally clogged with food debris. And since the culture of cleaning tooth gaps in Russia has not yet taken root sufficiently, the wall of the tooth begins to dissolve with the appearance of even larger cavities for food retention. Moreover, the adjacent wall, even taking into account the initially normal mineral structure, begins to deteriorate after such a frank “dump of food residues”.
By the way, this is precisely why people with large gaps between their teeth often do not suffer from caries on their side walls. Well, for those who regularly and correctly use dental floss or irrigator in addition to brushes.
How to quickly relieve pain without resorting to pills
Medium caries may be asymptomatic, but in most cases there are characteristic clinical manifestations of the disease.If even short-term pain from sweet, hot and (or) cold appears, it is important to consult a dentist as soon as possible so as not to bring the matter to pulpitis.
If in a private clinic they can still meet, making an appointment in the very near future, then in a budgetary institution they can put in a queue: for a week, or even for a month - depending on the workload of the dentist. This is especially true for compulsory medical insurance reception (that is, free of charge).
In other words, most people with a bad tooth will need to wait some time before visiting a doctor. Let's see how during this time you can reduce pain so that you can feel as comfortable as possible before visiting a doctor.
With moderate caries, pains can be short-lived, but sometimes quite strong. A classic of the "genre" is the ingestion of sweet candy (for example, toffee) in the fissures (fossa) of the chewing tooth. In this case, we are talking about the appearance of pain from sweets, which is eliminated by the rapid removal of the stimulus: when rinsing the mouth with warm water, sugars are evacuated from the area of the carious defect, and the pain instantly passes.

On a note
With deep caries, closing the cavity in the cavity with a piece of fleece helps and periodically replacing it several times a day.
With regular pains from cold and hot, there is only one correct way out - for a while, refrain from taking cold and hot food and drinks (before treatment). It is not advisable to take painkillers in this situation.
It is interesting
A carious defect can be localized not only on the chewing surface of molars and premolars, but also in the cervical region - next to the gum, or even slightly below it. From here it is also important to remove food irritants so as not to provoke the appearance of pain.
In addition, as noted above, carious cavities are often present on the contact surfaces of the teeth (in other words, between the teeth where the brush does not penetrate). Moreover, in some cases, it turns out that a person may experience prolonged pain, since he is not aware of clearing the tooth gap from “garbage”, which can be candy, meat and gingerbread. To quickly relieve pain, it is enough to use toothpicks, flosses, special brushes or an irrigator.
What can cause medium caries if delayed with tooth treatment
It should be understood that average caries already corresponds to irreversible destruction of tooth tissues (these tissues cannot be restored, but you can only put a seal, which to some extent will replace them). Whenever a tooth is prepared, it weakens - sometimes slightly, and sometimes to a large extent. And the longer you delay the treatment, the more the cavity will be, the more necrotic tissues the doctor will have to excise, and the less durable the tooth walls may be.
If in time you do not start treatment, then usually caries first leads to the formation of a deep defect with the subsequent penetration of the infection into the pulp chamber, where it will cause inflammation of the neurovascular bundle. The result is pulpitis or periodontitis. Most often, the sequence is as follows: first, pulpitis occurs in the tooth with acute spontaneous pains, and after some time the pain disappears - the tooth “nerve” dies and an inflammation center forms on the root of the tooth (periodontitis).
The timing of the transition of secondary caries to pulpitis is individual. It is quite possible to fall into the category of “lucky” (and such are found in the practice of a dentist), when all stages of tooth decay pass either asymptomatically or practically without pain. After a while, only a rotten dead tooth remains in the mouth with pouches of pus on the roots (cysts) - as a rule, the doctor can only suggest its removal.
There are also many examples where untreated caries in a few months passes into a form of pulpitis in which the patient can literally take handful painkillers, but they do not help him. And even if pulpitis goes into periodontitis, this still does not mean a decrease in pain. Periodontitis is often a purulent process, when the face becomes asymmetric, and in the best case, the pus is secreted into the oral cavity through the fistula, and in the worst, it is located under the gum near the damaged tooth, which is accompanied by severe pulsating pain, which intensifies when biting on the tooth.
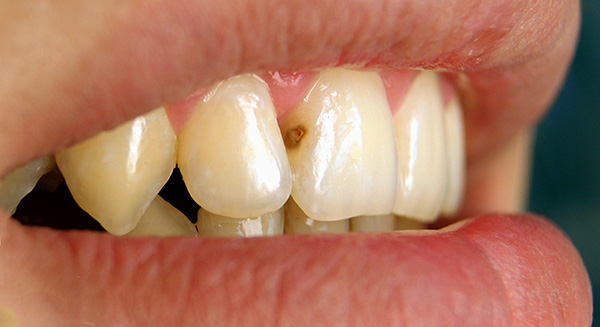
The photograph below shows a fistula on the gum above a “dead” front tooth:
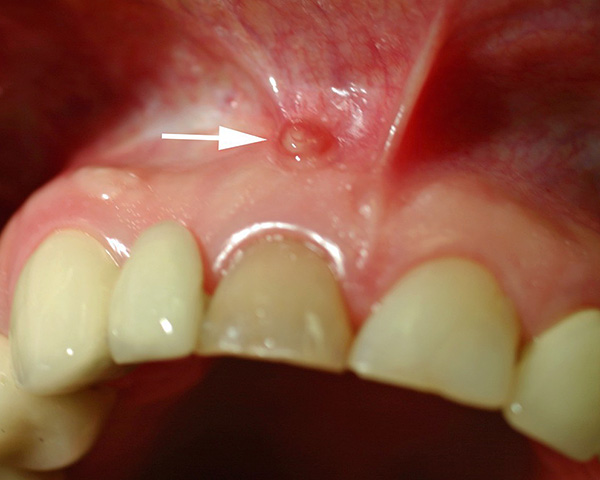
From the practice of the dentist
It is very difficult to conduct anesthesia for such patients in the place where the purulent exudate is located. Often, several approaches have to be done in order to inject at least some anesthetic solution, since the near-root area simply does not physically contain excess fluid. That is why a number of dentists are limited to the first visit only with a cut along the transitional fold, so that on the next visit to deal with more comfortable conditions during treatment (primarily for the patient).
In addition to pulpitis and periodontitis, there are other negative consequences. In particular, carious infection can ultimately negatively affect overall health:
- Undermining the immune system;
- Provoking cardiovascular disease;
- Initiating inflammatory processes in the joints.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the serious mistake of parents who deliberately do not treat caries on baby teeth in children, guided by the following principles:
- If it hurts badly, then we will treat or pull it out - all the same, after all, milk teeth will fall out;
- Why treat milk teeth if they are replaced by permanent ones.
Unfortunately, a huge number of people still follow these principles, thus putting their children's health at risk (and this is not just about dental health). The fact is that in children with milk teeth, the stages of caries "fly by" in a matter of weeks, and a tooth can become a threat of infection spreading throughout the body within 1-2 months. In this case, a purulent infection can be irreversibly damaged and the rudiments of permanent teeth, which will never be cut through.
Timely treated initial, medium or deep decay of deciduous teeth in pediatric dentistry will not only protect the rudiment of a permanent tooth from the negative effects of infection, but also protect the child from difficult moments of difficult treatment in case of acute pain, from premature removal, and in some cases from phlegmon, sepsis and other life-threatening odontogenic complications.
What awaits you in the dentist's office: stages of treatment of secondary caries
When a doctor makes a diagnosis of “medium caries” (or, in the case of the designation according to ICD-10, “caries of dentin”), treatment is usually carried out in one visit.
At the same time, perhaps the most burning question that interests patients - how painful will the procedure be? So, it all depends on the specific clinical situation - in some cases, an anesthetic injection may not be done before caries treatment.
Previously (in Soviet dentistry) this question was almost always decided by a doctor. As a result, many people even have a certain stereotype that anesthesia is done only to remove the tooth or to remove the “nerve”. Now everything has fundamentally changed: often patients, experiencing a panic fear of an injection, ask the dentist to treat secondary caries without anesthesia; or, conversely, they are asked to give an injection, even if the most minimal use of the drill is to be done.
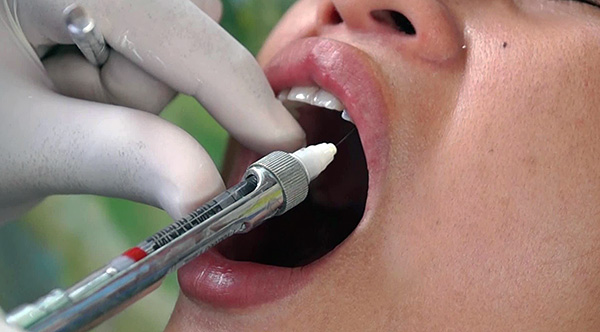
On a note
Since modern dental units are equipped with air-water cooling with minimum tip vibration parameters, in about half of cases, even without anesthesia, during the preparation of a tooth with moderate caries, pain will not occur.
Can I choose anesthesia in the treatment of caries?
General anesthesia (anesthesia) is practically not used in the treatment of caries (with rare exceptions, when there are a number of indications - for example, intolerance to local anesthetics, a pronounced gag reflex that interferes with manipulations, panic fear of any dental procedures). Choosing anesthesia only on a whim carries a lot more risks than using local anesthesia.
Most often they use sedation when the patient is conscious and able to carry out the doctor’s commands, but remains in a relaxed state (the use of sedation in pediatric dentistry is especially important).
Understood with anesthesia (this is the first stage) - now we will go on to consider the further stages of caries treatment:
- Tooth preparation. In other words, this is cleansing it of "caries", that is, those tissues that are softened and infected. This is a darkened (black) enamel, softened and pigmented dentin, etc. It depends on the quality of the implementation of this stage whether caries under the seal will continue or not. If the doctor did not pay attention to cleansing the cavity of everything superfluous, then after some time you can observe a darkening under the seal and around it, loss of the seal, and in more serious cases - the development of pulpitis or periodontitis;

- Drug treatment of the prepared cavity. This is an important stage in the final design of the cavity for the future filling, which involves the medical treatment of the bottom and walls with antiseptics. One of the most popular at present is the 2% aqueous solution of chlorhexidine and preparations based on it (Consepsis, for example), compatible with modern light-cured composite materials;
- Making an insulating pad under the seal. This stage is relevant only when using filling materials containing components that aggressively act on the tooth pulp. Currently, in connection with the use of modern technologies for filling with “light” materials, with the observance of protocols for working with adhesive systems, laying (lining) is not required. Adhesive systems are special adhesives that allow you to connect dissimilar materials;
- The final stage in the treatment of caries is the placement of a filling (filling) or aesthetic restoration.
On a note
Here it is worth saying a few words about the difference between filling and aesthetic restoration. When it comes to filling, we mean materials or technology that does not allow us to sufficiently restore the lost aesthetics of the tooth. First of all, this applies to fillings that cannot be made in layers, that is, work with them proceeds according to the principle: kneaded - introduced into the cavity - waited, and when it hardens - sanded, polished. If the function can still be returned somehow with such materials (cements, amalgams, chemical composites), then the aesthetics and the original form cannot be restored exactly.
To restore the unique shape and color of the tooth is possible only with light-cured composites suitable for restoration. Especially valuable are materials for artistic restoration. It is the artistic restoration that allows us to create all the unique aspects of the shape and color characteristics of the tooth so that it cannot be distinguished from its own tooth, even upon closer examination. Often such works are copyrighted, and such treatment of caries is time-consuming.
What affects the cost of treatment
From the point of view of logic and common sense, the price for caries treatment should consist of the cost of the spent materials (anesthesia, filling material, etc.) and the cost of the service.

In budgetary institutions there are no such categories at a free admission, but often there is also neither a doctor’s interest in performing quality work, nor materials that are necessary for this. The exception is those cases when materials and preparations are used that are not included in the compulsory medical insurance category and allow the doctor to get his percentage of the work done, and the patient - to have a guarantee for this service in the form of a receipt.

In private clinics, the price of dental treatment is sometimes unpredictable, and it is absolutely impossible to independently guess how the final cost is formed for a person far from medicine. Moreover, even the doctors of neighboring clinics sometimes can not figure out all the tricks of the pricing of a particular organization.

In addition to the quality of materials for fillings and anesthesia (cheaper, more expensive), there are a number of points that also affect the rating. For instance:
- Black carious defect class. Depending on the location of the cavity and the configuration of the affected area, the price is determined for each class, since treatment in some cases is significantly complicated and requires additional materials and time;
- The number of restored tooth surfaces. Many clinics even charge for the treatment of secondary caries not only according to the classes of carious cavities, but also take into account the number of tooth surfaces with which to work. For example, if the contact surface of the molar is destroyed, the price for the second class according to Black is one, and if not only the front, but also the back surface of the tooth is involved in the treatment, then the clinic may request separately for an additional fill;
- Application of a gasket under the seal. The introduction of an insulating pad before filling can also affect the cost of treatment;
- Additional manipulations. For example, it is often observed in the price lists of clinics that in certain categories there is a use of a laser for preparation of teeth, ultrasonic antiseptic treatment to increase sterility, grinding and polishing of fillings, etc.
In addition, the higher the status of the clinic, the level of organization and equipment, as well as the higher the professionalism and (or) the greater the number of diplomas (certificates) at the dentist, the higher the average price for treatment.
It should also be noted that the cost of dental services in different regions of Russia is significantly different - according to the levels of financial well-being of the population. For example, in Moscow, an ideally performed treatment of secondary caries can cost 3-4 thousand rubles, while in Voronezh or Izhevsk the cost of the same procedures can fit in 1500-2000 rubles. If you treat a lot of teeth, you get a decent savings. Therefore, there is such a thing as dental tourism.
From the practice of the dentist
Many people mistakenly believe that the quality of work is almost 100% determined by the quality (cost) of the filling material. In fact, the lion's share of the success of treatment depends, first of all, on the skill of the doctor, working conditions and suitable equipment. You can explain with a good example from practice.
Aunt doctor works at the state hospital, who puts Filtek, one of the best and most expensive materials, for a fee. At the same time, it fits within 15-20 minutes of the allotted time for admission of one patient (this is very small). As a result, the patient receives a seal made of excellent material with carious tissues left under it (the doctor simply does not have time for each patient to carefully clean everything). And then someone is lucky: someone has a seal that lasts longer, someone less. So patients go around - they remake from year to year.And in the next private office, one uncle slowly puts the seals, which are cheaper to purchase than Filtek - from the Charisma Gluma Comfort Bond. At the same time, the fillings hold well, and the tooth under them does not deteriorate and does not hurt, as in the first case.
If you have personal experience of “dating” with caries, be sure to share your impressions by leaving your review at the bottom of this page. How bad is the situation and are you going to treat your teeth? Does caries cause any inconvenience, or does it not manifest itself in any way? Thousands of people are in the same situation, and perhaps this information will be useful to them.
An interesting video with a good example of the treatment of caries on the lower chewing teeth: all stages of the process are shown
It turns out you can get caries?