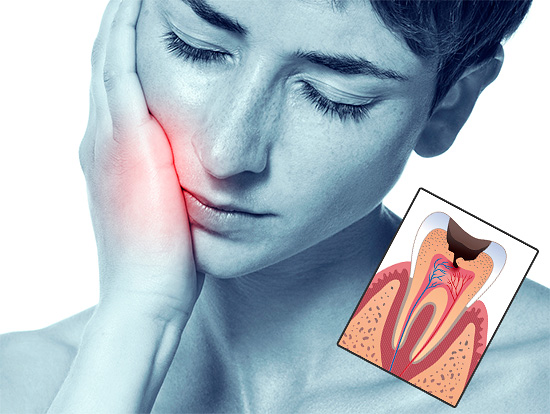
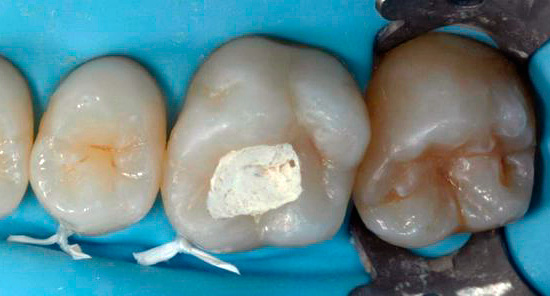
Oddly enough, but today there is still a widespread misconception among the people that while the tooth does not hurt, then treating it, in general, is not necessary. However, one should not forget that caries is often asymptomatic or with mild symptoms, until the tooth collapses so deep that the microbial infection comes close to the pulp chamber of the tooth and then penetrates into it (that is, the so-called dental "nerve") .
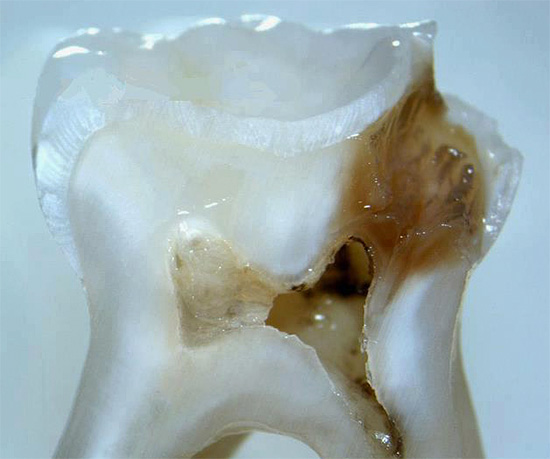
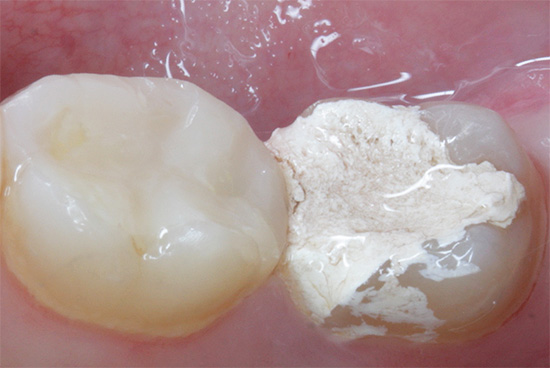
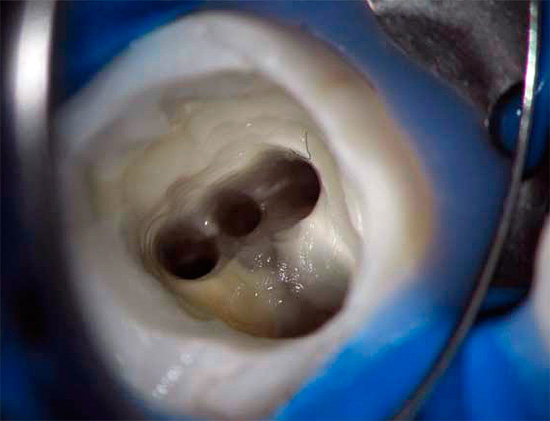
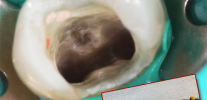
The photo below shows a section of a tooth with a carious cavity through which the infection entered the pulp chamber:
When there is an acute pulsating pain in the tooth, this is already a clear signal for immediate treatment, indicating in most cases the development of pulpitis. But it is very strange that even in this case, some people consciously decide to endure pain in the hope that they will pass, that everything will somehow "resolve", and try to postpone the treatment of pulpitis for an indefinite time.
In some cases, this happens for quite simple reasons: not all people know what pulpitis is, and even more so about how it is treated (and even more so they are not tormented by fears about possible complications, otherwise they would have immediately run to the clinic). Following the expression “aware - means armed”, everyone should have at least a general idea of pulpitis and its treatment, although in order to preserve its teeth in critical situations.
Why is pulpitis treated?
Imagine a person to whom a career, a constant lack of time or another reason gives, it would seem, a reasonable reason not to rush with the treatment of pulpitis, despite regular and severe pain in the tooth. Funds come to the rescue Ketanov, Nurofen, Ketorolac, Baralgin, Nise and others related to painkillers.
It is important to understand that even if the pain has subsided, a huge number of bacteria continue to be in the pulp chamber of the tooth and conduct their destructive work. Irreversible changes gradually occur inside the tooth, sooner or later leading to the death of the “nerve” with the formation of pus in the root canals.
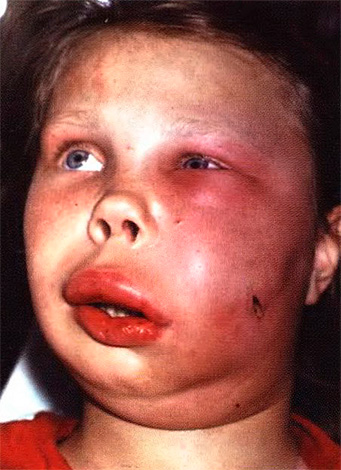
When pus extends beyond the root toward the gums, a “flux” occurs. In fact, this can be expressed not only in the slight swelling of the cheeks, sometimes the face can literally inflate with a strong violation of symmetry. In severe cases, it can not only be about preserving the tooth, but a spilled purulent inflammation - phlegmon - can also develop. And this is only part of the possible problems, in reality there are much more options for serious complications, including damage to the jaw bone, blood poisoning, etc.
The photo shows phlegmon - a terrible complication of pulpitis:
To prevent complications of pulpitis, it is very important to start treatment on time. In some clinical cases, during treatment, the entire neurovascular bundle can be preserved without resorting to its extraction from the canal, but more often amputation (partial extraction) or extirpation (complete removal) of the pulp is performed.
The meaning of the pulp removal procedure is to completely rid the tooth of the source of infection and to prevent the spread of bacteria through the roots to the gums. This is the only way to protect the tooth and its surrounding tissues from additional problems.
On a note
Many years ago, there was a popular method of treating pulpitis with the resorcinol-formalin method, which is still relevant in some institutions. Quite often people come to dentists with such teeth - pink and red, as sooner or later they begin to bother.It is difficult or impossible to cure a tooth in an advanced stage (in exacerbation) after such treatment. The sooner you start replacing the resorcinol-formalin paste and flushing the canal from “infection”, the easier it is to keep the tooth from inevitable removal.
Classical methods and approaches to the treatment of pulpitis
All known methods of treating pulpitis can be divided into two large groups:
- treatment with full preservation of live pulp in the tooth;
- and pulp removal treatment.
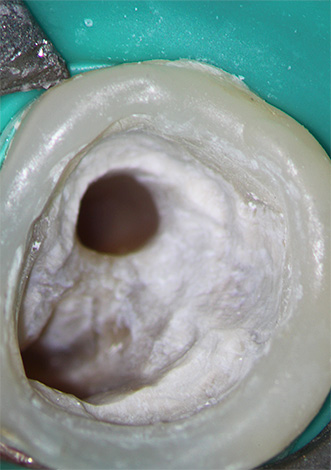
The last group is still subdivided into partial (amputation) and complete (extirpation) pulp extraction.
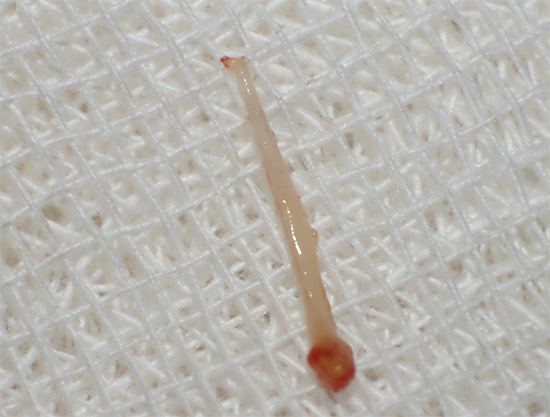
The photo below shows the pulp removed from the tooth:
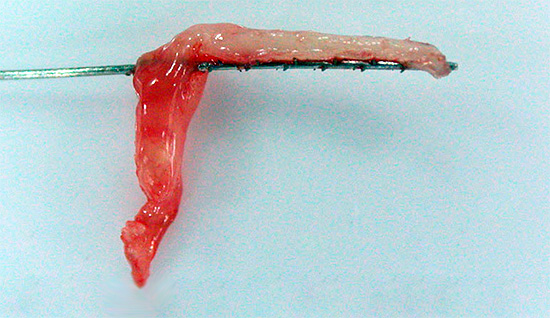
In order to assess the possibility of applying this or that method and approach to the treatment of pulpitis, it is necessary to first understand what condition the “nerve” is in the dental canal. The most gentle biological treatment method for pulp can be applied only if there is no inflammation in it, or if it is in the very initial stage.
It is interesting
The biological method of treating pulpitis, in addition to observing strict indications for it and the rules of asepsis and antiseptics (sterility during work), has even more than 10 basic requirements, starting from the young age of the patient and his absence of acute infectious diseases, to the use of effective air-water cooling , a large number of sterile burs, etc. That is why in most dentistry this method is not used to treat pulpitis, since high risks of failure (repeated pulpitis pain) provoke doctors to use methods aimed at complete removal pulp from the canalsto prevent conflict situations.
Surgical treatments for pulpitis, as noted above, include methods for partial or complete removal of pulp from the tooth:
- if partial removal of the "nerve" (an amputation method of treating pulpitis) is performed immediately under anesthesia, then this is vital amputation;
- if at the first stage of pulpitis treatment a devitalizing paste is placed (in order to “kill a nerve” beforehand), then the method is called devital amputation.
Similarly, extirpation, that is, the complete removal of pulp, is divided into vital and devital.
On a note
Vital amputation, as one of the most difficult to implement methods of treating pulpitis, also has a whole set of indications and strict requirements for observing the necessary conditions during the procedure. These include: a healthy periodontium (a complex of tissues surrounding the tooth), an age limit of up to 45 years, adherence to ideal sterility during work, and others.
Amputation of the pulp requires painstaking work, followed by the formulation of drugs (powerful anti-inflammatory drugs). Most dentists (except for children), who for many years have successfully practiced removing the entire “nerve” (extirpation), already from realizing the risk of not observing the maximum sterility of the working field, when the patient has millions of microbes in his mouth, are not ready to undertake complex and lengthy work on partial removal of the pulp.
Vital and devital extirpation have long been included in practical dentistry as the most effective and reliable methods of treating pulpitis. A significant difference between them is that vital extirpation, or the complete extraction of pulp from the canals, is performed immediately and under effective anesthesia. A devital extirpation can be performed without anesthesia (although in practice it is also more often performed with it), but with preliminary setting during the first visit to a special paste to kill the “nerve”.
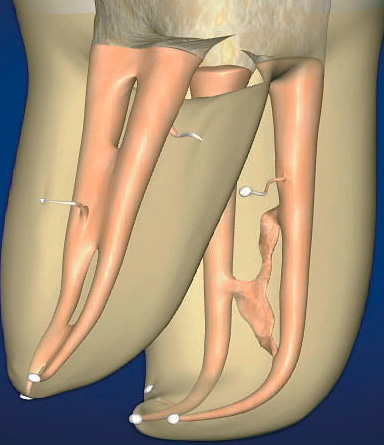
A special place in Russian dentistry is occupied by the method of devital amputation, which in Soviet times in many dental institutions was the only possible way to cure pulpitis and keep the tooth in the face of a shortage of imported drugs, lack of time, the dentist’s lack of knowledge of the search and processing of channels, etc. This technique is surprising in its simplicity and false effectiveness.
Removal of only that part of the neurovascular bundle that is located inside the tooth crown with partial or complete preservation of the root pulp creates the conditions for the continued development of the infection. Despite the use of various potent solutions and pastes for the root pulp, which could turn it into a kind of “mummy” (dry antiseptic cord), the presence of voids in the treated canal with the remains of killed and weakened microflora created all the conditions for a sluggish flow on the root or roots, inflammation extended over years with the gradual dissolution of bone tissue.
Unexplained facts
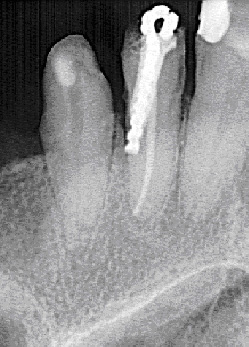
Most often, a mummifying resorcinol-formalin paste, which has long been banned in many countries of the world because of its irritating, toxic and even possible carcinogenic effects (that is, the ability to provoke), was used and is still used in a number of dentists to turn pulp into a “mummy” the formation of cancer cells). Russia in this regard is one of the few countries that still has not taken into account the results of research by world-famous scientists.
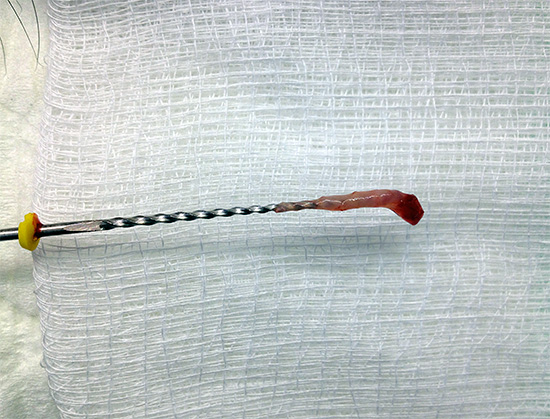
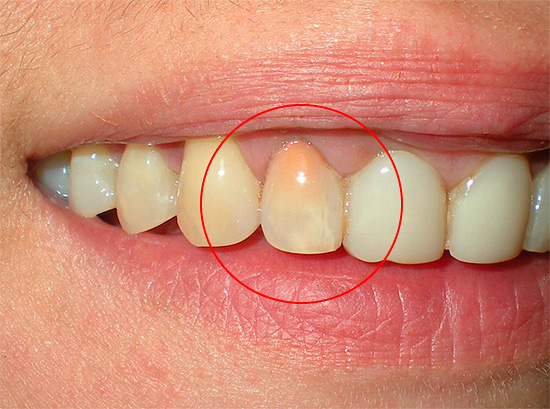
In this photo you can observe how the tooth looks after the treatment of pulpitis using the resorcinol-formalin method (devital amputation):
The combined treatment of pulpitis is the use of, as a rule, two methods, for example, extraction of the entire root pulp from accessible channels (devital extirpation) and partial removal of the “nerve” (devital amputation) from channels with complex anatomy, for example, strongly curved, or breaking of the tool and the impossibility of removing it. Unlike devital amputation, with the combined method the prognosis is more favorable, but only if most of the channels are nevertheless covered along the entire length and sealed with reliable filling materials.
It is also useful to read about the problems that sometimes arise when removing the dental "nerve".
Important nuances of the treatment procedure
Modern dentistry and the dental market are aimed at implementing programs to improve the treatment of pulpitis by vital extirpation - that is, the complete removal of the pulp without first killing it. Every year there are new tools and devices aimed at preventing errors during treatment and the convenience of a dentist.
Thanks to modern anesthetics and devices for their controlled administration, it is no longer necessary to put the paste for devitalization on the opened "nerve" - the so-called "arsenic". Since anesthesia is effective, even intracanal treatment of the lower large molars difficult to “freeze”, associated with the extraction of pulp from the canal system, can now be safely carried out in one visit.
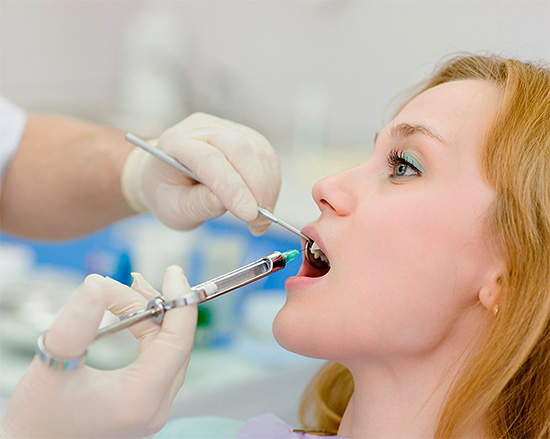
Pulp removal is carried out under local anesthesia, for which articaine series preparations are more often used: Ubistesin, Alfacain, Septonest, Ultracain, etc. After the tooth has reached a stable “freeze”, the dentist first amputates the pulp (by boron or excavator), and then extirpates, removing it from the channel, the neurovascular bundle is immediately whole or in parts. After this, the most critical stage of treatment of pulpitis begins, when with the help of small "needles" (rimers and files) the doctor passes the channels along the entire length, expands them and simultaneously treats them with medication with antiseptic solutions.
It is no accident that many leading dentists adhere to the following principle in their work: it does not play a significant role in what the channel will be sealed with, it is important how well prepared it is.Just this “quality” includes long and painstaking work of washing out all “dirt” from the canals: microbes of the living and the dead, sawdust from the infected inner walls of the canal, blood impurities, nerve residues from all canals, etc.
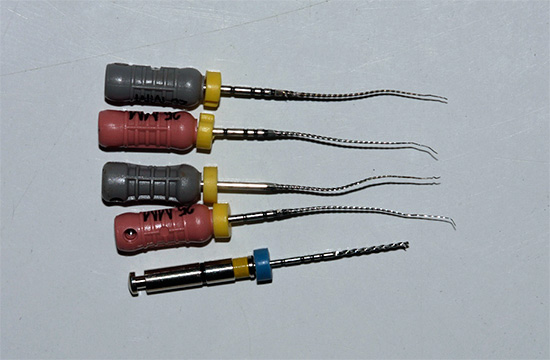
Tooth canals can be compared to a tree that has numerous large and small branches. With the help of “needles” (pulp extractors, files, etc.) it is possible to remove the nerve only from the main channels (maximum 4-5), but thin branches extending from the main ones into the thickness of the tooth walls are difficult to clean mechanically. That is why drug treatment with modern antiseptics allows not only to make the channel sterile, but also to dissolve the nerve residues in the inaccessible zone. This takes time and a sufficient amount of antiseptic solution.
It is interesting
Among the most effective antiseptics used in the treatment of pulpitis, sodium hypochlorite solution still remains. Both 3% and 5% solutions can be used. Successful channel processing consists in accurate and safe inkjet processing from a special syringe. Professionalism, hardware control of work, lack of rush, etc. avoids serious errors in the form of removing the solution beyond the root, where it can have a strong irritating effect.
The treatment of the canals ends with their filling up to the apex - physiological narrowing or maximum point of narrowing.
Popular filling materials are pasta-kneading pastes (Endometasone, AN Plus, etc.) and gutta-percha pins. The high application rating remains with the volumetric sealing technique of all branches of the hot gutta-percha channel of the Termafil system. As a rule, according to the protocol, cure pulpitis is obtained in 2-3 visits.
Photo of a pulpitis tooth at the beginning of treatment and upon its completion:
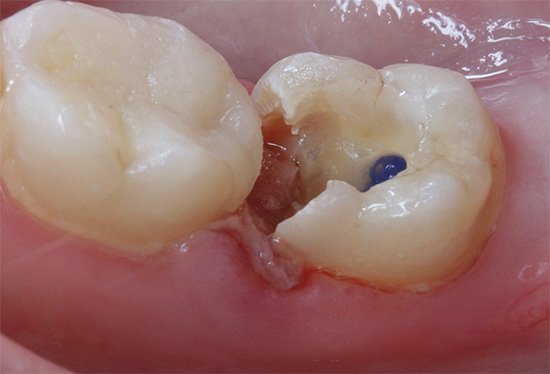
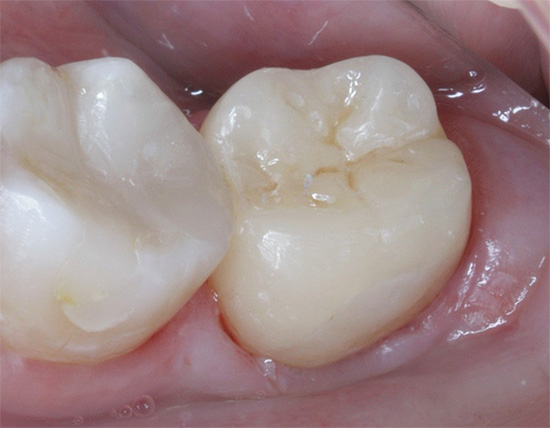
Pulp removal with its preliminary killing has the same principles and treatment steps for pulpitis, but only during the second visit. And on the first visit with or without anesthesia, a small piece of paste (arsenic or non-arsenic) is placed on the opened pulp horn.
Arsenic paste is placed for 24 hours (treatment of single-root teeth) and for 48 hours (multi-root pulpitis treatment) Due to the fact that this type of treatment is difficult to control, and often the patient may appear later than the appointed time, there are frequent cases of emergency care with the toxic effect of arsenic on the root of the tooth. Constant complaints from patients and the study of the effect of the paste on the tissues surrounding the root led doctors to conclude that it is better to abandon the use of arsenic-containing substances in the treatment of pulpitis in favor of alternative arsenic-free pastes.
New techniques and devices for the successful treatment of pulpitis
If pediatric dentists continue to actively use to treat pulpitis dairy and permanent teeth with unformed roots vital and devital amputation, for the adult population the most acceptable methods of complete removal of the pulp. To create maximum sterility in the canals, the dental market releases new devices and drugs every year, and new methods of treating pulpitis are developed that allow you to save your tooth for life.
Enhanced disinfection of channels can be carried out using ultrasound and laser devices and tools. Depophoresis of copper-calcium hydroxide is also considered an effective treatment method.

It is interesting
Copper-calcium hydroxide not only has a bactericidal effect, but also destroys spores and fungi in the channels. Due to the destructive effect on proteins, even small branches of the canal are cleansed of any life form.
Physiotherapy for pulpitis, as well as for periodontitis, is a method that is most often used to treat post-filling pains, which often arise against the background of adaptation to the filling material. Within the framework of physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, the DiaDENS device, darsonvalization apparatus, Amplipulse and others can be used. In general, it should be noted that physiotherapy is rarely used in the treatment of pulpitis.
Common mistakes in the treatment of pulpitis and how it can threaten
Modern methods of treating pulpitis make it possible to avoid most of the mistakes made by dentists of the last century during the processing and filling of dental canals. Despite this, for a number of reasons (for example, rush, lack of professionalism, poor equipment of the clinic), such errors appear as a violation of the integrity of the canal, breaking off the instrument, incomplete filling, or excessive filling.
Violation of the integrity of the canal is perhaps one of the most problematic complications during the treatment of pulpitis: this creates a false hole or perforation at a certain root level: at the beginning, end and its middle. In this case, the tool for passing or expanding the channel accidentally appears outside the root in the surrounding tissues. This complication complicates the normal processing and filling of the real canal, and also provokes the presence of a focus of inflammation in the place of the “wound” on the root in the future.
It is interesting
During perforation, the patient often notices himself, as if the doctor had pierced the gum, moved away from the tooth, “touched the flesh”. This manifests itself as a sudden pain somewhere in the depths. Moreover, blood often appears in the spittoon when spitting.
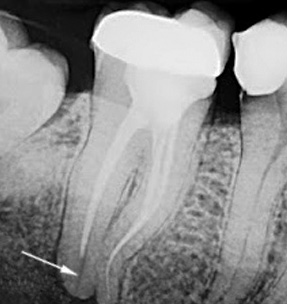
Broken instrument in the canal: if improperly operated with small endodontic instruments, it is possible to jam the end of the “needle” with its subsequent breaking, which does not allow to cure pulpitis qualitatively. Part of the channel is not processed and not sealed. If microbes continue to multiply in the voids of the root, this leads to the occurrence of periodontitis pain, indicating inflammation of the root.
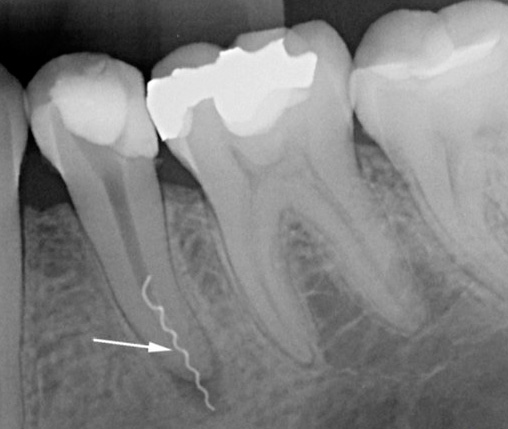
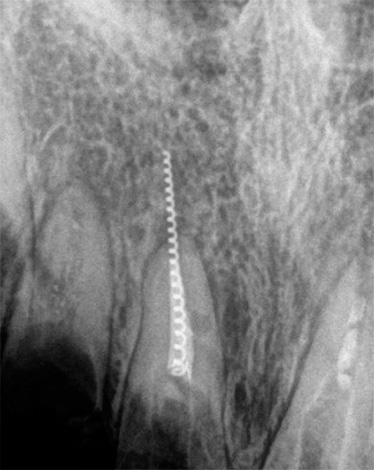
An incompletely sealed canal: normally it should be sealed to a physiological narrowing, that is, not reaching the visually determined radiological apex of the tooth root by about 1-2 mm. Regardless of the material chosen, this requirement must satisfy the pulpitis treatment protocol. Otherwise, root inflammation will occur.
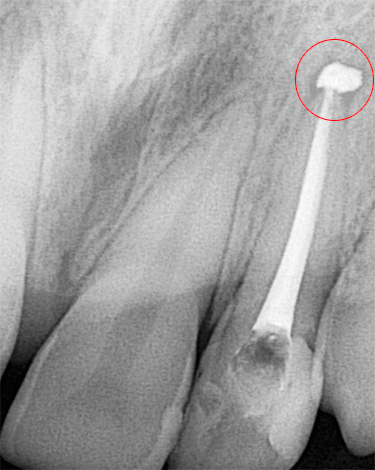
An overly sealed canal: when a large amount of filling material is removed outside the root, the dentist risks giving the patient in addition to severe tooth pain after pulpitis treatment, also big problems in the future. The fact is that the standards for the treatment of pulpitis provide for a clear filling of the channel according to its working length, measured with a ruler, using a special device, X-ray, etc. If material enters the apex of the root, it is perceived as a foreign body, which entails a response and provokes inflammation of the tissues surrounding the root.
Very rarely, even cases of removal of filling material in the maxillary sinus with the development of sinusitis and in the mandibular canal with numbness of the jaw for a long time are recorded. All this is quite serious.
Now let's talk about the prices for treating pulpitis ...
How much does cure pulpitis cost?
The cost of treating pulpitis is determined in part by the geographical location of the dental institution. For example, treatment in a small town may differ markedly in price for the same services, but already in St. Petersburg or Moscow. To better understand what you are actually paying for, it’s useful to know a little about the pricing policy of clinics.
Most dentists include in the cost of treating tooth pulpitis anesthesia, passage of channels, use of tools for their mechanical and drug treatment, material for the “root filling”, filling material at the end of treatment, as well as some other stages and materials used. Low-budget organizations almost do not include advertising, high service, comfort level, etc. in the price of pulpitis treatment.

From the observations of the dentist
Some advanced patients who do not have a good life during the treatment of pulpitis act like the real Ostap Bender. The most difficult canal treatment, which requires a lot of time, a high level of equipment, a doctor’s professionalism, quality control in the form of pictures, they spend in a good clinic at a decent level. At the same time, a person asks a dentist to treat pulpitis without filling, so that they can then install it for free or for a minimal fee in a budgetary institution (clinic or hospital). Unfortunately, this event can be doomed to failure, since the low quality of a budget filling often affects the possibility of microbes from entering the oral cavity into a well-sealed canal system after a couple of years or earlier. The result is a repeated expensive retreatment of the tooth.
A number of dentists treat pulpitis in one go with immediate payment for it. Studies have shown that the clinic’s commercial desire to quickly receive the full amount for the difficult work done is fraught with future complications for the patient, since most dentistry institutions work with such a set of materials that can either not be combined or may not adhere well during filling tooth immediately after treatment. There is also a risk of micro-shrinkage (“falling through") of the seal when the material placed in the channels begins to harden, and the seal naturally falls into the voids formed with the formation of cracks along its edges.
The best way to avoid costly treatment is to prevent pulpitis. It is made up of timely caries treatment at any stage of the process, professional oral hygiene from plaque and stone, as well as from the formation of a proper food culture with the restriction of sweets in all types, the correct and regular brushing of teeth, the use of dental floss and conditioners.
An interesting video showing what you can expect in the clinic during the treatment of pulpitis
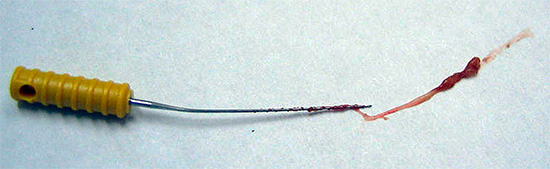
Removing a broken instrument from the tooth canal


I worked as a dentist for about 40 years and I can say about the resorcinol-formalin method that this method has proven itself over the decades of its use in dentistry. The only minus is staining of the tooth, but teeth cured by this method stand for decades and until the end of patients' lives. Another thing is that this method is cheap, and now everyone wants to get as much money from the patient as possible, and expensive imported drugs are being introduced.
The method, of course, is cheap, but it stains the tooth and, moreover, the tooth becomes brittle. This can further negatively affect the ability to perceive the chewing load, and if you need to remove, the removal will be difficult. The tooth will constantly crumble, which means it will need to be cut out from the jaw. And then suturing, etc.
Yeah, my friend during his studies at the institute treated his teeth in this way, they stained like that. Having stood for more than 5 years, they began to become inflamed! Still mother of that doctor from urban dentistry. There were just such painted teeth ...
When the nerves are removed from the canals, the tooth becomes dead, gradually becoming more fragile and collapsing. I understand that sooner or later it will collapse and it will have to be removed? So isn’t it easier to immediately remove such a tooth without treating pulpitis and insert an artificial one?
Hello! A quote from one film that has not yet been shot: “If we die anyway, isn’t it easier right away ...”
Firstly, you are right, a tooth becomes more fragile than a living one (with pulp), but this does not mean that it will crumble during life. Secondly, a dead tooth with 4 full walls (that is, a seal is in the middle of the tooth) can completely collapse without correction in 10-20 years, and this is not the option to say: “isn’t it easier to immediately remove such a tooth ? "
Moreover, studies have proven: while it’s difficult to build something better than your teeth in terms of anatomy and functionality, and more often it turns out more expensive. You can’t even imagine how many people justifiably cling to each of their teeth, try to treat, even if it lasts for only a couple of years. Thirdly, about those teeth that do not have completely reliable walls, or there are not so many of these walls: they do a tooth restoration on a pin, or (which is justified and more reliable, but more expensive) put a stump insert in the tooth canal, and then a crown . With the right manipulation, this extends the life of a dead tooth up to 15-20 years or more. Of course, no one argues with the fact that dental work should be revised once every 1-3 years.
They often said to me even cooler: “Isn't it easier to remove all teeth and insert implants, prostheses?” In order to reason like this, you need to have at least 400-800 thousand rubles or more, since the whole mouth of high-quality implants is expensive, or prepare for cheaper counterparts, where problems can wait at every turn. So what you are talking about can lead to rash financial expenses (at best), or to disappointment with the loss of your teeth.
Even if you have cured pulpitis according to the protocol, there is no guarantee that the tooth will not hurt when you catch a cold, freeze, etc. As a rule, pain appears in the treated tooth, which indicates that it is very difficult to maintain sterility in the canals during treatment. Yes, endometasone paste and gutta-percha pins will reach the tops of the roots, but this, alas, is not a guarantee of a complete cure from the residual pulpitis. Absorbers, files, protapers, etc. - everything is sterile only when not unpacked. Everything has relative sterility. Often it is simply impossible to maintain this sterility, based on the rules of asepsis and antiseptics. The dentist’s office is not a large operating room, where the air is constantly sterilized, where the patient is covered with sterile sheets, where only sterile instruments are served, where doctors and sisters in sterile gowns, shoe covers, masks, etc. There is a lot of infection in the oral cavity. Therefore, the effectiveness of the treatment of pulpitis is not always high, and the complaints of patients after dental treatment for teeth or doctors are sometimes unreasonable. It is best to treat caries and not bring to pulpitis, periodontitis, and there is not much sweet.It would be well understood by experts and judges who take part in the analysis of “flights”.
I went to a private clinic to treat pulpitis. Only for the reorganization and filling of the channels, they told me the price - put the whole salary for the month (I have an average salary, not the smallest). And this is with a temporary seal, albeit a polymer one. Constantly set - pay separately ... For that kind of money, I did an operation on the thyroid gland in the state clinic + 5 days of the hospital and tests. So, taking this kind of money, they could have provided sterility to the maximum, and not to slip the contract at the checkout - “I have no complaints in case of complications”. And I clean my teeth on time, try. It’s not my fault that I did a pulp burn out of the blue, although the caries was not very deep (it was treated in an inexpensive private clinic initially).
Tinplate
How to understand from all the complicated price lists of dentistry how much it will cost to treat pulpitis? All stages of me, as a simple layman, are of little interest, to be honest. It's important for me:
a) To the maximum, keep the tooth alive (and not as before, even 10 years ago - to remove the teeth in the treatment of any caries and then grind and put the crown).
b) That the cost of all work is not bent. With the salary of a state employee in the minimum wage, how can one set such prices for treatment? And now, even for compulsory medical insurance, everything is all paid, and there are no materials of the previous generation and doctors 🙁
Hello Veronica! The cost of treatment can only be calculated after studying your picture and in-person examination. Doing it yourself (in advance, without visiting a doctor) will be quite problematic.
After studying the history and X-ray examination, it will be possible to judge - either save the pulp of the tooth (nerve), or remove it. This greatly affects the cost of treatment. The cost is also significantly affected by the number of tooth channels. And without carrying out diagnostic procedures, the range of probable prices for treatment will be very wide - from about 2,000 rubles to 10,000 rubles.